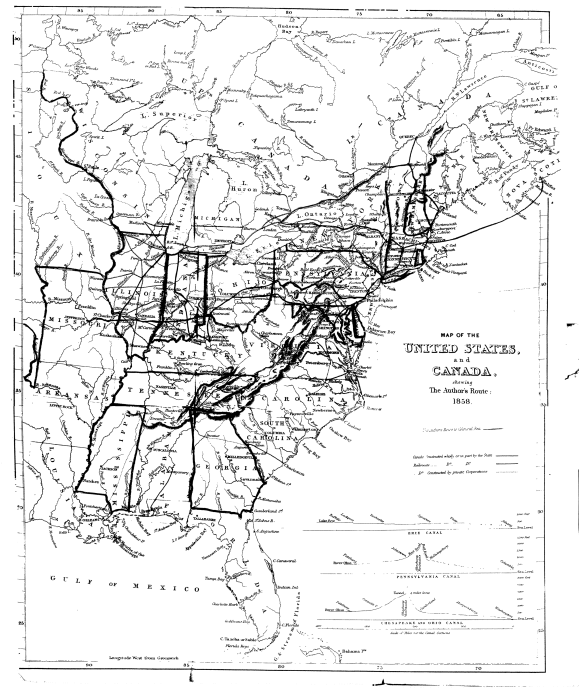
Map of the UNITED STATES,
and
CANADA,
shewing
The Author's Route; 1858.
The Project Gutenberg EBook of First Impressions of the New World, by
Isabella Strange Trotter
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
Title: First Impressions of the New World
On Two Travellers from the Old in the Autumn of 1858
Author: Isabella Strange Trotter
Release Date: June 20, 2006 [EBook #18634]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK FIRST IMPRESSIONS OF THE NEW WORLD ***
Produced by Robert Cicconetti, Martin Pettit and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This
file was produced from images generously made available
by the Canadian Institute for Historical Microreproductions
(www.canadiana.org))

Map of the UNITED STATES,
and
CANADA,
shewing
The Author's Route; 1858.
Voyage.—Arrival at New York.—Burning of Quarantine Buildings.—Cable Rejoicings.—Description of the Town
West Point.—Steamer to Newport.—Newport.—Bishop Berkeley.—Bathing.—Arrival at Boston
Journey to Boston.—Boston.—Prison.—Hospital.—Springfield.—Albany.—Trenton Falls.—Journey to Niagara.—Niagara
Niagara.—Maid of the Mist.—Arrival at Toronto.—Toronto.—Thousand Islands.—Rapids of the St. Lawrence.—Montreal.—Victoria Bridge
Journey from Montreal to Quebec.—Quebec.—Falls of Montmorency.—Island Pond.—White Mountains.—Portland.—Return to Boston.—Harvard University.—Newhaven.—Yale University.—Return to New York
Destruction of the Crystal Palace.—Philadelphia.—Cemetery.—Girard College.—Baltimore.—American Liturgy.—Return to Philadelphia.—Penitentiary.—Return to New York
William's Departure.—Greenwood Cemetery.—Journey to Washington.—Arrangements for our Journey to the Far West.—Topsy
Washington.—Baptist Class-Meeting.—Public Buildings.—Venus by Daylight.—Baltimore and Ohio Railway.—Wheeling.—Arrival at Columbus
Journey from Wheeling to Columbus.—Fire in the Mountains.—Mr. Tyson's Stories.—Columbus.—Penitentiary.—Capitol—Governor Chase.—Charitable Institutions.—Arrival at Cincinnati
Cincinnati.—Mr. Longworth.—German Population.—"Over the Rhine."—Environs of Cincinnati.—Gardens.—Fruits.—Common Schools.—Journey to St. Louis
St. Louis.—Jefferson City.—Return to St. Louis.—Alton.—Springfield.—Fires on the Prairies.—Chicago—Granaries.—Packing Houses.—Lake Michigan.—Arrival at Indianapolis
Indianapolis.—Louisville.—Louisville and Portland Canal.—Portland.—The Pacific Steamer.—Journey to Lexington.—Ashland.—Slave Pens at Lexington.—Return to Cincinnati.—Pennsylvania Central Railway.—Return to New York
New York.—Astor Library.—Cooper Institute.—Bible House.—Dr. Rae.—Dr. Tyng.—Tarrytown.—Albany.—Sleighing.—Final Return to Boston.—Halifax.—Voyage Home.—Conclusion
My dear little Girl,
I dedicate this little book to you; the letters it contains were meant to let you know how your father and I and your brother William fared in a rapid journey, during the autumn of last year, through part of Canada and the United States, and are here presented to you in another form more likely to ensure their preservation.
You are not yet old enough fully to understand them, but the time will, I trust, come when it will give you pleasure to read them. I can safely say they were written without any intention of going beyond yourself and our own family circle; but some friends have persuaded me to publish [Pg vi]them, for which I ought, I suppose, to ask your pardon, as the letters have become your property.
The reason which has made your father and me consent to this is, that we scarcely think that travellers in general have done justice to our good brothers in America. We do not mean to say that we have accomplished this, or that others have not fairly described what they have seen; but different impressions of a country are made on persons who see it under different aspects, and who travel under different circumstances.
When William, for example, was separated from us he found the treatment he received very unlike what it was while he travelled in our company; and as many bachelors pass through the country and record their experience, it is not surprising if some of them describe things very differently to what we do.
The way to arrive at truth in this, as in all other cases, is to hear what every one has to say, and to compare one account with another; and if these letters to you help others to understand better the nature and [Pg vii]character of the country and the people of America, my object in making them public will be attained.
With some few alterations, the letters are left just as you received them, for I have been anxious not to alter in any way what I have told you of my First Impressions. When, therefore, I have had reason to change my opinions, I have thought it better to subjoin a foot-note; and in this way, too, I have sometimes added a few things which I forgot at the time to mention in the letters themselves.
There is only one thing more to tell you, which is, that though I wrote and signed all the letters myself many parts are of your father's dictating. I leave you and others to judge which these are. Without his help I never could have sent you such full accounts of the engine of the Newport steamer, or of our journey across the Alleghanies and other such subjects; and you will, I know, like the letters all the better for his having taken a part in them.
Believe me ever,
Your affectionate Mother.
June, 1859.
VOYAGE.— ARRIVAL AT NEW YORK.— BURNING OF QUARANTINE BUILDINGS.— CABLE REJOICINGS.— DESCRIPTION OF THE TOWN.
New York, September 3, 1858.
We landed here yesterday afternoon, at about six o'clock, after a very prosperous voyage; and, as the Southampton mail goes to-morrow, I must begin this letter to you to-night. I had fully intended writing to you daily during the voyage, but I was quite laid up for the first week with violent sea sickness, living upon water-gruel and chicken-broth. I believe I was the greatest sufferer in this respect on board; but the doctor was most attentive, and a[Pg 2] change in the weather came to my relief on Sunday,—not that we had any rough weather, but there was rather more motion than suited me at first.
Papa and William were well throughout the voyage, eating and drinking and walking on deck all day. Our companions were chiefly Americans, and many of them were very agreeable and intelligent. Amongst the number I may mention the poet Bryant, who was returning home with his wife and daughter after a long visit to Europe; but they, too, have suffered much from sea sickness, and, as this is a great bar to all intercourse, I had not as much with them as I could have wished.
The north coast of Ireland delighted us much on our first Sunday. We passed green hills and high cliffs on our left, while we could see the distant outline of the Mull of Cantire, in Scotland, on our right. We had no service on that Sunday, but on the one following we had two services, which were read by the doctor; and we had two good sermons from two dissenting ministers. The second was preached by a Wesleyan from Nova Scotia, who was familiar with my father's name there. He was a good and superior man, and we had some interesting conversations with him.
We saw no icebergs, which disappointed me much;[Pg 3] but we passed a few whales last Tuesday, spouting up their graceful fountains in the distance. One came very near the ship, and we had a distinct view of its enormous body. We had a good deal of fog when off Newfoundland, which obliged us to use the fog-whistle frequently; and a most dismal sounding instrument it is. The fog prevented our having any communication with Cape Race, from whence a boat would otherwise have come off to receive the latest news from England, and our arrival would have been telegraphed to New York.
The coast of Long Island came in sight yesterday, and our excitement was naturally great as we approached the American shore.
Before rounding Sandy Hook, which forms the entrance on one side to the bay of New York, we ran along the eastern coast of Long Island, which presents nothing very remarkable in appearance, although the pretty little bright town of Rockaway, with its white houses studded along the beach, and glittering in the sun, gave a pleasing impression of the country. This was greatly increased when, running up the bay, we came to what are called the Narrows, and had Staten Island on our left and Long Island on the right. The former, something like the Isle of Wight in appearance, is a thickly-wooded hill covered with[Pg 4] pretty country villas, and the Americans were unceasing in their demands for admiration of the scenery.[1]
Before entering the Narrows, indeed shortly after passing Sandy Hook, a little boat with a yellow flag came from the quarantine station to see if we were free from yellow fever and other disorders. There were many ships from the West Indies performing quarantine, but we were happily exempted, being all well on board. It was getting dark when we reached the wharf; and, after taking leave of our passenger friends, we landed, and proceeded to an adjoining custom-house, where, through the influence of one of our fellow-passengers, our boxes were not opened, but it was a scene of great bustle and confusion. After much delay we were at length hoisted into a wonderful old coach, apparently of the date of Queen Anne. We made a struggle with the driver not to take in more than our own party. Up, however, others mounted, and on we drove into a ferry-[Pg 5]boat, which steamed us, carriage and all, across the harbour, for we had landed from the ship on the New Jersey side. After reaching New York by means of this ferry-boat, we still had to drive along a considerable part of Broadway, and finally reached this comfortable hotel—the Brevoort House—at about eight o'clock.
The master of the hotel shook hands with papa on entering, and again this morning treated him with the same republican familiarity. The hotel is very quiet, and not a specimen of the large kind, which we intend seeing later. We had fortunately secured rooms beforehand, as the town is very full, owing to the rejoicings at the successful laying of the cable, and many of our fellow-passengers were obliged to get lodgings where they could.
We found that Lord Napier was in the hotel, so we sent our letters to him, and had a long visit from him this morning.
Two topics seem at present to occupy the minds of everybody here; one, the successful laying of the cable, the other the burning of the quarantine buildings on Staten Island. We were quite unconscious, when passing the spot yesterday, that the whole of these buildings had been destroyed on the preceding night by an incendiary mob; for such we[Pg 6] must style the miscreants, although they comprised a large portion, it is said, of the influential inhabitants of the place. The alleged reason was that the Quarantine establishment was a nuisance, and the residents had for months been boasting of their intention to destroy the obnoxious buildings. The miserable inmates would have perished in the flames, had not some, more charitable than the rest, dragged them from their beds. The Yellow Fever Hospital is destroyed, and the houses of the physicians and health officers are burnt to the ground. At the very same moment New York itself was the scene of the splendid festivities in honour of the successful laying of the Atlantic Telegraph Cable, to which we have alluded.
We came in for the finale of these yesterday, when the streets were still much decorated. In Trinity Church we saw these decorations undisturbed: the floral ornaments in front of the altar were more remarkable, however, for their profusion than for their good taste. On a temporary screen, consisting of three pointed gothic arches, stood a cross of considerable dimensions, the screen and cross being together about fifty feet high. The columns supporting the arches, the arches themselves, and all the lines of construction, were[Pg 7] heavily covered with fir, box, holly, and other evergreens, so as to completely hide all trace of the wooden frame. The columns and arches of the church were also decorated with wreaths and garlands of flowers.
On a panel on the temporary structure already mentioned was the inscription, "Glory be to God on high, and on earth peace, good will towards men," all done in letters of flowers of different colours; the cross itself being covered with white roses and lilies. In the streets were all sorts of devices, a very conspicuous one being the cable slung between two rocks, and Queen Victoria and the President standing, looking very much astonished at each other from either side. The absurdity of all this was, that the cable had really by this time come to grief: at least, on the morning after our landing, an unsuccessful attempt was made to transmit the news of our arrival to our friends in England. It was rather absurd to see the credit the Americans took to themselves for the success, such as it was, of the undertaking.
Besides seeing all this, we have to-day driven and walked about the town a good deal, and admire it much. It is very Parisian in the appearance of its high houses, covered with large bright letterings;[Pg 8] and the shops are very large and much gayer looking on the outside than ours; but, on examination, we were disappointed with their contents. The streets seem badly paved, and are consequently noisy, and there are few fine buildings or sights of any kind; but the dwelling-houses are not unfrequently built of white marble, and are all handsome and substantial. In our drive to-day we were much struck with the general appearance of the streets and avenues, as the streets which run parallel to Broadway are called. The weather has been sultry, but with a good deal of wind; and the ladies must think it hot, as most of them appear at breakfast in high dresses with short sleeves, and walk about in this attire with a slight black lace mantle over their shoulders, their naked elbows showing through. We go to-morrow to West Point, on the Hudson River, to spend Sunday, and return here on Monday, on which day William leaves us to make a tour in the White Mountains, and he is to join us at Boston on Monday week.
You must consider this as the first chapter of my Journal, which I hope now to continue regularly.
[1] The admiration thus claimed for the scenery was sometimes so extravagant as to make us look for a continuance of it, a reproach of this kind being so often made against the Americans; but we are bound to add this note, to say that we very seldom met afterwards with anything of the kind, and the expressions used on this occasion were hardly, after all, more than the real beauty of the scenery warranted.
WEST POINT.— STEAMER TO NEWPORT.— NEWPORT.— BISHOP BERKELEY.— BATHING.— ARRIVAL AT BOSTON.
Brevoort House, 5th Avenue, New York,
8th Sept., 1858.
My letter to you of the 3rd instant gave you an account of our voyage, and of our first impressions of this city. In the afternoon of the 4th, William went by steamboat to West Point, on the river Hudson, and we went by railway. This was our first experience of an American Railway, and it certainly bore no comparison in comfort either to our own, or to those we have been so familiar with on the Continent. The carriages are about forty feet long, without any distinction of first and second classes: the benches, with low backs, carrying each two people, are arranged along the two sides, with a passage down the middle. The consequence is, that one may be brought into close contact with people, who, at home, would be in a third-class carriage. There are two other serious drawbacks in a long journey;[Pg 10] the one being that there is no rest for the head, and therefore no possible way of sleeping comfortably; the other, that owing to the long range of windows on either side, the unhappy traveller may be exposed to a thorough draught, without any way of escape, unless by closing the window at his side, if he is fortunate enough to have a seat which places it within his reach. Another serious objection is the noise, which is so great as to make conversation most laborious. They are painstaking in their care of the luggage, for besides pasting on labels, each article has a numbered check attached to it, a duplicate of which is given to the owner; time is saved in giving up the tickets, which is done without stoppage, there being a free passage from one end of the train to the other. This enables not only ticket-takers, but sellers of newspapers and railway guides, to pass up and down the carriages; iced water is also offered gratis.
The road to Garrison, where we had to cross the river, runs along the left bank of the Hudson, a distance of fifty miles, close to the water's edge nearly the whole way, and we were much struck by the magnificence of the scenery. The river, generally from two to three miles in breadth, winds between ranges of rocks and hills, mostly covered with wood, and[Pg 11] sometimes rising to a height of 800 feet. Owing to the windings and the islands, the river frequently takes the appearance of a lake; while the clearness of the atmosphere, and the colouring of the sunset, added to the beauty of the scene. We travelled at the rate of twenty miles an hour, and arrived in darkness at Garrison. Here we crossed the river in a ferry-boat to West Point, and found William, who had come at the same speed in the steamer. The hotel being full, we accepted the offer of rooms made us by Mr. Osborn, an American friend of papa's, at a little cottage close to the hotel. Mr. and Mrs. Osborn and their two children had passed some weeks there, and said they frequently thus received over-flowings from the hotel, and but for their hospitality on this occasion, we should have been houseless for the night. This cottage belonged to the landlord of the hotel, and there being no cooking accommodation in it, we all took our meals in the public dining-room. The hotel itself is a very spacious building, with a wide verandah at each end. We found an endless variety of cakes spread for tea, which did not exactly suit our appetites, but we made the best of it, and then went into the public drawing-room, where we found all the guests of the hotel assembled, and the room brilliantly lighted. Here balls, or as[Pg 12] they call them "hops," take place three or four times a week. The scene is thoroughly foreign, more German than French. The ladies' hoops are extravagant in circumference; the colouring of their dresses is violent and heavy; and there is scarcely a man to be seen without moustachios, a beard, a straw hat, and a cigar. West Point is the Sandhurst of the United States, and is also the nearest summer rendezvous of the fashionables of New York. It is beautifully situated on the heights above the river, and the Military Academy, about ten minutes' drive from the hotel, commands a most splendid view of the Hudson, and the hills on either side.
We went to the chapel on Sunday the 5th, where we joined, for the first time, in the service in America. It differs but little from our own, and was followed by a not very striking sermon. The Holy Communion was afterwards administered, and it was a comfort to us to join in it on this our first Sunday in America. The cadets filled the centre of the chapel, and are a very good-looking set of youths, wearing a pretty uniform, the jacket being pale grey with large silver buttons. We dined at four o'clock at the table d'hôte, in a room capable of holding about four hundred. We sat next to the landlord, who carved at one of the long tables. The dinner[Pg 13] was remarkably well cooked in the French style, but most deficient in quantity, and we rose from table nearly as hungry as we sat down. Some of the ladies appeared at dinner in evening dresses, with short sleeves (made very short) and low bodies, a tulle pelerine being stretched tight over their bare necks. In some cases the hair was dressed with large ornamental pins and artificial flowers, as for an evening party. We met them out walking later in the evening, with light shawls or visites on their shoulders, no bonnets, and large fans in their hands. This toilette was fully accounted for by the heat, the thermometer being at 80° in the shade. Many of the younger women were very pretty, and pleasing in their manners.
We left West Point early on Monday morning, the 6th, taking the steamboat back to New York, leaving William to pursue his journey to the White Mountains and Montreal alone, and we are to meet him again at Boston next week. The steamboat was well worth seeing, being a wonderful floating house or palace, three stories high, almost consisting of two or three large saloons, much gilt and decorated, and hung with prints and filled with passengers. The machinery rises in the centre of the vessel, as high nearly as the funnel. We went at[Pg 14] the rate of twenty miles an hour. We again enjoyed the beauties of the river, and could this time see both sides, which we were unable to do on the railway, by which means too we saw many pretty towns and villas which we had missed on Saturday. We were back at the hotel by twelve o'clock, and are to make our next move to-morrow afternoon to Newport, a sea-bathing place, a little way north of this. We are doing this at the strong recommendation of Lord Napier, who says, at this time of the year Newport is worth seeing, as giving a better idea of an American watering-place than Saratoga, where the season is now drawing to a close.
We have now become more familiar with this place, and I think are beginning to feel the total want of interest of any sort beyond a general admiration of the handsome wide streets and well-built houses. The Brevoort House is in the fifth avenue, which, in point of fashion, answers to Belgrave Square with us, and consists of a long line of houses of large dimensions. A friend, who accompanied us in our drive yesterday evening, pointed out many of the best of them as belonging to button-makers, makers of sarsaparilla, and rich parvenus, who have risen from the shop counter. He took us to his own house in this line, which was[Pg 15] moderate in size, and prettily fitted up. He is a collector of pictures, and has one very fine oil painting of a splendid range of mountainous scenery, in the Andes. It is by Church, a rising young American, whose view of the Falls of Niagara was exhibited this year in London. We have made frequent use of the omnibus here; the fares are half the price of the London ones, and the carriages are very clean and superior in every way to ours. Great trust is shown in the honesty of the passengers, there being no one to receive payment at the door, but a notice within directs the money to be paid to the driver, which is done through a hole in the roof, and he presents his fingers to receive it, without apparently knowing how many passengers have entered. We frequently meet woolly-headed negroes in our walks, and they seem to form a large proportion of the servants, both male and female, and of porters and the like. We are disappointed in the fruit. The peaches are cheap, and in great quantities, but they are very inferior to ours in flavour, and the melons are also tasteless. The water-melons are cut in long slices and sold in the streets, and the people eat them as they walk along. The great luxury of the place is ice, which travels about the streets in carts, the blocks being three or[Pg 16] four feet thick, and a glass of iced water is the first thing placed on the table at each meal. The cookery at this hotel is French, and first rate. We have had a few dishes that are new to us. The corn-bread and whaffles are cakes made principally of Indian-corn; and the Okra-vegetable, which was to us new, is cut into slices to flavour soup. Lima beans are very good; we have also had yams, and yesterday tasted the Cincinnati champagne, which we thought very poor stuff.
Fillmore House, Newport, Rhode Island, September 13th.—We left New York on Thursday afternoon, and embarked in a Brobdingnagian steamboat, which it would not be very easy to describe. The cabin is on the upper deck, so that at either end you can walk out on to the stern or bow of the vessel; it is about eleven feet high, and most splendidly fitted up and lighted at night with four ormolu lustres, each having eight large globe lights. We paced the length of the cabin and made it 115 paces, so that walking nine times up and down made a nice walk of a mile. The engine of the steamboat in America rises far above the deck in the centre of the vessel, so this formed an obstruction to our seeing the whole length, unless on each side of the engine, where a broad and clear passage allowed a full view[Pg 17] from end to end; but instead of taking away from the fine effect, the engine-room added greatly thereto, for it was divided from the cabin, on one side, by a huge sheet of plate glass, through which the most minute workings of the engines could be seen. There was in front a large clock, and dials of every description, to show the atmospheric pressure, the number of revolutions of the wheel, &c. This latter dial was a most beautiful piece of mechanism. Its face showed six digits, so that the number of revolutions could be shown up to 999,999. The series of course began with 000,001, and at the end of the first turn the nothings remained, and the 1 changed first into 2, then into 3, &c., till at the end of the tenth revolution the two last digits changed together, and it stood at 000,010, and at the 1,012th revolution it stood at 001,012.
To go back to the saloon itself; the walls and ceiling were very much carved, gilt, and ornamented with engravings which, though not equal to our Albert Durers, or Raphael Morghens at home, were respectable modern performances, and gave a drawing-room look to the place. The carpet was gorgeous in colour, and very pretty in design, and the arm-chairs, of which 120 were fixtures ranged round[Pg 18] the wall, besides quantities dispersed about the room, were uniform in make, and very comfortable. They were covered with French woven tapestry, very similar to the specimens we bought at Pau. There were no sofas, which was doubtless wise, as they might have been turned to sleeping purposes. Little passages having windows at the end, ran out of the saloon, each opening into little state cabins on either side, containing two berths each, as large as those on board the Africa, and much more airy; but the wonderful part was below stairs. Under the after-part of the saloon was the general sleeping cabin for the ladies who could not afford to pay for state cabins, of which, however, there were nearly a hundred. Our maid slept in this ladies' cabin, and her berth was No. 306, but how many more berths there may have been here we cannot tell. This must have occupied about a quarter of the space underneath the upper saloon. The remaining three quarters of the space constituted the gentlemen's sleeping cabin, and this was a marvellous sight. The berths are ranged in four tiers, forming the sides of the cabin, which was at least fourteen feet high; and as these partook of the curve of the vessel, the line of berths did the same, so as[Pg 19] not to be quite one over the other. There were muslin curtains in front of the berths, forming, when drawn, a wall of light floating drapery along each side of the cabin, and this curved appearance of the wall was very pretty; but the prettiest effect was when the supper tables were laid out and the room brilliantly lighted up. Two long tables stretched the whole length, on which were placed alternately bouquets and trash of the sweet-cake kind, though the peaches, water-melons, and ices were very good, and as we had luckily dined at New York, we were satisfied. The waiters were all niggers, grinning from ear to ear, white jacketed, active, and clever, about forty strong. The stewardesses, also of African origin, wore hoops of extravagant dimensions, and open bodies in front, displaying dark brown necks many of them lighted up by a necklace or diamond cross, rivalling Venus herself if she were black. They were really fearful objects to contemplate, for there was a look of display about them which read one a severe lesson on female vanity, so frightful did they appear, and yet rigged out like modern beauties. It was the most lovely afternoon conceivable, and we stayed on deck, sometimes on the bow and sometimes on the stern of the vessel, till[Pg 20] long after dark. We preferred the bow, as there was no awning there, and the air was more fresh and invigorating.
The passage through Long Island Sound was like a river studded on both sides with villas and green lawns, something like the Thames between Kingston and Hampton, but much wider, and with higher background, and altogether on a larger scale. When, owing to the darkness, we lost sight of these, they were replaced by lighthouses constantly recurring. This huge Leviathan, considerably longer than the Africa, proceeded at the rate of about eighteen miles an hour, going half-speed only, on account of the darkness of the night. The full speed was twenty-four miles an hour, and remember this was not a high-pressure engine. After proceeding through this narrow channel for about 120 miles, we again entered the Atlantic, but speedily reached the narrow inlet which extends up to this place. You may wonder at our having been able to make such minute observations upon the saloon, &c.; but having tried our state cabin, and not relishing it, we paced up and down the saloon, and occupied by turns most of its 120 chairs, till three o'clock in the morning brought us to the end of our voyage.[Pg 21] There was no real objection to the cabin, beyond the feeling that it was not worth while to undress and lie down for so short a time; besides which, papa was in one of his fidgetty states, which he could only relieve by exercise.
But how now to describe Newport? Papa is looking out of the window, and facing it is an avenue of trees running between two lawns of grass as green as any to be seen in England, though certainly the grass is coarser than at home. In these lawns stand houses of every shape and form, and we, being au troisième have a distant view of the sea, which looks like the Mediterranean studded with ships. As this place (the Brighton of New York) stands on a small island, this sea view is discernible from all sides of the house. We walked yesterday a long way round the cliffs, which are covered with houses far superior to the average villas in England, the buildings being of a brilliant white and sometimes stone colour, and of elaborate architecture, with colonnades, verandahs, balconies, bay windows of every shape and variety, and all built of wood. The churches are some of them very beautiful, both Gothic and Grecian. A Gothic one to which we went yesterday afternoon, was[Pg 22] high, high, high in its decorations, but not in the least in the doctrine we heard, which was thoroughly sound on "God so loved the world," &c. The fittings up were very simple, and the exterior of the church remarkable for the grace and simplicity of its outline; for being, like the houses, built entirely of wood, elaborate carving cannot be indulged in.
The church which we went to in the morning offered a great contrast to this, the interior being fitted up with high old-fashioned pews, like many a village church at home; but besides this, a further interest attached to Trinity Church, as being the one in which Dean Berkeley used to preach, and from its remaining unaltered in its internal appearance from what it was in his days. The pulpit is still the same, and there is still in the church the organ which he presented to it, at least the original case of English oak is there, and part of the works are the same, though some pipes have lately been added. Independently of Trinity Church, the town of Newport has many associations connected with Bishop Berkeley's memory, the place where he lived, and where he wrote his "Minute Philosopher" being still pointed out, as well as the spot on the beach[Pg 23] where he used to sit and meditate. The most striking buildings, however, are the hotels, one of which, the "Ocean House," is the largest building of the kind we have ever seen. It has very much the appearance of the huge convents one sees in Italy, and, standing on the top of the cliffs, it has a most remarkable effect. There are some very good streets, but the greatest part of the town consists of detached houses standing in gardens. There are very few stone buildings of any kind. The hotel we are in is not the largest, but is considered the best, and in the height of the season the place must be very gay.
The next, perhaps the greatest, feature here is the bathing. There are three beaches formed round a succession of points, the whole forming a lovely drive on dry hard sand; and such a sun as we gazed upon yesterday setting over these distant sands passes description. On the first of these beaches are ranged more than a hundred bathing machines at about a hundred yards above high-water mark, looking like sentry boxes on a large scale, with fine dry sand between them and the sea. We went down on Saturday to see the bathing, which is here quite a public affair; and having fixed our eyes on a[Pg 24] machine about a dozen yards off, we saw two damsels enter it, while a young gentleman, who accompanied them went into an adjoining one. In a few minutes he came out attired in his bathing dress and knocked at the ladies' door. As the damsels were apparently not ready, he went into the water to wait their coming, and in due time they sallied forth dressed in thick red baize trowsers and a short dress of the same colour and material, drawn in at the waist by a girdle. The gentleman's toilet was coloured trowsers and a tight flannel jacket without sleeves. He wore no hat, but the ladies had on very piquante straw hats trimmed with velvet, very like the Nice ones, to preserve them from a coup de soleil. They joined each other in the water, where they amused themselves together for a long time; a gentleman friend's presence on these occasions is essential, from the Atlantic surf being sometimes very heavy; but the young gentleman in question did not enact the part of Mr. Jacob, of Cromer, not being professional. The number of bathers is generally very great, though now the season being nearly over there are not many, but there were still enough to let us judge of the fun that is said to go on.[Pg 25]
There are few guests in this house now. A "hop" was attempted on Friday evening in the entrance hall, but the unhappy musicians exerted themselves in playing the Lancers' Quadrilles and all sorts of ugly jerking polkas without success, although an attempt at one quadrille, we were told, was made after we had retired for the night. The table d'hôte toilettes here now are much quieter than they were at Westpoint, there being but two short sleevers yesterday at our two o'clock dinner. There is a large and handsome public drawing-room, where we can rock in rocking chairs (even the bed-rooms have them), or pass an hour in the evening. We are waited on at dinner by twelve darkies, as the niggers are called, marshalled by a head waiter as tall as papa and as black as his hat. A black thumb on your plate, as he hands it to you, is not pleasant. The housemaids are also niggeresses, and usually go about in coloured cotton sun bonnets. I now leave off, as we start for Boston in an hour.
Boston, 14th September, 1858.—We reached this yesterday, and were looking for William all the evening, but were disappointed at his non-appearance. He arrived here, however, at three this morning by the steamer, and is now recounting his[Pg 26] adventures; he enjoyed himself very much, and looks all the better for his trip.
I ought to tell you of a few Yankee expressions, but I believe the most racy of them are used by the young men whom we do not come across: "I guess" is as common as "I think" in England. In directing you on any road or street, they tell you always to go "right away." If you do not feel very well, and think you are headachy, and that perhaps the weather is the cause, you are told you are "under the weather this morning." An excellent expression we think; so truly describing the state papa is often in when in dear old England. Then when you ask for information on any subject, the answer is frequently, "I can't say, sir, for I am not posted up on that subject." I asked an American gentleman, who was walking with us last night, not to walk quite so fast, and he answered, "Oh, I understand; you do not like that Yankee hitch." "Yankee" is no term of offence among themselves. Our friend certainly made use of the last expression as a quotation, but said it was a common one. They will "fix you a little ginger in your tea, if you wish it;" and they all, ladies and gentlemen, say, Sir, and Ma'am, at every sentence, and all through the conversation,[Pg 27] giving a most common style to all they say; although papa declares it is Grandisonian, and that they have retained good manners, from which we have fallen off.
I reserve my description of the journey here, and of this town, for my next letter.
JOURNEY TO BOSTON.— BOSTON.— PRISON.— HOSPITAL.— SPRINGFIELD.— ALBANY.— TRENTON FALLS.— JOURNEY TO NIAGARA.— NIAGARA.
Delavan House, Albany, Sept. 15th, 1858.
I find it at present impossible to keep up my letter to you from day to day, but I am so afraid of arrears accumulating upon me that I shall begin this to-night, though it is late and we are to start early to-morrow. My last letter brought us up to our arrival at Boston, but I have not yet described to you our delightful journey there.
We left Newport with our friends, Mr. and Miss Morgan, at two o'clock on the 13th, and embarked in a small steamer, which took us up the Narragansett Bay to the interesting manufacturing town of Providence. We were about two hours on the steamer, and kept pace with the railway cars which were running on the shores parallel to us, and also going to Providence. The shores were very pretty, green and sloping, and dotted with bright and clean[Pg 29] white wooden houses and churches. We passed the pretty-looking town of Bristol on our right. The day was lovely, brilliant and cool, with a delightfully bracing wind caused by our own speed through the water.
The boat brought us to Providence in time only to walk quickly to the railway, but we had an opportunity of getting a glance at the place. It is one of the oldest towns in America, dating as far back as 1635; but its original importance is much gone off, Boston, which is in some respects more conveniently situated, having carried off much of its trade. It is most beautifully situated on the Narragansett Bay, the upper end of which is quite encircled by the town, the city rising beyond it on a rather abrupt hill. Among the manufactories which still exist here, those for jewellery are very numerous.
We were now to try the railway for the second time in America, and having been told that the noise of the Hudson River line was caused by the reverberation of the rocks, and was peculiar to that railway, we hoped for better things on this, our second journey. We found, however, to our disappointment, that there was scarcely any improvement as to quiet; and as papa would eat a dinner instead of a luncheon at Newport, this and the noise together[Pg 30] soon worried his poor head into a headache. We were confirmed in our dislike of the cars and railways, which have many serious faults. The one window over which papa and I (sitting together) were able to exercise entire control, opened like all others by pushing it up. A consequence of this arrangement is that the shoulder next to it is in danger of many a rheumatic twinge, being so exposed to cold; whereas, if the window opened the reverse way, air could be let in without the shoulder being thus exposed. I forgot in my description of the cars, to tell you that the seats are all reversible, enabling four persons to sit in pairs facing each other, and also if their opposite neighbours are amiably disposed, enabling each pair to rest their feet on the opposite seat, and if the opposite seat is empty, the repose across from seat to seat can be still more complete; but it is an odious contrivance, and neither repose nor rest can be thought of in these most uncomfortable carriages. Our seats faced the front door, and were close to it, which was very desirable as the air is clearer at that end, and not so loaded with the impurities of so large a mass of all classes as at the other end. We made various purchases as we went along. First came the ticket man, then cheap periodicals, then apples and pears,[Pg 31] common bon-bons, and corn pop, of which I am trying to keep a specimen to send you. It is a kind of corn which is roasted on the fire, and in so doing, makes a popping noise, whence its name. It is pleasant to nibble. Then came iced water, highly necessary after the dry corn pop, and finally about twenty good and well-chosen books. Papa bought the Life of Stephenson.
But if we had room to grumble about discomforts within, we could only admire unceasingly without the very lovely road along which we were rapidly passing. The country consisted of undulating hills and slopes, prettily wooded, while bright white wooden houses and churches rapidly succeeded each other; the tall, sharp, white church spire contrasting beautifully with the dark back-ground of trees. It was delightful to see all the houses and cottages looking trim and neat, and in perfect order and repair. There was no such thing as dilapidation or poverty apparent, and the necessary repairs being so easily made, and the paint-brush readily available, all looked in the most perfect order. We could do little else than admire the scenery, and arrived at Boston at about six o'clock; the last few minutes of the journey being over a long wooden bridge or viaduct, which connects the mainland with the peninsula on[Pg 32] which Boston is built. We found rooms ready for us at Tremont House. It is an enormous hotel, but the passages are close, and the rooms small. They were otherwise, however, very luxurious, for I had a small dressing-room out of my bedroom in which was a warm bath and a plentiful supply of hot and cold water laid on, besides other conveniences.
The next morning we found Lord and Lady Radstock in the breakfast-room; and papa accompanied Lord Radstock to see an hospital and prison.
The prison was the jail in which prisoners are detained before their trial, as well as when the duration of their imprisonment is not to be very long. Nothing, by papa's description, can exceed the excellency of the arrangements as far as the airiness and cleanliness of the cells, and even the comforts of the prisoners, are concerned, but the system is one of strict solitary confinement. Papa and Lord R. were surprised to find that some unhappy persons, who were kept there merely in the character of witnesses, were subject to the same rigorous treatment. Lord R. remarked, that he would take good care not to see any offence committed while in this country, but the jailor replied, "Oh, it would be quite enough if any one declared you saw it."
The hospital appears to be a model of what such an[Pg 33] establishment ought to be. The wards are large, and, like the prison cells, very airy and clean, but with a great contrast in the character of the inmates for whose benefit they are provided. The great space which can usually be allotted, in a country like this, to institutions of this description, may perhaps give this hospital an advantage over one situated in the centre of a large city like London; though the semi-insular position of Boston must render space there comparatively valuable; but even this cannot take away from the merit of the people in showing such attention to the comforts of the needy sick. But what papa was most pleased with, was the provision made, on the plan which has been often tried in London, but never with the success it deserves, of an hospital, or home for the better classes of the sick. In the Boston hospital, patients are received who pay various sums up to ten dollars a week, for which they can have a comfortable room to themselves, and the best medical advice which the town affords. Papa and Lord R. were shown over this institution by Dr. Shaw, who was particularly attentive and obliging in answering all their questions.
We have since been exploring the town, and are quite delighted with it. It has none of the stiff regularity of New York, and the dwelling houses[Pg 34] have an air of respectable quiet comfort which is much wanted in that city of wealth and display. The "stores" too are far more attractive than in New York, though their way of asking you to describe exactly what you want before they show you anything, except what is displayed, reminded me much of France. The city is altogether very foreign-looking in its appearance, and we are glad to think we are to return and make a better acquaintance with it later in the month. There is a delightful "common," as they call it, or park, which is well kept, and much prized by the inhabitants. Some beautiful elm trees in it are the largest we have seen in this country. Around one side are the best dwelling houses, some of which are really magnificent. The hotel, which is a very large one, has some beautiful public sitting rooms, greatly larger than those at the Brevoort House at New York, which is much more quiet in this respect; but these large rooms form an agreeable adjunct to an hotel, as they are in general well filled by the guests in the house, and yet sufficiently large to let each party have their own little coterie.
The character of the inhabitants for honesty seems to be called in question by the hotel-keepers, for all over these hotels there are alarming notices to beware[Pg 35] of hotel thieves (probably English pickpockets); and in Boston we were not only told to lock our doors, but not to leave the key on the outside at any time, for fear it should be stolen.
Trenton Falls, Sept. 16th.—We left Boston on Tuesday afternoon, and got as far as Springfield, a town beautifully situated on the river Connecticut, and celebrated for a government institution of great importance, where they make and store up fire-arms. It is just 100 miles from Boston, and the railway runs through a beautifully wooded country the whole way, which made the journey appear a very short one. The villages we passed had the same character as those between Providence and Boston, and were, like them, built altogether of wood, generally painted white, but occasionally varied by stone-colour, and sometimes by a warm red or maroon colour picked out with white.
Springfield lay on our way to Albany, and as we had heard much of the beauty of the place, we were not deterred from sleeping there by being told that a great annual horse-fair was to be held there, but to secure rooms we telegraphed for them the day before. At the telegraph station they took upon themselves to say, there was no room at the established hotels, but that a new one on the "Euro[Pg 36]pean plan" had been opened the day before, where we could be taken in; at this we greatly rejoiced, but to our dismay on arriving, we found its existence ignored by every one, and we were almost in despair when we bethought ourselves to go to the telegraph office, where we were directed to a small new cabaret, whose only merit was that we, being its first occupants, found everything most perfectly fresh and clean; but having been only opened that day, and the town being very full, everything was in disorder, and there were but two bedrooms for papa, myself, William, and Thrower.[2] It became an anxious question how to appropriate them, as there was but one bed in one of the rooms, and two in the other. However, it was finally arranged, that papa and William should sleep in the double-bedded room, and Thrower and I together in the single bed. We called Thrower a lady of the party, and made her dine with us, for had they known she was only a "help," she might probably have fared badly.
After getting some dinner, at which the people are never at a loss in America, any more than in France, we sallied forth to see the town, and were exceed[Pg 37]ingly pleased with its appearance. Nothing could be brighter or fresher than it looked, and the flags and streamers across the street, and general lighting up, were foreign-looking and picturesque. Although the town is but small compared with those we had just left, the shops were spacious and well filled, and the things in them of a good quality. Hearing that there was a meeting at the City Hall, we went to it, little expecting to find such a splendid room. In order to reach it, we had to pass through a corridor, where the names of the officers of the corporation were painted over doors on each side, and were struck with amazement, when, at the end of this, we entered a hall, as light and bright-looking as St. James' Hall in London, and though not perhaps so large, still of considerable dimensions, and well proportioned. The walls were stone-colour, and the wood-work of the roof and light galleries were buff, picked out with the brightest scarlet. On a platform at one end of the room were seated the Mayor of Springfield, and many guests whom he introduced one by one to the audience in short speeches. These worthies delivered harangues on the subject of horses and their uses; and the speeches were really very respectable, and not too long, but were delivered in general with a strong[Pg 38] nasal twang. There were persons from all parts of America; Ohio, Carolina, &c. &c.
We made out our night tolerably well, and next morning went to look at the arsenal, and depôt of arms, and were shown over the place by a person connected with the establishment, who was most civil and obliging in explaining the nature of all we saw. The view from the tower was most lovely. The panorama was encircled by high hills, clothed with wood; and the town, and many villages and churches, all of dazzling whiteness, lay scattered before the eye. We drove next to the Horse Fair, which was very well arranged. There was a circus of half a mile, forming a wide carriage road, on which horses were ridden or driven, to show off their merits. The quickest trotted at the rate of twenty miles an hour. When the horses were driven in pairs, the driver held a rein in each hand. There was a platform at one end filled with well-conducted people, and a judge's seat near it. The horses in single-harness went faster even than those in pairs: one horse, called Ethan Allen, performing about twenty-four miles an hour; though Edward may arrive nearer than this "about," by calculating at the rate of two minutes and thirty-seven seconds, in which it went twice round this circle. The[Pg 39] owner of this horse has refused $15,000 or 3000l. for it. It is said to be the fastest horse in America, and a beautiful animal, but most of the horses were very fine. The people seemed to enjoy themselves much, and all appeared most quiet and decorous, but the whole population surprised us in this respect. We have seen but one drunken man since we landed. Even in our new cabaret, the opening of which might have given occasion for a carousal, every thing was most orderly. Our landlord, however, seemed very full of the importance of his position, and could think and talk of nothing but of this said cabaret. Their phraseology, is often very odd. In the evening, he said, "Now, will you like your dinner right away?" As we walked along the streets, and tried to get a room elsewhere, a man said, smacking his hands together, "No, they are already threbled in every room."
But I must now tell you of our journey from Springfield to Albany: the distance between the two is exactly 100 miles; Boston being 200 from Albany. We left Springfield by train at twelve o'clock, and reached Pittsfield, a distance of fifty miles, at half-past two. This part of the road presented a succession of beautiful views. Your sisters[Pg 40] will remember that part of the road near Chaudes Fontaines, where it runs through the valley, and crosses the Vesdre every five minutes. If they can imagine this part of it extended for fifty miles, and on a much larger scale, they may form some notion of what we saw. The railway crossed the river at least thirty times, so we had it on the right hand and left hand alternately, as on that little bit in Belgium. The river, called the Westfield, was very rapid in places, and the water, when deep, almost of a rich coffee colour. At Pittsfield we got on to the plateau which separates the Connecticut River and the Hudson. The plain is elevated more than 1000 feet above the sea. We then began rapidly to descend. The country was still as pretty as before, but more open, with hills in the back-ground, for till we reached Pittsfield these were close to us, and beautifully wooded to the top. At Pittsfield, in the centre of the town, there is a very large elm tree, the elm being the great tree of the country, but this surpassed all its neighbours, its height being 120 feet, and the stem 90 feet before any branches sprang from it.
We reached Albany at five o'clock; and a most beautiful town it is. The great street, as well as one at right angles to it leading up to the Capitol, is[Pg 41] wider, I think, than any street we ever saw; and the shops on both sides are very splendid. The hotel is very large and good; but, alas! instead of our dear darkies at Newport, we had some twenty pale-faced damsels to wait at table, all dressed alike in pink cottons, their bare necks much displayed in front, with large white collars, two little frills to form the short sleeves, large, bare, clean, white arms, and short white aprons not reaching to the knees. They had no caps, and such a circumference of hoops! quite Yankeeish in their style; and most careless, flirtatious-looking and impertinent in their manners. We were quite disgusted with them; and even papa could not defend any one of them. We were naturally very badly waited upon; they sailing majestically about the room instead of rushing to get what we wanted, as the niggers at Newport did. Men-servants answered the bed-room bells, and brought our hot water; the ladies being employed only as waiters.
This morning the fine weather we had hitherto enjoyed began to fail us, as it rained in torrents. Notwithstanding this, we started at half-past seven; passing through what in sunshine must be a lovely country, to Utica on the New York Central Railway, and thence by a branch railway of fifteen miles[Pg 42] to Trenton Falls. The country was much more cultivated than any we have yet seen. There were large fields of Indian corn, and many of another kind, called broom corn, being grown only to make brooms. We passed many fields of a brilliant orange-red pumpkin, which, when cooked, looks something like mashed turnips, and is called squash: it is very delicate and nice. But beautiful as the country was, even in the rain, we soon found out that we had left New England and its bright-looking wooden houses. The material of which the houses are built remains the same; but instead of being painted, and looking trim and neat as in New England, they consisted of the natural unpainted wood; though twelve hours of pouring rain may have made them more melancholy-looking than usual; for they were all of a dingy brown, and had a look bordering on poverty and dilapidation in some instances, to which we were quite unaccustomed.
On reaching this place we found the hotel was closed for the season; but rooms had been secured in a very fair country inn, where we had a tolerable dinner. We were glad to see the rain gradually cease; and the promise of a fine afternoon caused us to sally out as soon after dinner as we could to[Pg 43] see the falls. These are very beautiful: they are formed by a tributary of the Mohawk River, along the banks of which (of the Mohawk itself I mean) our railway this morning passed for about forty miles. The Erie Canal, a most celebrated work, is carried along the other bank of the river; so that, during all this distance, the river, the railway, and the canal were running parallel to each other, and not a pistol shot across the three.[3] We had been warned by some Swiss friends at Newport against carelessness and rashness in walking along the narrow ledge cut in the face of the rock, so we took a guide and found the pass very slippery from the heavy rain. The amiable young guide took possession of me, and for a time I got on tolerably well, clinging to the chain which in places was fastened against the face of the rock; but as the path narrowed, my head began to spin, and as the guide discouraged me, under these circumstances, from going any further, I turned back with Thrower and regained dry land, while the rest of the party were accomplishing their difficult task. They re[Pg 44]turned much sooner than we expected, delighted with all they had seen, though papa said I was right not to have pursued the narrow ledge. He then took me through a delightful wood to the head of the falls, where a seat in a little summer-house enabled me to enjoy the lovely scene. The river takes three leaps over rocks, the highest about 40 feet; though in two miles the descent is 312 feet. Beautifully wooded rocks rise up on either side; and the sunshine this afternoon lighting up the wet leaves added to the beauty of the scene. We scrambled down from the summer-house to the bed of the river, and walked on to the foot of the upper fall; which, though not so high as the others, was very pretty. In returning home we had glimpses of the falls through the trees. Many of the firs and maples are of a great height, rising an immense way without any branches, reminding us of the oaks at Fontainebleau.
We had to change our damp clothes on our return to the inn; and after partaking of tea-cakes, stewed pears, and honey, I am now sitting in the public room in my white dressing-gown. This toilette, I have no doubt, is thought quite en régle, for white dresses are much worn in America; and the company here this evening is not very refined[Pg 45] or capable of appreciating the points in which mine may be deficient. There is dancing at the great hotel every night in the season; but that is now over. Some sad accidents have happened here, by falls over the precipice into the river. The last occurred this year, when a young boy of eight, a twin son of a family staying here, from New York, was drowned: but these accidents, we are told, generally happen in the safest places from carelessness. We go on, to-morrow, probably to Rochester, where there are some pretty small falls; and on Saturday, the 17th, we hope to reach Niagara, from whence this letter is to be posted for England.
A nigger, and our guide of this afternoon, have just seated themselves in the corner of the drawing room where I am writing, and are playing, one the fiddle, and the other the guitar. Perhaps they are trying to get up a "hop," later, but there do not seem materials enough for it, and their tune is at present squeaky—jerky—with an attempt at an adagio. The nigger is now playing "Comin' thro' the Rye," with much expression, both of face and fiddle! Oh, such, squeaks! I wish Louisa heard them. Here come the variations with accompaniment of guitar.—Later.—The nigger is now singing plaintive love ditties![Pg 46]
International Hotel, Niagara Falls, September 18th.—We had gone from the station at Trenton to Trenton Falls in a close, lumbering, heavy coach, which is of very ordinary use in America. But yesterday morning we went over the same ground in an omnibus, which allowed us to see the great beauty of the country to perfection; and, although we had occasional heavy showers, the day was, on the whole, much more propitious for travelling, as the atmosphere was very clear, and the sandy dust was laid. We returned to Utica, or "Utikay," as they call it, and, having an hour to spare, went and saw the State Lunatic Asylum; but there was not much to remark upon it, although everything, as seems generally the case in this country, was very orderly and well kept.
The building, however, was not seen to advantage, as a very large portion of it was burnt down last year, and the new buildings were not entirely finished. The gentleman who showed us round was very attentive, and gave us a report of the establishment, which shows how creditably every one acted in the trying emergency of the fire. He gave us, also, two numbers of a little periodical, which is written and published by the inmates.
We left Utica soon after eleven, and came on to[Pg 47] Syracuse, through a well wooded and better cultivated country than we have yet passed. The aspect of the country is varied by fields of Indian corn, and tracts of burnt and charred stumps of trees, the remains of burnt forests. These stumps are left for some time to rot in the ground, and a few taller stems, without branches, are left standing, giving the whole a forlorn appearance but for the thought that the land will soon be cultivated and return a great produce; were it not for this, one would regret the loss of the trees, which are turned everywhere here to good account. The houses and cottages are all wood. The hurdles, used everywhere instead of hedges, are wood. The floorings of both the large and small stations are wood, worn to shreds, sometimes, by the tramp of feet. The engine burns wood. The forests are burnt to get rid of the wood. Long and enormous stacks of wood line the road continually, and often obstruct the view. All this made our journey to Syracuse, though interesting, much tamer than on the preceding days. An accident happened to the boiler, which detained us at Rome, but, as we were luckily near the station, we soon got another engine. On the whole, one travels with quite as great a feeling of security as in England.[Pg 48]
From Syracuse to Rochester there are two roads, one short and direct, and another, which, by taking a southern direction, passes through Auburn, Cayuga, Geneva, and Canandaigua. We were well repaid by taking the longer route, as the road went round the heads of the lakes, and in one case, indeed, crossed the head of the lake where these beautiful little towns are situated. The views of all these lakes, but especially of lake Cayuga, and of lake Seneca on which Geneva is situated, are very lovely. They stretch "right away" between high banks, varying from two to five miles apart, each forming a beautiful vista, closed up by distant blue hills at the further end. These lakes vary from thirty to forty miles in length, and by means of steamboats form an easy communication, though a more tedious one than the railways, between this and the southern part of the State of New York. We had a capital cicerone to explain all that we saw as we went along, in a Yankee, who told us he was "raised" in these parts, though he lived in "Virginny." He looked like a small farmer, but had a countenance of the keenest intelligence. He told papa, before he had spoken five minutes with him, that it was quite right a person of his intelligence should come to this country. When we came to Auburn,[Pg 49] he quoted "'Sweet Auburn, loveliest village of the plain;' a beautiful poem, sir, written by Goldsmith, one of your own poets." We told him we thought of going to St. Paul, beyond the Mississippi, when he said, "Oh yes! that's a new country—that's a cold country too. If you are there in the winter, it will make you snap."
At Rochester we stopped for an hour to dine. We had intended to sleep there, but none of us being tired, we changed our plan in order to come on here last night. During this hour we went to see the Falls of the Genessee, which in some respects surpassed Trenton, as the river is very broad, and falls in one sheet, from a height of ninety-six feet, over a perpendicular wall of rock. We dined, and then papa and I took a rapid walk to the post office, to post a letter to Alfred O., at Toronto. The streets, as usual, were very wide, with spacious "stores" running very far back, as they all seem to do in America. I asked when the letter would reach Toronto, and the man answered, "It ought to do so to-morrow, but it is uncertain when it will." Papa asked our guide from the hotel where he was "raised," (papa is getting quite a Yankee), to which he replied, "in Ireland." I slept, wonderful to say, through part of our journey here, in one of those[Pg 50] most uncomfortable cars, but woke up as we approached the station. The night was splendid (we had seen the comet at Rochester), and the moon was so bright as to make it almost as light as day; you may imagine our excitement when we saw, in the distance, rising above the trees, a light cloud of mist from the Falls of Niagara.?
Clifton House, September 18th.—Papa got into a melancholy mood at the International Hotel yesterday evening, on account of the hotel being an enormous one, and like a huge barrack; half of it we suspect is shut up, for they gave us small room au second, though they acknowledged they made up four hundred beds, and had only one hundred guests in the house. The dining room was about one hundred and fifty feet long, and the hotel was half in darkness from the lateness of the hour, and had no view of the Falls; so papa got more and more miserable, and I could only comfort him by reminding him we could be off to this hotel early in the morning; for as it is the fashion to try first one side for the view, and then the other, there was no offence in going from the United States to our own English possessions. On this he cheered up and we went out, and the first sight we got of this glorious river was at about eleven o'clock, when he insisted upon my[Pg 51] passing over the bridge to Goat Island. It was the most lovely moonlight night conceivable, and the beams lit up the crests of the foaming waves as they came boiling over the rapids. It was a glorious sight, though I was rather frightened, not knowing what perils might be in store for us.
To-day we made out our move to the Canada side, and are most comfortably lodged. Before coming to this hotel, we took a long drive down the river, on the American side. We got out of the carriage to see the Devil's Hole, a deep ravine, often full of water, but now dry. We stood on a high precipice, and had a grand view of the river. The river is generally passed over in silence in all descriptions of Niagara, and yet it is one of the most lovely parts of the scene. Its colour after it has left the Falls, and proceeds on its rapid way, full of life and animation, to Lake Ontario, is a most tender sea green. We drove on about six miles, and then crossed a slight suspension bridge (the suspension bridge being a ponderous structure for the railroad trains to pass over); but the one by which we crossed looked like a spider's-web; and the view midway, whether we looked up or down, was the finest specimen of river scenery I ever beheld. We then turned up the stream, and came by the English side to a most[Pg 52] wonderful whirlpool, formed by the river making a rapid bend, and proceeding in a course at right angles to the one it had been previously pursuing; but the violence of the stream had caused it to proceed a long way first in the original direction; and it was evidently not till it had scooped, or hollowed out, a large basin, that it was forced to yield to the barrier that was opposed to it. This is the sort of bend it takes.
After dinner we went to deliver a letter which papa had brought for Mr. Street, who has a house above the Falls. He was not at home; but we went through the grounds and over a suspension bridge he has built to connect a large island, also his property, with the mainland. There are, in fact, not one but many islands, into which one large one has probably, in the course of time, become divided by the raging torrent. It is just above the Horse-Shoe Fall, in the midst of the most boisterous part of the rapids; and it was quite sublime on looking up the river to see the horizon formed at a considerable level above our heads by the mass of foaming water. But now for the Falls!
You must fill up this blank with your imagination,[Pg 53] for no words can convey any idea of the scene. They far surpass anything we could have believed of them. This, however, I write after a thorough study of them from various points of view; for when we first caught a glimpse, in our drive to-day, of the Fall on the American side, it disappointed us; but from the verandah of this hotel, on which our bed-room windows open, we had the first astounding view of the two Falls, with Goat Island dividing them; and that sight baffles all description. The Horse-Shoe Fall is magnificent. The curve is so graceful and beautiful; and the mist so mysterious, rising, as it does, from the depths below, and presenting the appearance of a moving veil as it glides past, whether yielding to every breath of wind, or, as now, when driven quickly by a gale; then the height of the clouds of light white mist rising above the trees; and, above all, the delicate emerald green where the curve itself takes place: all these elements of beauty combined, fill the mind with wonder, when contemplating so glorious a work of God's hand; so simple, and yet so striking and magnificent. We can gaze at the whole all day and all night, if we please, from our own windows. The moon being nearly full, is a great addition to the beauty of the scene. I have frequently risen[Pg 54] from my seat while writing this, to look first at the rapids above the American Fall, lit up and shining like the brightest silver; then at the moon on the mist, illuminating first one part of it and then another. I must proceed with my description of our doings (if I can) on Monday, before leaving this for Toronto, which we are to do on Monday afternoon; but this must be posted here, and I should like to finish my description of Niagara in this letter. We met a real Indian to-day. He had somewhat of a Chinese cast of countenance. Perhaps we shall see more of them. It is said that some of the black waiters in this hotel are escaped slaves, having come to English ground for safety.
September 19th.—This being Sunday, we went to a chapel in a village of native Indians of the Tuscarrara tribe. The chapel was about half filled with these poor Indians and half with visitors like ourselves. They have had a missionary among them for about fifty years, and it is to be hoped that former missionaries talked more sense to them, and taught them better truths, than the one we heard to-day. His sermon was both long and tedious, and was interpreted into the Tuscarrara language sentence by sentence as the preacher, who was a Presbyterian, delivered it. The burden of it was their ingrati[Pg 55]tude, not to God, but to the Government of the United States, which had devoted an untold number of dollars for their conversion; and he ended by a threat that this generosity on their part would be withdrawn if they did not alter their wicked course of life. As we were there for half an hour before the service began, we had an opportunity of conversing with many of these poor people, who seemed little to deserve this severe censure, for many of them had evidently come from a distance, having brought their food with them, and the people seemed of a quiet and harmless disposition. Few of them seemed to understand English, and these only the men, as the women professed, at least, not to understand papa when he tried to talk to them. They had all of them remarkably piercing and intelligent black eyes, but were not otherwise good looking. There were two little babies in their mothers' arms, one in a bright yellow dress. The women wore handkerchiefs tied over their heads, except one or two who wore round hats and feathers. Some in hoops and crinolines! All wore bead necklaces. They are the makers of the well-known mohair and bark and beadwork. In the churchyard were many tombstones with English inscriptions. The following is the copy we made of one:[Pg 56]—
In the 61st year of his age.
The memory of his many virtues will be embalmed in the hearts of
his people, and posterity will speak of his praise.
He was a good man, and a just.
He held the office of Grand Sachem 30 years, and was
Missionary Interpreter 29 years."
After chapel we returned to the American side of the Fall, where the table d'hôte dinner was later than at the Clifton Hotel, which we had missed. While waiting for dinner, we went again to Goat Island, and had some splendid views of the Falls, the day being magnificent beyond all description. Papa and William afterwards took a long walk to get a new view of the whirlpool. Papa has made me dreadfully anxious all day by going too close to the edges of the precipices; and as the rock is very brittle and easily crumbles off, and as his feet often trip in walking, you may suppose the agonies I have been in; at last I began to wish myself and him safe in the streets of Toronto. I was not the least frightened for myself, but it was trying to see him always looking over, and about to lean against old crazy wooden balustrades that William said must have[Pg 57] given way from sheer rottenness with any weight upon them. This is such a night, not a single cloud; the clearest possible sky and the moon shining brightly, as it did over the two Falls the first night we were here. Papa calls me every minute—"Oh come, do come, this minute; I do not believe you have ever yet seen the Falls!!!" To-morrow we have one remaining expedition,—to go in a small steamer called the "Maid of the Mist," which pokes her nose into the two Falls about six times a day. The passengers are put into waterproof dresses. This I hope to describe to you to-morrow, and shall despatch my letter before starting for Toronto.
[2] My English maid.
[3] The Erie Canal is one of the three great means of communication which existed previous to the introduction of railways between the Eastern States and those that lie to the west of the Alleghanies; the other two being the Pennsylvania and the Baltimore and Ohio Canals. Sections of these great works are shown on the map.
NIAGARA.— MAID OF THE MIST.— ARRIVAL AT TORONTO.— TORONTO.— THOUSAND ISLANDS.— RAPIDS OF THE ST. LAWRENCE.— MONTREAL.— VICTORIA BRIDGE.
Clifton Hotel, Falls of Niagara,
Sept. 20th, 1858.
I intended to have wound up the description of Niagara in the letter I despatched to you two hours ago, but we returned home from our expedition this morning only five minutes before the post hour for England, so that our packet had to be hastily closed.
We had rather a chapter of accidents this morning, but all has ended well. We went out immediately after breakfast, the weather being splendid, though there was a high wind, and finding the mist driving very hard, we decided on going over to the opposite shore across the suspension bridge, rather than be ferried over to the steamer in a small open boat, which can never, I imagine, be very pleasant in such a near neighbourhood to the two Falls. William, however, remained on this side, preferring the ferry, and we were to meet on the opposite bank and take[Pg 59] to the little steamer; but though our drive took half-an-hour and his row five minutes, he was not at the place of rendezvous when, we arrived, nor did he appear after we had waited for him some time. Papa then went in a sort of open car down an inclined plane, contrived to save the fatigue of a long stair. On getting to the bottom he saw nothing of William, and in walking on the wet planks he slipped down and fell on his side, and cut his face and bruised his eye; he says his eye was within a hair's breadth of being put out by the sharp corner of a rock. He walked up the long stair, being too giddy after his fall to attempt the car, and he felt very headachy and unwell in consequence all the morning. At last William made his appearance. There had been no ferryman for a long time, and when he came he knew so little how to manage the boat, that had not William rowed they would have been down the river and over the rapids! At last we all four (Thrower included), started down the inclined plane to the steamer, and were warned by papa's tumble to take care of our footing. It might easily be made a more pleasant landing-place than it is by means of their everlasting wood. We got on to the "Maid of the Mist," and were made to take off our bonnets and hats, and put on a sort of waterproof capuchin cloak[Pg 60] and hood, and up we went on deck. In one moment we were drenched; the deck was a running sea, and the mist drove upon us much harder than pouring rain. I went there with a cold, and if it gets no worse, shall think fresh water is as innocuous as salt. It was quite a question whether the thing was worth doing: the day was probably unfavourable, as the mist drove on us instead of the other way, but some parts were very fine. We returned to the same landing-place, as they most stupidly have none on this side; so up we went again in the open cars, and on landing we had our photographs done twice with views of the Falls as a background. They were very well and rapidly done. We then drove William towards the Cave of the Winds, which is a passage behind what looks from these windows a mere thread of a waterfall, but is really a very considerable one. Ladies, however, perform this feat as well as gentlemen, but they have entirely to change their dress—it is like walking through a great shower-bath to a cul de sac in the rock. Circular rainbows are seen here, and William saw two; he seemed to be standing on one which made a perfect circle round him. A certificate was given him of his having accomplished this feat. While he was doing this we bought a few things made by the[Pg 61] Indians and the Shakers, and then met William, and hurried home in time only to sign and despatch our letters to England. We then dined, and I am now obliged suddenly to stop short in writing, as my despatch-box must be packed, for we leave this at half-past four for Toronto.
Rossin House, Toronto, Sept. 21st.—Our journey here yesterday was not through as pretty a country as usual, and this part of Canada strikes us as much tamer than anything we have yet seen in America. We changed trains at Hamilton and remained there nearly an hour. Sir Allan McNab has a country house in the neighbourhood, said to be a very pretty one, and we shall probably go in the train to-morrow to see him. The railroad, for some time towards the end of our journey yesterday, ran along the shore of Lake Ontario. The sky was pure and clear, with the moon shining brightly on the waters of the quiet lake. It was difficult to believe that the immense expanse of water was not salt. It looked so like the sea, especially when within a few miles of Toronto we saw tiny waves and minute pebbles and sand, which gave it an appearance of a miniature sea beach. Had I not been on a railway when I saw these small pebbles, I should have picked up some for you, and I think you would have valued[Pg 62] them as much as your cornelians at Cromer. I searched for them later, and never came up with such a pretty pebbly beach again.
Montreal, Sept. 25th.—Unhappily this sheet has been packed up by mistake for some days, and I have not been able to go on with my journal, but I resume it this evening, for it must be despatched to you the day after to-morrow.
We passed the 22nd and 23rd at Toronto, and had much pleasure there in seeing a great deal of the Alfred O.'s, and their very nice children, and it was quite touching to see the pleasure our visit gave them. We had the sorrow, however, of parting from William, who left us on the morning of the 23rd for the Far West. He went with Mr. Latham and Mr. Kilburn, and it was a very great comfort to us that he had such pleasant companions, instead of travelling such a distance alone. We had an early visit at Toronto from Mr. and Mrs. W., friends of the O.'s: they begged us so earnestly to remain over the 23rd to dine with them, that we consented to do so. Toronto is a most melancholy-looking place. It has suffered in the "crisis," and the consequence is that wide streets seem to have been begun but never finished, giving the town a very disastrous look. There is one wide handsome street with good[Pg 63] shops, and our hotel was an enormous one; but when this is said, there is little more to add about it, for it looks otherwise very forlorn, and altogether the town is the least inviting one we have yet seen in our travels.
In the course of our drive we had an opportunity of seeing the interiors of some of the houses, many of which display considerable wealth; the rooms being large, and filled with ornaments of every sort. The ladies dress magnificently; a handsome coral brooch is often worn, and is almost an infallible sign, both here and in the United States, of a tour to Italy having been accomplished; indeed I can feel nearly as certain that the wearer has travelled so far, by seeing her collar fastened with it, as if she told me the fact, and many such journeys must have been performed, judging by the number of coral brooches we see.
We did little the first day but drive about the streets. We drank tea at the A. O.'s, and the next day they took us to see one very beautiful sight; the New University, which is in course of building, and is the most beautiful structure we have seen in America. Indeed it is the only one which makes the least attempt at Mediæval architecture, and is a very correct specimen of the twelfth century. The[Pg 64] funds for building this university arise out of the misappropriation (by secularising them) of the clergy reserves; the lands appropriated to the college giving them possession of funds to the amount of about three hundred thousand pounds. Of this the building, it is supposed, will absorb about one hundred and twenty thousand pounds, and they propose to lay out a large sum to increase an already very good library, which is rich in works on natural history and English topography. Dr. McCaul, who is the president of the college, is a brother of the preacher in London.
We dined at the W.'s on the evening of the 23rd. Their house is very large, having been lately added to, and the town being very busy, preparing for an Agricultural Meeting, the upholsterer had not time to put down the carpets or put up the curtains, and the night being cold, we felt a little twinge of what a Canadian winter is; but the drawing-rooms were exceedingly pretty,—the walls being very light stucco, with ornaments in relief, and they were brilliantly lighted. We were eighteen at dinner, the party including the O.'s, the Mayor, Dr. and Mrs. McCaul, and Sir Allan McNab, who had come from his country-place to meet us. The dinner was as well appointed, in all respects, as if it had[Pg 65] taken place in London. In the evening Mrs. W. sang "Where the bee sucks" most beautifully. Papa encored it, and was quite delighted at hearing so favourite a song so well sung. The mayoress also sang, and so did another lady. The furniture of the rooms was of American oak and black walnut, which are favourite woods; but we did not much admire them. When we were leaving, Mrs. W. showed us her bed-room, which was really splendid,—so spacious, and so beautifully furnished; there was a bath-room near it, and other bed-rooms also of large dimensions. We drove back to our hotel in the moonlight, so bright and clear that it was difficult not to suppose it daylight, except that the planets were so brilliant.
We took leave that night of the O.'s, as we had to make an early start next day, and were very sorry to part from them. On the 24th, we were off at eight in the morning by train to Kingston, arriving there early in the afternoon. It is the best sleeping-place between Toronto and Montreal. The road was uninteresting, though at times we came upon the broad waters of the lake, which varied the scenery. We had an excellent dinner at the station, and I ought to mention, that as we were travelling on the Grand Trunk Railway, and on English soil, we had[Pg 66] first class carriages; there being both first and second class on this line, but varying only in the softness of the seats. There was no other difference from other lines.
Kingston is a prosperous little town on the borders of the lake, and the hotel quite a small country inn. We drove out to see the Penitentiary, or prison, for the whole of the Two Canadas,—a most massive stone structure. I never was within prison-walls before, so that I cannot compare it with others; but, though papa had much admired the prison at Boston, he preferred the principle of giving the prisoners work in public (which is the case at Kingston), to the solitary system at Boston. We saw the men hard at work making furniture, and in the blacksmith's forge, and making an enormous quantity of boots; they work ten hours a day in total silence, and all had a subdued look; but we were glad to think they had employment, and could see each other. Their food is excellent,—a good meat diet, and the best bread. The sleeping-places seemed to us dreadful little solitary dens, though the man who showed us over them said they were better than they would have had on board ship. There were sixty female prisoners employed in making the men's clothes, but these we were not allowed to see. One lady is per[Pg 67]mitted to visit them, in order to give them religious instruction, but they do not otherwise see the visitors to the prison. There are prisoners of all religious denominations, a good many being Roman Catholics; and there are chaplains to suit their creeds, and morning and evening prayers.
We walked back to Kingston, and on the walls observed notices of a meeting to be held in the town that evening, to remonstrate against the work done by the prisoners, which is said to injure trade; but, as we were to make a very early start in the morning, we did not go to it.
We were called at half-past four to be ready for the boat which started at six for Montreal. It was a rainy morning, and I awoke in a rather depressed state of mind, with the prospect before me of having to descend the rapids of the St. Lawrence in the steamer; and as the captain of our vessel in crossing the Atlantic had said, he was not a little nervous at going down them, I thought I might be so too. We had first, however, to go through the Thousand Islands, which sounds very romantic, but turned out rather a failure. There are in reality about 1,400 of these islands, where the river St. Lawrence issues from Lake Ontario. The morning was unpropitious, it being very rainy, and this, no doubt,[Pg 68] helped to give them a dismal appearance. They are of all forms and sizes, some three miles long, and some hardly appearing above the water. The disappointment to us was their flatness, and their all being alike in their general aspect, being covered with light wood. When this is lit up by the sun, they are probably very pretty, as we experienced later in the day, which turned out to be a most brilliant one. The islands are generally uninhabited, except by wild ducks, deer, foxes, raccoons, squirrels, musk-rats, and minxes, and also by partridges in abundance. We have tasted the wild duck, which is very good.
About one o'clock in the day we lost sight of the islands, except a few, which occasionally are scattered along the river; we had no longer however to thread our way among them, as we had done earlier in the day. Dinner was at two, but we were not much disposed to go down, for we had just passed one rapid, and were coming to the finest of all, the Cedars; but they turned out to be by no means alarming to an unpractised eye. The water is much disturbed, and full of small crests of waves. There were four men at the wheel, besides four at the tiller, and they had no doubt to keep a sharp look out; we stood on deck, and received a good sea in our faces, and were much excited by the scene.[Pg 69] The longest rapid occupied us about twenty minutes, being nine miles long. It is called the Long Sault. The banks on either side continued flat; we stopped occasionally at pretty little villages to take in passengers or wood, but these stoppages told much against our progress, and the days now being short, we were informed that the vessel could not reach Montreal that night. There is a rapid a few miles above Montreal, which is the most dangerous of them all, and cannot be passed in the dark. The boat, therefore, stopped at La Chine for the night, and we had our choice of sleeping on board or landing and taking the train for eight miles to Montreal; and as we had seen all the rest of the rapids, and did not feel much disposed for the pleasure of a night in a small cabin, we decided on landing. We had tea first, with plenty of cold meat on the table, and the fare was excellent on board, with no extra charge for it.
Before landing we had a most magnificent sunset. The sun sank at the stern of the vessel; and the sky remained for an hour after in the most exquisite shades of colouring, from clear blue, shading to a pale green, and then to a most glorious golden colour. The water was of the deepest blue, and the great width of the noble river added to the[Pg 70] grandeur of the scene. The Canadian evenings and nights are surpassingly beautiful. The atmosphere is so light, and the colouring of the sunset and the bright light of the moon are beyond all description. We made acquaintance with a couple of Yankees on board, who amused us much. They were a young couple, travelling, they said, for pleasure. They looked of the middle class, and were an amusing specimen of Yankee vulgarity. The lady's expression for admiration was "ullegant:" the dinner was "ullegant," the sunset was "ullegant," and so was the moonrise, and so were the corn-cakes and corn-pops fixed by herself or her mother. She was delighted with the bead bracelet I was making, and I gave her a pattern of the beads. She was astonished to find that the English made the electric cable. She and her husband mean to go to England and Scotland in two years. I was obliged to prepare her for bad hotels and thick atmosphere, at both of which she seemed astonished. She was also much surprised that she would not find Negro waiters in London. They remained on board for the night; and on meeting her in the street yesterday, she assured us the last rapid was "ullegant," and that we had missed much in not seeing it.[Pg 71]
We arrived at Montreal at eight o'clock on the evening of the 24th, and walked a little about the town. The moon was so bright that colours could be clearly distinguished. We yesterday spent many hours on the Victoria bridge which is building here across the river in connection with the Grand Trunk Railway. It is a most wonderful work, and I must refer you to an interesting article in the last Edinburgh Review for a full account of it. Papa had letters to the chief officials of the railway, which procured us the advantage of being shown the work in every detail by Mr. Hodges (an Englishman), who has undertaken the superintendence of it—the plans having been given him by Stephenson. The expense will be enormous—about a million and a quarter sterling; almost all raised in England. The great difficulties to be contended with are:—the width of the river—it being two miles wide at this point; its rapidity—the current running at the rate of seven miles an hour; and the enormous masses of ice which accumulate in the river in the winter; rising as high sometimes as the houses on either side, and then bursting their bounds and covering the road. The stone piers are built with a view to resist as much as possible this pressure; and a great number of them are finished, and have[Pg 72] never yet received a scratch from the ice, which is satisfactory. Their profile is of this form. And this knife-like edge cuts the ice through as it passes down the river, enabling the blocks to divide at the piers and pass under the bridge on each side. The piers are built of limestone, in blocks varying from eight to ten feet high: but in sinking a foundation for them, springs are frequently met with under some large boulders in the bed of the river, and this causes great delay, as the water has to be pumped out before the building can proceed. The bridge will be an iron tubular one; the tubes come out from Birkenhead in pieces, and are riveted together here. We first rowed across the river with Mr. Hodges in a six-oared boat; and the day being warm and very fine, we enjoyed it much. This gave us some idea of the breadth of the river and of the length of the bridge, of which it is impossible to judge when seen fore-shortened from the shore.
We then mounted the bridge and were astonished at the magnitude of the work. There is an immense forest of woodwork underneath most of it at present, but they are glad to clear this away as fast as the progress of the upper work admits, as if left till[Pg 73] winter the force of the ice cuts through these enormous beams as if they were straw. We could only proceed across two piers at the end furthest from the town, but here we had a very fine view of Montreal, lying at the foot of the hill from which it takes its name. It has many large churches, the largest being the Roman Catholic cathedral, and the tin roofs of the houses and churches glittered in the sun and gave a brilliant effect. We returned to the boat and rowed again across the river below the bridge, and here, owing to the strength of the current our boat had to pursue a most zig-zag path, pulling up under the eddy of each buttress, but our boatmen knew well what they were about, as they are in the habit of taking Mr. Hodges daily to the bridge and it was very pretty to hear the warning of doucement! doucement! from the helmsman as we approached any peril. Mr. H. said that without the familiarity they had with the river, the boat would in an instant be carried down the stream and out of all control. The French language is much more spoken than the English, there being a large body of French Roman Catholic Canadians here and at Quebec. I say this to account for the doucement; but must now leave this wonderful bridge, and tell you that after seeing it we drove to the Bishop of Montreal's.[Pg 74] We found him and Mrs. Fulford at home, and sat some time with them, and they asked us to drink tea with them, which we did. There was no one there but ourselves, and we passed an agreeable evening with them, and came home by moonlight with the comet also beaming on us.
September 27th.—We went yesterday morning to a small church in the suburbs where the bishop preached. We found Lord and Lady Radstock in the hotel, and papa walked with him in the afternoon, and endeavoured to learn something of the Christian Young Men's Association here. They found the secretary at home, and from him learnt that the revivals of religion here have lately been of a satisfactory nature, and that there is a great deal of religious feeling at work among the middle classes. I forgot to mention that on Saturday we met a long procession of nuns going to the church of Notre Dame, which gave the place a very foreign look. We went into the church for a few minutes. It was very large, part of it was well filled, and a French sermon going on. There are a good many convents here, and I shall try to visit one. The Jesuits are said to be very busy. We hear French constantly spoken in the streets. We went to church again[Pg 75] yesterday evening, when the bishop preached on the text, "Demas hath forsaken me."
To-day we took Lord and Lady Radstock to Mr. Hodges, who promised to show them over the bridge, and since that papa and I have had a pleasant drive round the mountain. From one part we had a good view of the Ottawa river, celebrated by Moore, who wrote his Canadian boat song in a canoe on the rapids of that river. The town of Ottawa has been named by the Queen as the seat of Government; but after consulting her on the subject, the inhabitants seem disinclined to take her advice. The views were very pretty, and the day warm and pleasant. As we drove we frequently saw on the walls, large placards with a single text in French or English, an evidence of the work of the revival going on here. We wound up our visit to Montreal by buying some furs, this being the best place to get them: they are to be shipped from here in a sailing vessel, and therefore will not reach London for some time, but notice will be sent of their coming; so be on the look out for them some day. We are off this afternoon for Quebec, where we hope to find some good news from you all. So adieu, my dear child.
JOURNEY FROM MONTREAL TO QUEBEC.— QUEBEC.— FALLS OF MONTMORENCY.— ISLAND POND.— WHITE MOUNTAINS.— PORTLAND.— RETURN TO BOSTON.— HARVARD UNIVERSITY.— NEWHAVEN.— YALE UNIVERSITY.— RETURN TO NEW YORK.
Portland Maine, Sept. 29th, 1858.
I closed my last letter to you at Montreal, since which we have been travelling so much that I have had no time for writing till to-night. I must now, therefore, endeavour to resume the thread of my narrative, though it is a little perplexing to do so after going over so much ground as we have done lately in a short space of time.
We left Montreal early in the afternoon of the 27th, in company with Mr. and Mrs. Bailey. He is one of the managers of the Grand Trunk Railway, and came with us as far as Quebec, as a sort of guard of honour or escort, papa having been specially commended to the care of the employés on this line. Both he and his wife are English. We crossed the St.[Pg 77] Lawrence in a steam-ferry to join the railway, and as long as it was light we had a most delightful journey through a highly cultivated country, covered with small farms, which came in quick succession on both sides of the road. These farms are all the property of French Canadians, and on each one there is a wooden dwelling-house, with barns and out-houses attached to it, and the land runs down from the front of the tenement to the railroad. There is no hedge to be seen anywhere, and these long strips of fields looked very like allotment lands in England, though on a larger scale. These proprietors have been possessors of the soil from the time of the first settlement of the French in Canada, and the farms have suffered from the subdivision of property consequent on the French law of succession. They are so close together that, when seen at a distance, the houses look like a continuous line of street as far as the eye can reach, but we soon lost sight of them in the obscurity occasioned by forests and the approach of night. We passed many log huts, which, though very rude, do not seem uncomfortable dwellings.
We saw little of the country as we approached Quebec, and were conscious only of crossing the Chaudière river and of going along its banks for some way, and afterwards along those of the St. Law[Pg 78]rence, till we reached Point Levi, opposite Quebec. Here we got into a steamer to cross the river, and from the steamer we had a grand view of the citadel and town of Quebec, the tin spires shining jointly with the moon and the comet; for we beg to say we do not require telescopes of high power, as we see by the papers you do in England, to detect the latter luminary, which really does look here almost as if it added to the light of the night. Papa and I differ greatly as to the length of its tail. I say it looks two yards long, but papa says it is difficult to tell this, but that it is really about a degree and a half in length, or about six diameters of the moon. The nucleus is larger and brighter than any star in the Great Bear, and these are all bright here to a degree of which you can form no idea. The planets look as large as fourpenny-pieces. Papa has made me reduce them to this estimate, as I originally said as large as sixpences; but he questions altogether my appreciation of the size of the heavenly bodies, which do all seem wonderfully large to my eyes.
On reaching the north side of the river, on which Quebec stands, we got into an omnibus and drove up streets of a most tremendous ascent; it was really quite alarming, as the pavement was in the[Pg 79] most dreadful state, and the omnibus, which was very rickety, was crammed with passengers. Next morning we got up very early, and papa went out before breakfast to inquire for the letters which we expected to receive from England, but which had not yet arrived.
After an early breakfast we went in an open carriage to the Falls of Montmorency, and I think I never had a more lovely drive. We passed through several most prosperous-looking villages, and between farm houses so closely adjoining each other as to give the appearance of a long suburb to the city. At Beauport, about half-way between Quebec and Montmorency, there is a splendid Roman Catholic church, which would do credit to any country. The inhabitants here and at Quebec generally are entirely French Canadians, and the driver here, as at Montreal, was quite in the Coharé[4] style for intelligence and respectable appearance. The falls of Montmorency are a little way off the road, and the approach to the top of the fall down a flight of wooden stairs is very easy. The river here descends in one great fall of 250 feet, and as the river is 60 feet wide, the proportion between the height and the breadth[Pg 80] of the fall seems nearly perfect. It falls almost into the St. Lawrence, as it tumbles over the very bank of the latter river, and the view up and down the glorious St. Lawrence is here very beautiful. We were elevated so far above the bottom of the chasm that the spray apparently rose up only a short way, but it really does rise upwards of 150 feet, and in winter it freezes and forms a cone of ice exceeding 100 feet in height, which is said to present a most wonderful appearance.
Returning to Quebec we had a splendid view of the town. The fortress on Cape Diamond seemed to jut out into the river, along the banks of which, and rising to a great height above it, the town lay in all its glory. The tops of the houses and the spires of the churches are covered with tin, and from the dryness of the atmosphere it looks as fresh and polished as if just put up. The sun was shining splendidly, and the effect was almost dazzling. This and the richness of the intervening country produced an impression which it would be difficult to efface from the memory. The citadel, I should think, is hardly as high as the castles of Edinburgh or Stirling, but in this country everything (even to the heavenly bodies!!!) is on such a scale that it is not easy to draw comparisons. The guide book, how[Pg 81]ever, says that the rock rises 350 feet perpendicularly from the river, so that by looking at some of your books of reference, you may find out which is the highest. The approach is from the town behind, by a zig-zag road, and the fortifications seem very formidable and considerable, though papa says greatly inferior to Gibraltar, or to Malta, which it more strongly resembles as a work of art.
Mr. Baily procured us an order for admission, so that we went to the highest point, and the view up and down the river was truly magnificent. A little below the town it is divided by an island of considerable size, and as the river takes a bend here, it is rather difficult to make out its exact course. The town is situated at the junction of the St. Lawrence and the St. Charles, and as the latter forms a large bay or estuary at the confluence, the whole has a very lake-like appearance.
We left the citadel at the gate opposite the one at which we entered, and getting out upon the plains of Abraham, saw the monument erected on the spot where Wolfe fell; close to it is an old well from which water was brought to him to relieve his thirst after he had received his mortal wound. Another monument is erected within the citadel, in[Pg 82] what is called the Governor's Garden. This is raised to the joint memories of Wolfe and the French general, Montcalm, who was also mortally wounded in the same action. From the plains of Abraham there is a beautiful view up the river, and here, as on the other side of the town, the country at a distance is studded with farm houses. In a circuit we made of two or three miles in the vicinity of the town, we passed a number of really splendid villas belonging to English residents, but with this exception all seemed much more French than English, excepting that in la vieille France we never saw such order, cleanliness, and comfort, nor could these be well surpassed in any country.
The small farmers here live entirely upon the produce of their farms; they knit their own stockings, and weave their own grey coarse cloth. We looked into several of their houses, and the extreme cleanliness of every little corner of their dwellings was wonderful. The children seem very healthy and robust-looking. The whole population talk French. The crosses by the roadside proclaim them to be Roman Catholics, and the extensive convents in the town tend doubtless to the promotion of the temporal comforts of the poorer inhabitants. The principal church was richly decorated with gilding up[Pg 83] to the roof, and the gold, from the dryness of the climate, was as bright as if newly laid on.
The extreme clearness of the air of Canada contributed, no doubt, greatly to the beauty of everything we saw, though we found the cold that accompanied it rather sharper than we liked. Mrs. Baily told me that it is a curious sight to see the market in the winter, everything being sold in a frozen state. The vegetables are dug up in the beginning of winter, and are kept in cellars and from thence brought to market. A month's consumption can be bought at a time, without the provisions spoiling, as all remains frozen till it is cooked. The sheep and pigs are seen standing, as if alive, but in a thoroughly frozen state. The winter lasts from November till April. Sleighing is the universal and only mode of travelling. The sleighs, which are very gay, are covered with bells, and the travellers in them are usually clothed in expensive furs. Pic-nics are carried on in the winter, to arrange which committees are formed, each member inviting his friends till the parties often number 100. They then hire a large room for dancing, and the guests dress themselves in their ball dresses, and then envelope themselves in their furs, and start at six in the evening for their ball, frequently driving in their sleighs for several miles[Pg 84] by moonlight to the place of rendezvous. Open sleighs are almost always used for evening parties, and apparently without any risk, although the evening dress is put on before starting. There is great danger without care of being frost-bitten during a Canadian winter, but it must be a very gay and pretty sight to see sleighs everywhere, and all seem to enjoy the winter much, though the cold is very intense.
We left Quebec early in the afternoon of the 28th, having called at the post-office on our way to the train, and got our English letters. We now passed during the day what we missed seeing the night before, on our approach to Quebec. In crossing the Chaudière we could see the place where this large river plunges over a perpendicular rock 130 feet high, and the river being here very broad, the falls must be very fine, but though we passed close above them, we could only distinguish the difference of level between the top and the bottom, and see the cloud of spray rising above the whole. The road till night-fall passed chiefly through forest lands. The stations were good, though sometimes very small, and at one of the smallest the station-master was the son of an English clergyman.
At Richmond we parted company with the Bailys[Pg 85] and got on to Island Pond, where we slept at a large and most comfortable hotel. From Richmond the road passes through a very pretty country, but its beauties were lost upon us, as the night was very dark and there was no moon. This also caused us to miss seeing the beauties of Island Pond on our arrival there, but we were fully repaid by the sight which greeted our eyes in the morning, when we looked out of our window. The Americans certainly have grand notions of things, this Island Pond being a lake of considerable dimensions studded with beautiful islands, and surrounded on all sides by finely wooded hills, up which the heavy mist rose half way, presenting the appearance we have so often seen in Switzerland, of hills apparently rising out of a frozen ocean. The mist too, covering the surface of the water, gave it a snow-like look, and altogether the sight was very lovely. The road from this to Gorham was most interesting, being down the course of the Androscoggan river through a very wide valley, with high hills on both sides.
We left the train at the Alpine House at Gorham, to take a peep at the White Mountains. We were kept waiting some little time at Gorham, while the wheels of the buggy, that was to take us to the foot of Mount Washington, were being examined. This[Pg 86] vehicle was a sort of double-bodied pony chair, of a very rickety description, the front seat being contrived to turn over, so as to make more room for those at the back to get in and out, the consequence was that it was always disposed, even with papa's weight upon it, to turn over, and throw him upon the horses' tails. Thrower and I sat behind, and papa and the driver in the front, and I held on tightly by the back, which had the double advantage of keeping me in, and of preventing his tumbling out. We had two capital horses, and were driven for eight miles by the side of a mountain torrent called by the unromantic name of the Peabody River. The woods through which we passed were extremely pretty, and the torrent was our companion throughout the drive. The road was of the roughest possible description, over large boulders and up and down hills. The only wonder was, that we were not tossed out of our carriage and into the torrent. The leaves were beginning to turn, and some of the foliage was extremely beautiful, particularly that of the moosewood, the large leaf of which turns to a rich mulberry colour. We picked several of them to dry.
On reaching the Glen House, we found ourselves in front of a very large hotel, standing in an amphi[Pg 87]theatre of mountains. These are called by the names of the presidents, Washington, Monroe, Adams, Jefferson, and Madison. Washington is 6500 feet high, and seven others, which form a continuous line of peaks, are higher than Ben Nevis. Although snow has fallen this year, they seem free from snow just now, but they all have a white appearance from the greyish stone of which they are formed, and hence the name of the White Mountains. We went a short way up the ascent to Mount Washington, and judging from this beginning, the road up the mountain must be very beautiful. For two-thirds of the height they are covered with splendid forest trees. When, at this season, the leaves are changing in places to a deep crimson, the effect is very fine. The upper part of these mountains seems to consist of barren rocks. We returned and dined at the Alpine House. Both papa and I were seriously frightened in our walks, especially at the Glen House, by encountering three savage-looking bears. Luckily before we had shouted for help, we discovered they were chained, but the first being exactly in a path we were trying to walk along, really alarmed us.
We left Gorham for Portland at about four o'clock. The road the greater part of the way is perfectly[Pg 88] beautiful. It continued along the course of the Androscoggan, with the White Mountains on one side, and with a range, which to our eyes appeared quite as high, on the other. When we left the river, the road was diversified by passing several large lakes, one of which, called Bryant's Pond, resembled Island Pond in beauty.
October 1st.—We got up betimes yesterday to see Portland, which it was too late to do to any purpose on the evening of our arrival. Papa delivered his letter to Mr. Miller, the agent here of the Grand Trunk Railway, and he accompanied us on the heights, from which we were able to look down upon the town and its noble harbour—the finest in the United States. As it is here that the Leviathan is destined to come if she ever does cross the Atlantic, they have, at a great expense, made a wharf to receive her. The harbour is entirely land-locked and studded with islands. The day was very fine, but not so clear as the day before, or we should have seen the White Mountains, which are clearly visible from this, although sixty miles distant in a right line. The city is very beautiful, and, like all the New England towns, most clean and well conditioned. Each street is embellished by avenues of elm trees[Pg 89] of a larger size than we have yet seen in America, with the exception of those in the park of Boston.
We had here an opportunity of witnessing a very pretty sight, which was the exercising of the Fire Companies, of which there are nine in this town. Each Company had an engine as clean and bright as if it had just come out of the maker's hands, and the firemen attached to them were dressed in uniforms, each of a different colour. Long ropes were fastened to these engines, by which the men drew them along. To each engine there was also attached a brigade of men, wearing helmets, and fire-proof dresses. They seemed altogether a fine body of men. We did not wait to see the result of the trial, as to which engine could pump furthest, which, with a reward of $100 to be given to the successful engine, was the object of their practising. These Fire Companies seem to be a great "Institution" everywhere in the United States, the troop at New York having figured greatly in the Cable rejoicings. The companies of different towns are in the habit of paying visits to each other, when great fêtes take place, and much good-fellowship is shown. Fires are very frequent in the great towns, but the means of extinguishing them must be great in proportion, judging from what we have seen here. These companies[Pg 90] are said to be very well organised, and as they act as a police also, very little pilfering takes place. Mr. Miller afterwards took us to a part of the suburbs to show us some very pretty villas, with gardens more cared for than any we have yet seen.
We left Portland in the afternoon. There are two railways from Portland to Boston, and we selected the lower or sea-coast road. The country was not very pretty, the shore being flat, but as we approached the seaports of Portsmouth, Newburyport, and Salem, the views improved, especially in the neighbourhood of Portsmouth, which stands on a neck of land jutting far into the sea. There was a great deal of hay standing on meadows which were flooded by the sea water; to protect the stacks, they were built upon platforms supported by stone pillars, which had a curious effect. The crops seemed very abundant, for the stacks were large and close together and spread over a wide area. The quality of this salted hay is said to be good, and the animals like it very much.
We got to Boston late last night, and to-day papa paid a long visit to Judge Curtis, and we went afterwards on a railway, drawn by horses, to see the famous Harvard University, in the town of Cambridge, which lies about four miles to the west of Boston.[Pg 91] When Mr. Jared Sparkes, the late president, was in England, papa, at Mr. Morgan's request, gave him letters to Cambridge, and upon the strength of this we called on him and were most graciously received by Mrs. Sparkes, who entertained us till Mr. Sparkes returned from Boston. He is a very pleasing and intelligent man; before parting they gave us letters to Professor Silliman, of the sister University of Yale, at New Haven. We met here too Mr. and Mrs. Stevens, who accompanied us back to Boston, and loaded us with introductions to the same place.
The town of Cambridge occupies a good deal of ground, for the so-called streets are avenues of beautiful trees, with villas interspersed between them. In an open space in the centre of the town, there is a most magnificent tree, called the Washington Elm, noted, not only for its size, but for its being historically connected with Washington. There is a large library belonging to the college; and the college is in every way very flourishing; but as we mean to return here again, we did not think it worth while now to see it in detail.[5]
October 2nd.—Papa went last night to a meeting, which is held every night for prayer, at the Young[Pg 92] Men's Christian Association, and was extremely pleased with what he saw and heard. He was there for half an hour before the prayers began. These lasted from nine till ten. Papa was placed in the seat of honour, in a chair beside the President, and was asked by him to address the meeting; but he got out of it by saying that he came to listen and not to speak, and added only a few words on the great interest with which these revivals in America were looked upon in England. He was very much interested with the whole of the proceedings, which were conducted with extreme moderation and right feeling.
To-day we made an early start, and at first went over the ground which we travelled when we left Boston for Niagara; but instead of leaving the Connecticut river at Springfield, as we did on that occasion, we followed its course to Hartford, and finally came on to New Haven, from which place I am now writing.
We arrived at two o'clock, and, after getting some food, called on Professor Silliman, who took us over the University, and showed us the museum, where there are some wonderful foot-prints on slabs of rock, which have been found in this country. There is also here one of the largest meteoric stones that is known. In the library there are many books which[Pg 93] were given to it by Bishop Berkeley, whose memory seems as much respected here as it is at Newport.
October 3rd.—Professor Silliman called on us this morning at ten o'clock, and brought with him Mr. Sheffield, an influential person in this neighbourhood, and a great patron of the University. As Mr. Sheffield was an Episcopalian, he took us to his church, where we heard a most striking sermon, and afterwards received the Communion. The number of communicants was very large. We are very much struck at seeing how well Sunday is observed in America. There are about thirty churches in New Haven, and they are all, we are told, well filled. These churches are of various denominations; but there seems a total want of anything like a parochial system.
Papa went afterwards to the College chapel, or rather church, where the young men attached to the University were assembled in the body of the building. Papa was in the gallery, which is appropriated to the Professors and their families. There are no less than forty-one Professors at Yale, including those of theology, law, and medicine, which are all studied here.
The sciences take greatly the lead over the classics. When we remarked to Professor Silliman[Pg 94] how great the proportion of scientific Professors seemed to be, he said the practical education which was given in this country, rendered this more necessary than in England, where men have more time and leisure for literary pursuits. This is no doubt the case, and in this country the devotion of every one's time and talents to money-making is much to be regretted, for it is the non-existence of a highly educated class that tends to keep down the general tone of society here, by not affording any standard to look up to. It is curious what a depressing effect is caused in our minds by the equality we see every where around us; it is very similar to what we lately felt when on the shores of their vast lakes,—tideless, and therefore lifeless, when compared to the sea with its ever-varying heights. If I may carry this idea further, I might say there is another point of resemblance between the physical and moral features of the country, inasmuch as when the waters of these lakes of theirs are stirred up and agitated by storms, they are both more noisy and more dangerous than those of the real ocean.
New Haven is considered to be the most beautiful town in America, and it is marvellously beautiful. The elm is a very fine tree on this continent. It is of a peculiar kind, rising to a great height[Pg 95] before any branches shoot out, thus producing large overhanging branches like a candelabrum. It is common in all American towns, but this is called by pre-eminence the City of Elms. There are broad avenues in every direction, the branches of the trees meeting across and forming shady walks on the hottest day.
The shops, relatively to the size of the town, are as good as any we have seen in the larger cities. Next to the booksellers' shops, or book stores as they call them, the most striking, if they are not the most striking of all, are the chemists' shops, which abound here as elsewhere. They are of enormous size, and are kept in perfect order, though the marvel is lessened when the variety of their contents is considered, this being of a very miscellaneous description, chiefly perfumery, at all events not restricted to drugs. Hat stores and boot stores are very numerous, and labels of "Misses' Hats" and "Gents' Pants fixed to patterns," are put up in the windows.
In the afternoon Professor Silliman took papa a long walk in the country, and geologised him among basaltic rocks of great beauty; and in passing through the woods, they made a grand collection of red leaves. I had, during this walk, been deposited with Mrs. Silliman, and we remained and[Pg 96] drank tea with them. The professor's father, also Professor Silliman, a most energetic gentleman, upwards of eighty years old, came to meet us, as did Professor Dana and one or two others, including the gentleman who preached to the boys. I cannot get papa to tell me how he preached, and must draw my own conclusion from his silence. He will only admit that the pew was very comfortable and the cushion soft, and as he was kept awake all last night by mosquitoes, the inference to be drawn is not difficult. I have since been employed in arranging my leaves in a blotting-book, which I got at Boston for that purpose, and as it is late must close this for to-night.
New York, October 4th.—We left New Haven this morning and arrived here this afternoon. The intermediate country along the northern shore of Long Island Sound is very interesting. We crossed a great many rivers which in England would be deemed large ones, at the mouths of which were pretty villages, but we passed so rapidly that we had scarcely time to do more than catch a glimpse of them. As the mail leaves to-morrow, I must conclude this.
[4] Our driver, some years ago, at Pau.
[5] We, unfortunately, never had an opportunity of returning to Cambridge.
DESTRUCTION OF THE CRYSTAL PALACE.— PHILADELPHIA.— CEMETERY.— GIRARD COLLEGE.— BALTIMORE.— AMERICAN LITURGY.— RETURN TO PHILADELPHIA.— PENITENTIARY.— RETURN TO NEW YORK.
New York, 12th Oct. 1858.
We have seen comparatively so little since I last wrote to you, that I have hesitated about sending by this mail any account of our travels; but I believe, upon the whole, it may be as well to give you an account of our movements up to this time.
My last letter would tell you of our arrival at this place. The evening was so fine, that papa and I were induced to go to the Crystal Palace. Although very inferior to ours at Sydenham, it was interesting as being filled with an immense variety of farming implements, which had been brought together for the great annual agricultural show. There were also large collections of sewing machines, hydraulic presses, and steam engines, besides collections of[Pg 98] smaller articles, watches, jewellery, &c.; and a great many statues, including the original models of Thorwaldsen's colossal group of our Saviour and the Apostles. The place was brilliantly lighted up, and the effect was very striking.
Next day papa was returning home and saw a dense cloud of smoke hanging over the town; and on approaching the spot, found the poor palace and all its contents a thing of the past; one minaret only being left of the building. The whole had been consumed by fire in ten minutes; so rapid was the progress of the flames from the time of their first bursting out, that in that short space of time the dome had fallen in; and wonderful to say, though there were more than 2000 people, chiefly women and children, in the building when the alarm was given, the whole of them escaped uninjured.
We waited on in New York till Friday the 8th, vainly hoping to hear tidings of William; although by a letter received from him a day or two before, he said he should probably be at Baltimore on Saturday. With this uncertainty hanging over his plans, we determined on going there; and on Friday night got as far as Philadelphia by the Camden and Amboy Railway, through a country far from pretty, compared with what we have been accustomed to.[Pg 99]
Philadelphia is situated between the Delaware and the Schuylkill, at about six miles above the junction of the two rivers. In order to reach the town we had to cross the Delaware, which we did in a steamer of huge proportions. It was getting dark when we landed at Philadelphia; and we were much struck with the large and broad streets and well-lighted shops. It is said of New York, that the winding lanes and streets in the old part of the town, originated in the projectors of the city having decided to build their first houses along paths which had been established by the cattle when turned into the woods. The projectors of Philadelphia have certainly avoided this error, if error it was; for there the streets throughout the city are as regular as the squares of a chess board, which a map of the city much resembles. The streets extend from one river to the other.
We got up next morning betimes; and as it is our intention to see the town more thoroughly hereafter, we took advantage of a lovely day (but what day is not here beautiful) to see a cemetery situated upon a bend of the Schuylkill. It is very extensive; for they have so much elbow room in this country that they can afford to have things on a large scale; and everything here partook of this feature. The[Pg 100] plots of ground allotted to each family were capacious squares, ornamented with flowers, surrounded by white marble balustrades, and large enough to contain separate tombstones, often inside walks, and sometimes even iron arm-chairs and sofas. The monuments were all of white marble, of which material there seems here to be a great abundance, and none of them were offensive in their style, but on the contrary were in general in that good taste, which the Americans in some way or other, how we cannot make out, contrive to possess.
We went afterwards to see the famous Girard College, for the education of orphan boys. Mr. Girard bequeathed two millions of dollars to found it, and his executors have built a massive marble palace, quite unsuited, it struck us, to the purpose for which it was intended; and the education we are told, is unsuited likewise to the station in life of the boys who are brought up in it. As in most public institutions for the purposes of education in this country, no direct religious instruction is given. This does not seem in general to proceed from any want of appreciation of its importance, but is owing to the difficulty, where there is no predominant creed, of giving instruction in any: but in the case of the Girard institution, even this excuse for the[Pg 101] omission cannot be made, for a stipulation was imposed by Mr. Girard in his will, that no minister of any denomination should ever enter its walls, even as a visitor, though this, we understand is not carried out. For the first time in America we met here with a most taciturn official, and could learn much less than we wished of the manner in which the institution is managed.
On Saturday the 9th, being the same afternoon, we went on to Baltimore, and were perplexed at not finding letters from William; but to our great relief he made his appearance in the evening, much pleased with his travels.
The country from Philadelphia to Baltimore, like that which we passed through on the preceding day, is much less interesting than the country to the north of New York; but a grand feature of the road we travelled was the Susquehanna River, which is here very broad, and which we crossed in a large steamer, leaving the train we were in, and joining another which was in readiness on the other side. The point at which we crossed the river, was at the spot where it falls into the Chesapeake. The shores of this beautiful bay are profusely indented with arms or estuaries, the heads of which, as well as the mouths of several tributary rivers, we re[Pg 102]peatedly crossed on long bridges: this afforded a great variety in the scenery, and much enlivened the last part of our journey.
Next day being Sunday, we heard an admirable sermon from Dr. Cox. The church in which he preached was a large and handsome one, and the service was well performed. In describing the service at West Point, I mentioned that it differed in some respects from our own. We have now had frequent opportunities of becoming acquainted with the American liturgy; and, as it will interest some of you at home, I may as well tell you a little in what those differences consist, with which we were most forcibly struck.
Some alterations were of course rendered necessary by the establishment of a republic, but these seem to have been confined as far as possible to what the occasion called for. I think, however, in spite of their republicanism, they might have retained the Scriptural expression, "King of Kings, and Lord of Lords," instead of changing it to the inflated, "High and Mighty Ruler of the Universe." This reminded us of the doubt raised by some, when Queen Victoria came to the throne, if the words ought not then to have been changed to "King of Queens." It is pleasing, however, to observe[Pg 103] how small the variations in general are, if indeed there be any, which are at variance with either the doctrine or the discipline of the Church of England.
We are so much accustomed to the opening sentences of our own Liturgy, "When the wicked man turneth away from the wickedness that he hath committed," &c., that their opening words startled us at first; but their two or three initiatory sentences are well selected to begin the service; the first being, "The Lord is in his holy temple: let all the earth keep silence before him."
Some of the alterations are improvements rather than blemishes, for the constant repetitions in our service are avoided. The Lord's prayer is less frequently repeated, and the collect for the day, when it has to be read in the Communion Service, is omitted where it first occurs with us. A little more freedom of choice, too, is allowed to the minister in several parts of the service. For example: the Apostle's Creed or the Nicene Creed may be substituted for each other, as the latter is not used in the office for the Communion; and instead of reading the Psalter as divided into days in the daily service, some very good selections from the Psalms are made, which may be substituted either on the week days, or[Pg 104] on Sundays. The daily Lessons are shortened, and yet all the portions read by us, out of the Canonical Scriptures, are retained, which is managed by omitting all the Lessons taken from the Apocrypha.
The second lessons on Sundays are specially appointed as well as the first, and not made to depend, as with us, on the day of the month.
The Commination Service for Ash Wednesday is omitted, only the two prayers at the end being retained; these are read after the Litany. The Athanasian Creed is never used.
Some of the verbal alterations, however, grated harshly on our ears. They are of course obliged to pray for the President, but instead of the petition to "grant him in health and wealth long to live," they have substituted the word "prosperity" for the good old Saxon "wealth," for fear, apparently, of being misunderstood by it to mean dollars. They seem too, to have a remarkable aversion to all them thats, always substituting the words those who. But the peculiarity which pleased us most in the American service, was that, instead of the few words of intercession introduced into our Litany, "especially those for whom our prayers are desired," there are distinct and very beautiful prayers for the different circumstances under which the prayers of the congre[Pg 105]gation may be asked; as for example in sickness, or affliction, or going to sea, &c. There is, also, a special form of prayer for the visitation of prisoners, and one of thanksgiving after the harvest, also offices for the consecration of churches, and for the institution of ministers to churches; and some excellent forms of prayers authorised by the church to be used in families. These seem the chief alterations, excepting that the Communion Service differs very much from ours; the oblation and invocation, which I believe are used in the Scotch service, being introduced into theirs. To the whole is added, in their prayer books, a most excellent selection of psalms and hymns, in which one is glad to recognise almost all those which we admire most in our own hymn books.
But, after this long digression, to return to my journal. After the service, Mr. Morgan, who had accompanied us to Baltimore with his daughter, introduced us to Dr. Cox, and we were invited by him to return on Thursday to a great missionary meeting, which is to be held in Baltimore; but this, I am afraid, we shall hardly accomplish. In going and returning from church, we saw a good deal of the city. It is built upon slopes and terraces, which gives it a most picturesque appearance. It is in[Pg 106]deed generally reputed to be the most beautiful city in the United States, and from the number of monuments it contains, it has been called the "Monumental City." The principal structure of this kind is the Washington monument, situated on a large open area, and upwards of two hundred feet high. It is entirely constructed of white marble, and has a colossal statue of Washington on the top. The town is built on the banks of the Patapsco, about fourteen miles from where its flows into the Chesapeake. It is navigable here for large ships, and presents one of those enormous expanses of water, which form a constant subject of dispute between papa and William, as to whether they are rivers, lakes, or estuaries. Large as the expanse of water is, the distance from the sea is at least 200 miles, and the water is quite fresh.
We returned yesterday with William to Philadelphia, and went to see the famous water-works, which supply the town with water from the Schuylkill. The water is thrown up by forcing-pumps to large reservoirs above; the surrounding grounds are very pretty, and the whole is made into a fashionable promenade, which commands a fine view of the city. We afterwards went to the penitentiary, which has a world-wide renown from its being the model of[Pg 107] many which have been built in England and elsewhere. The solitary system is maintained, the prisoners never being allowed to see each other, nor could we see them. One poor man had been in confinement sixteen years out of twenty, to which he had been condemned. Any one remembering Dickens's account of this prison, must shudder at the recollection of it, and it was sad to feel oneself in the midst of a place of such sorrow. When here a few days ago, we had left our letters of introduction for Mr. Starr. He called to-day, and gave Papa some interesting information about the revivals. He takes great interest in the young gamins, whom I have described as "pedlering" in the railway cars, selling newspapers and cheap periodicals; they are a numerous class, and often sharp little fellows. Mr. Starr takes much pains in trying to improve their moral and religious characters. But I have no time at present for more. We returned to New York to-day, and are passing our last evening with William, who is to sail early to-morrow, and will be the bearer of this letter.
WILLIAM'S DEPARTURE.— GREENWOOD CEMETERY.— JOURNEY TO WASHINGTON.— ARRANGEMENTS FOR OUR JOURNEY TO THE FAR WEST.— TOPSY.
Washington, 16th Oct. 1858.
I closed my last letter to you on the 12th, and gave it to William to take to you. On the following day we bade him a sorrowful farewell, made all the more melancholy by the day being very rainy, which prevented our seeing him on board. We so very rarely see rain, that when it comes it is most depressing to our spirits, without any additional cause for lamentation; but it never lasts beyond a day, and is always succeeded by a renewal of most brilliant weather.
To console ourselves next day, although papa said it was an odd source of consolation, we went to see the Greenwood Cemetery, which is one of the four remaining sights of New York, the fifth, the Crystal Palace, being, as I wrote to you, burnt down. The[Pg 109] cemetery, however, proved a great "sell," as William would have called it; for it is not to be compared to the one at Philadelphia; and instead of the beautiful white marble, surrounding each family plot, we found grey stone, or, still more commonly, a cast iron rail. Moreover, it had to be reached by an endless series of steamer-ferries and tramways, which, though they did not consume much money (under 1s. a head), occupied a great deal more time than the thing was worth. The excursion, however, gave us an opportunity of seeing the town of Brooklyn, which, though insignificant, in point of size, as compared with New York, has nearly as many inhabitants as either Boston or Baltimore, and numbers more than twice those in the town from which I now write.
We left New York yesterday, end slept at Philadelphia. When we went there last week, the first thirty miles of our route was across the Bay of New York, in a steamer, and, on our return, we came the whole way by rail; but there is a third line, which we took on this occasion, called the New Jersey Line, by which we went as far as Burlington by rail, and thence a distance of nineteen miles in a steamboat down the Delaware. It was splendid moonlight, and the town of Philadelphia, which stretches along the[Pg 110] banks of the river for nearly five miles, was well lighted, and the river being crowded with ships, the whole effect was very pretty.
It is marvellous how well they manage these huge steam-boats. They come noiselessly up to the pier without the least shock in touching it, and it is almost impossible to know when one has left the boat and reached terra firma, so close do they bring the vessel up to the wharf. The whole process is directed by a man at the wheel, and regulated by sound of bell. There is a perfect absence of all yells, and cries, and strong expressions, so common in a French steamer, and not unfrequent in an English one.
We arrived too late at Philadelphia to be able to do much that evening, and this morning, we started early for Baltimore, en route for this place. We had two very pleasant and communicative fellow-travellers, one a coal merchant, who resides at Wilmington, the capital of Delaware, the other a Quaker, a retired merchant from Philadelphia, who gave us a good deal of information about some of the institutions and charities of that place. He stood up much for the Girard College, and justified the enormous cost of the building, by saying it was meant as a monument to the founder. He made a very good defence of the solitary system, which I mentioned in[Pg 111] my last as existing in the penitentiary, and we were beginning to think him a very wise "Friend," when he broke out on the merits of Phonography, which, by his account, seems to have made much progress in America, and he has asked us to call on Mr. Pitman, their great authority on that subject, at Cincinnati. The old gentleman's name was Sharpless, and it deserves to be recorded in this journal, he being the only American we have heard take anything like a high tone upon the subject of slavery. He gave us the names of some books upon the subject, which we, in the innocence of our hearts, have been asking for in Baltimore and here, forgetting that we are now in those states where it forms a happy (?) feature in their domestic institutions.
As we were about to part, the old gentleman addressed us both, and turning to me, said, "I must tell thee how well it was in thee to come out to this country with thy husband, and not to let him come alone. A man should never allow himself to be separated from a good wife, and thou doest well, both of thee, to keep together." To which complimentary speech I replied, that I had made it the one stipulation in giving my consent to papa's crossing the ocean that I should accompany him; and I confessed that I little thought at the time that I should[Pg 112] be taken at my word, or that our berths would be engaged the following day; but hoped rather, by such stipulation, to prevent his going altogether. I added that if all went well with our family at home, as I trusted it would, I had no reason to do otherwise than be very glad I had come. We arrived here at last. The Americans are very proud of their country. But, oh! it would do them all good to see this blessed Washington, which few of them do, except their Senators and Members of Congress, and others connected with government. Well may Dickens term it "the city of magnificent intentions." Such ambitious aspirings to make a great city! Such streets marked out; twice or three times the width of Portland Place! and scarcely anything completed, with the exception of some public buildings, which, to do them justice, are not only on a magnificent scale, but very beautiful. I shall, however, delay my account of Washington till we have seen more of it, as we stay here till Monday afternoon, when we return to Baltimore so as to allow us to make a start for the West on Tuesday.
We are to travel quite en prince, over the Ohio and Baltimore railroad, one of the most wonderful of all American railways. At New York we had introductions given us to request the officials[Pg 113] of this line to allow us to travel on the engine, or on the cowcatcher if we preferred it! either of which would undoubtedly have given us a fair opportunity of viewing the scenery; but papa saw to-day, at Baltimore, the managing director, who has arranged for the principal engineer to go with us, and he is to take us in the director's car, which we are to have to ourselves, and this gentleman, Mr. Tyson, is to let us stop whenever we have a fancy to do so. We are to go fast or slow as we may prefer. We are to start on Tuesday morning, at the tail of the express train, and we have only to give the signal when our car will be detached. There are only two or three trains daily for passengers; but there are goods' and extra trains for various purposes, which are constantly running at different speeds on the road. It is by reattaching ourselves to any of these, that we can, when we like, effect all this, and have an opportunity of seeing, in the most leisurely manner, and without any detriment to the other passengers, the various parts of the road that may be worth exploring. The line is very beautiful, and I hope Mr. Tyson will be prepared for my frequently stopping him when I see trees, with their splendid red leaves that I may wish particularly to gather. We are to take[Pg 114] our food in this carriage, if necessary, and have beds made up in it, so as to make us quite independent of inns, and we may pass as many days as we like upon the road. We are to do this because, though some of the hotels are good, we may not find them at the exact places where we wish to stop. Papa has no connection with this road, and it must be American appreciation of his virtues which has led the officials to deal with us in this luxurious way.
On Tuesday the 19th inst., therefore, we make our real start for the West, and shall probably the first night reach Harper's Ferry, a place which President Jefferson, in his "Notes on Virginia," which you will find in papa's library, said, was "one of the most stupendous scenes in nature, and well worth a voyage across the Atlantic to witness;" and this was written when these voyages were not so easily accomplished as they are now. But this railway has opened up scenery which was not known to Jefferson, and is said far to surpass, in beauty, even this celebrated Harper's Ferry; but of this we shall soon be able to judge for ourselves.
October 18th.—This must be posted to-day before we lionise this place, so I shall reserve all I have to say about Washington till my next, and shall fill up this page with a description of a real live "Topsy"[Pg 115] slave, with whom we have made acquaintance here. She is fourteen, the property of an old Miss D. We noticed her yesterday standing about in the passage, and asked her if she belonged to the hotel, and she said no, that she belonged to Miss D. We said, quite seriously, as we now always do to blacks and whites of the lower orders, "Where were you raised?" The creature answered us quietly, "In Virginny." She is a full, well grown girl, with a large bushy crop of wool on her head; a pleasant, large, round intelligent face, that is almost pretty. The young niggers have very little of the real negro cast of countenance, and the little boys and girls about the streets are really pretty, and almost loveable looking; while the elders, especially the females, are hideous to behold, and are only to be tolerated, in point of looks, when they wear coloured turbans. When I see one adorned in a bonnet at the back of her head, with a profusion, inside, of the brightest artificial flowers, a bright vulgar shawl and dress, and an enormous hoop, with very narrow petticoats, I always wish to rush home, light a large bonfire, and throw into the flames every article of ornamental dress that I possess.
But to return to dear Topsy. We asked her if she were a slave, feeling very backward to put so[Pg 116] trying a question to her; but she answered with the utmost simplicity, that she was, just as if we had asked her if she were from France or Germany. In reply to our questions, she said that her father and mother were slaves; that she has several younger brothers and sisters; that Miss D. is very rich. "'Spect she has above a hundred slaves;" and that she is very kind to them all. "Can you read?" "No; Miss D. has often tried to teach me, but I never could learn. 'Spect I am too large to learn now." We lectured her about this, and gave her Sir Edward Parry's favourite advice, to "try again." I then asked her if she went to church. "No, never." "Does Miss D.?" "Mighty seldom." "Do you know who made you?" "Yes, God." "Do you ever pray?" "No, never; used to, long ago; but," with a most sanctimonious drawl, "feel such a burden like, when I try to kneel down, that I can't." This was such a gratuitous imitation of what she must have heard the goody[6] niggers say, that I felt sorely disposed to give her[Pg 117] young black ears a sound boxing, for supposing such a piece of acting could impose upon us. However, leaving the dark ears alone, I urged the duty of prayer upon her, as strongly and simply as I could, and made her promise to kneel down every night and morning and pray. She had heard of Christ, and repeated some text (again a quotation, no doubt, from the goody niggers) about his death; but she did not know, on further examination, who He is, nor what death He died. She said Miss D. read to them all, every Sunday; but probably not in a very instructive manner. She said her name was Almira. I gave her Miss Marsh's "Light for the Line," which happened to be the only book I had by me which was at all suitable, and told her to get it read to her, and that I was sorry I had nothing else to give her; but I shall try this morning to get her an alphabet, in order to encourage her to make another attempt to learn to read. At parting last night, I spoke as solemnly as I could to her, and told her we should probably never meet again in this world, but that we should be sure to meet hereafter, at the judgment seat of God, and I entreated her to remember the advice I had given her.
As we do not know Miss D., who is a very deaf old lady, staying here, like ourselves, for a day or two,[Pg 118] our conferences with young Topsy have been necessarily very short, and constantly interrupted by Miss D.'s coming past us, and wanting her; but we should like very much to buy Almira, and bring her home to make a nursery maid of her, and teach her all she ought to know, and "'spect" after all she is not "too large" to learn, poor young slave! It was pleasant, in our first colloquy of the kind, to talk to such an innocent specimen of a slave. I mean innocent, as respects her ignorance of the horrors of slavery, of which she evidently had not even the faintest idea. I asked her what she did for Miss D.? "Dresses her, does her room, and fixes her up altogether." The real, original Topsy is no doubt a most correctly drawn character, judging by this specimen. And now adieu; you shall have a further chapter on Washington next time.
[6] I have tried, in vain, to alter this word, which is one coined at home, and used by the family, but cannot find a substitute for it. Lest, however, it be misunderstood, I must explain that it is applied in reference to the truly good and pious among our friends; as the word "saints," ought to be, had not that term been unhappily associated with the ridiculous, and a false pretension to religion.
WASHINGTON.— BAPTIST CLASS-MEETING.— PUBLIC BUILDINGS.— VENUS BY DAYLIGHT.— BALTIMORE AND OHIO RAILWAY.— WHEELING.— ARRIVAL AT COLUMBUS.
Washington, 18th Oct. 1808.
I despatched my last to you the day before yesterday, and now must give you an account of our employments yesterday (Sunday, 17th instant). The morning was very hot, and very lovely, with a clear blue sky, and I wished that impertinent young lady, Emily, could see what sort of weather we have here, and how her good wishes for us are accomplished, beyond anything she can suppose; for we can barely support the heat in the middle of the day.
The weather being so lovely, we set off to a church in Georgetown, a suburb of Washington, where many of the foreign ministers live, and a very pretty suburb it is; but when we got there, papa's head began to ache so much, that we thought it best to return to a church nearer the hotel, so that if he[Pg 120] became worse, he might leave the church, and walk home. We were able, however, to sit out the service, and heard a very dull sermon from a young missionary, who was to sail, two days afterwards, with his wife, from Baltimore, for Africa; his sermon was greatly taken from Livingstone's book, and he spoke more strongly against slavery than we should have looked for in a slave state. After the sermon, papa and I went to him, and we asked him a little about where he was going, &c. &c. He scarcely seemed to know, acknowledged he was but little acquainted with the work he had before him, and, finally, when papa put a piece of gold into his hand, he looked at it, and asked whether it was for himself or the Mission. We answered with some degree of inward surprise, that it was for any useful object connected with it, and we took leave of him, wishing him God-speed, but lamenting that a more efficient man was not going out.
Papa became much more head-achy during the day. Mr. Erskine called to see if we wanted anything, and strongly advised my going to a negro chapel in the evening, and hearing one of the blacks preach. They are mostly Methodists, that is Wesleyans, or Baptists. He said I should hear them singing as I passed the doors, and could go in.[Pg 121] Poor papa, by this time, was fit for nothing except to remain quiet, so Thrower and I set out in the evening, and found, not without some difficulty, an upper room, brilliantly lighted, over a grocer's warehouse. We went up two pairs of stairs, and I did so in fear and trembling, remembering what the odour is when a large dining-room is filled with black waiters: a sort of sickly, sour smell pervades the room, that makes one hate the thought, either of dinner, or of the poor niggers themselves. It seems it is inherent in their skin; to my surprise and satisfaction, however, we found nothing of the kind in this room, the windows of which had been well opened beforehand. It was a large, whitewashed apartment, half filled with blacks.
We were the only whites present; there were benches across the room, leaving a passage up the middle, the men and women occupying different sides. A pulpit was at the further end of the room, and in front of it stood a black preaching. He was in the middle of his sermon when we came in, so we did not hear the text, and sat down quietly at some distance from him, so as to be able to get out and go home to poor papa whenever we wished; a nigger came forward, and invited us to go further up the room, which we declined. The sermon went on for some[Pg 122] time; it described the happiness felt by God's true children: and how they would cling to each other in persecution. The preacher encouraged them all in the path of holiness, and explained the Gospel means of salvation with great clearness, and really with admirably chosen words; there was a little action but not too much; and there were no vulgarities. The discourse was at least equal to the sermons of many of our dissenting ministers, and appeared to come from the lips of an educated gentleman, although with a black skin. He finished, and an old negro rose, and gave out the text:—"And seeing the multitudes, He went up into a mountain," &c. His voice at first was faint, and I could not hear what were the various jokes he cut which produced loud laughter, so we advanced a little. He afterwards became more serious. His address was quite distinct from his text, being an earnest and very well delivered exhortation to the converted to grow in grace; at the end of every period he repeated his text as a refrain.
At first, I observed among the dark ladies a few suppressed murmurs of approbation, but as his discourse proceeded, these were turned into groans; and when he quoted a text, or said anything more than usually impressive, there was a regular rocking[Pg 123] and swaying of the figure among them, while one or two repeated aloud the last words of his text. While he was preaching, a tall thin young woman, in deep mourning, came in, and room was made for her to sit down next to a very fat negress, whom I had observed at our own church in the morning. The latter passed her arm round the shoulder of this young woman, as they sat together, and I observed that at various solemn passages of the old man's address, they began to rock their bodies, gently at first, but afterwards more and more violently, till at last they got into a way of rocking themselves quite forward off their seat, and then on it again, the fat woman cuddling up the thin one more and more closely to her. There seemed a sort of mesmeric influence between the two, occasioning in both similar twistings and contortions of the body, shakings of the head, lookings upward, lookings downward, and louder words of exclamation and approbation. This was not continuous in its violence, though there was generally some movement between them; but the violence of it came on in fits, and was the effect of the old man's words. It was very curious that whenever he repeated the text (a far from exciting one, I thought), the agitation became most violent. The other women continued to murmur applause,[Pg 124] and one woman in advance of the others (a very frightful one) looked upwards, and frequently smiled a heavenly (?) smile. I sat rather behind most of them, and on the side where the men were, so that unless when the women turned round, I could scarcely see their faces. After a time the old man commented upon the succeeding verses of the Chapter as far as the words, "Blessed are the poor in spirit," &c., and here he ceased, almost abruptly; a hymn was immediately given out by the first preacher, and was sung most loudly and vigorously by most of the congregation. The men's voices were very loud, but they all sang true, and with great spirit and energy. There were no musical instruments, and they sat while singing. The hymns seemed very stirring, but I am sorry I cannot give you the words of any of them, as there were no books, and they sung at first from memory, though in some of the after hymns the preacher gave them out by two lines at a time.
This being, as I was afterwards told, a Baptist class-meeting, the first man invited any brother or sister to tell the others "how the Lord had dealt with him," or "what He had done for his soul." (I quote his words.) Whereupon a tall well-dressed young negro rose from his seat, and standing up,[Pg 125] told us that he had been a great sinner, and that he had, through many difficulties, learnt to serve God. He spoke of persecutions from within in the struggles of a sinful nature and of great and bitter ones from without. He did not describe what these had been: but told us that the victory had been his. His language, and choice of expressions, were always good, though at times there was a little of the peculiar negro pronunciation. At all descriptions of the contest having been in his favour, the women swayed their bodies; and when he, and others after him, asserted to those around that what he had felt could not have been from Satan, and therefore must have been from God, there was great agitation, especially in my two friends, and grins and murmurs from the others. The men listened quietly, sometimes grinning with delight, and sometimes leaning their heads forward on their hands, as if meditating. A few of the men who sat at the upper end of the room leant their heads against the wall, and might have been asleep.
After this young man's "experience" was ended, came another singing of hymns, and then another invitation for more "experiences;" when a tall, fat, important-looking man rose: his figure reminded one of a fat, burly London butler; and his account[Pg 126] of himself was somewhat extravagant. "Heart was hard as stone; a great sinner; was standing in an orchard; couldn't love God or pray; seemed as if a great light came from the sky; got behind a tree; the light came nearer; seemed as if drawing me," &c. &c.; ending in the happy circumstance of his complete conversion; and he sat down, his discourse producing the same agitating effects, and of an increasing kind on all the women, specially on my fat and thin friends. Then came another hymn, and another invitation; which was followed by the preacher's going up to a young negress and speaking a few words to her in a whisper; whereupon he told us, that a young person, who had been wonderfully "dealt with by the Lord," was about to give an account of herself. The young girl, of about twenty, black, but pleasing-looking, advanced, and standing straight up before the preacher, repeated to him her experience almost as if it were a lesson she had learnt by heart. There was a cadence, or sort of chant, in her delivery; but with the most perfect quietness of manner. She had been, she said, a great sinner; and she then gave an account of herself at much greater length than the others. In speaking of the difficulties that had met her in her spiritual path, there was a very musical and[Pg 127] touching mournfulness in her voice that made her an object of great interest. The men, at least, seemed to think so; for they all became most lively, grinned gloriously, their splendid white teeth contrasting with their dark skins; my two friends became nearly frantic, the one in mourning especially, when shaken by the agitation of her fat friend, writhed her body in all directions. They both began shouting, "Glory! Glory!" with a loud voice; and finally the younger one fell forward on her face, in a sort of trance. After a time she got back upon her seat; but I never witnessed such a state of excitement, except once, years ago, when I saw a young woman in an epileptic fit. All this was evidently in a sort of small camp-meeting style. August is the month for these meetings when out of doors; but this was a minor one. The woman in front grinned, and even laughed outright, having great hollows or dimples in her cheeks. The young girl was really interesting, so perfectly calm and so modest; never looking to the right or left. She said she felt ashamed to appear before them all, but that she should not be ashamed to appear before God: and whenever interrupted, she resumed the thread of her narrative with the utmost composure. She ended after a time, but[Pg 128] remained standing before the preacher, who was seated, and who proceeded to examine her as to whether she thought she was really converted to God. Her answers were faint, as if from fatigue and exhaustion, her narrative having been a very long one; but still there was a quiet, unfaltering decision in her replies, which were given with much humility of manner. I could not help sometimes doubting whether the whole thing was really unprepared and extemporaneous, or whether she might not have learnt her lesson and repeated it by rote, or whether, in short, it might not have been a piece of acting. This impression lasted only for a moment, for there was such an artless and modest manner in the young girl, that I could not fail on the whole to give her the fullest credit for sincerity, and was angry only with her black male friends for requiring from her such a display of herself and her feelings in a public congregation; which made me feel much for the young girl throughout. After various warnings that she would meet with difficulties, that she was joining a "plain set of old Baptist saints," &c., she said she wished and desired to do so. The preacher then asked, almost in the words of the Liturgy, "Wilt thou be baptized?" and she[Pg 129] answered, "I will." Whereupon he asked the congregation to show by their hands if they approved of her being baptized; and there being a sufficient show of hands, she was told she was duly elected as a candidate for baptism; when another hymn being struck up in the same vociferous style as before, we rose and left the assembly, not liking to be longer absent from papa. We came out upon the lovely, calm, moonlight night, so sweet, so exquisitely heavenly; and I felt how differently nature looked without, to those distressing sights of bodily agitation and contortion we had witnessed within. I thought of the poor young negro girl's quiet testimony, and gentle voice and manner, and wondered if she, too, would learn in time to become uproarious, and shout, "Glory! Glory!" The probability is, that she will become like her neighbours; for I can tell you later other stories about the necessity these poor nigger women seem to be under to shout "Glory!" I was glad to have seen this specimen of the camp-meeting style.
Although I have felt it scarcely possible to describe the scene without a certain mixture of the ludicrous, no feeling of irreverence crossed my mind at the time. On the contrary, my sympathies were greatly drawn out towards these our poor[Pg 130] fellow-creatures; and there was something most instructive in the sight of them there assembled to enjoy those highest blessings—blessings of which no man could rob them. Religion seemed to be to them not a mere sentiment or feeling, but a real tangible possession; and one could read, in their appreciation of it, a lesson to one's own heart of its power to lift man above all earthly sorrow, privation, and degradation into an upper world, as it were, even here below, of "joy and peace in believing."
To-day, after posting our letters for England, papa went to General Cass, Secretary of State for the United States, and delivered his letter of introduction from Mr. Dallas, the American Minister in London. He had a long and interesting interview with him.
We went afterwards to the Capitol, and all over it, under the guidance of our coachman, a very intelligent and civil Irishman. We were quite taken by surprise at what we saw; for not only is the building itself, which is of white marble, a very fine one, but the internal fittings, or "fixings," as they perpetually call them here, show a degree of taste for which before leaving England we had not given the Americans credit. Two wings are now being added[Pg 131] to the original building, and are nearly completed; and a new and higher dome than the original one is being built over the centre. The wings are destined to be occupied, one by the Senate, and the other by the House of Representatives: in fact, the House of Representatives already make use of their wing; but the Senate will still hold another session in the old Senate House, as the Senators have not yet quite decided upon their "fixings." The new chamber is, however, sufficiently advanced to enable us to form a judgment of what it will be; and although, perhaps, inferior in beauty to that of the House of Representatives, it is in very good taste: but the room where the Representatives meet is really most beautiful. The seats are ranged in semi-circles, with desks before each, in much the same manner as in Paris; which gives a more dignified appearance than the arrangement of the seats in our House of Commons. The floors throughout a great part of the building are in very good tesselated work, made by Minton, in England; as the tiles made in this country do not preserve their colour like the English ones. The ceilings of some of the passages are beautifully decorated; and one of the committee rooms, appropriated to agricultural matters, is remarkably well painted in fresco; all the subjects[Pg 132] have allusion to agricultural pursuits. In the centre of the building, round the circular part, under the dome, are some very indifferent pictures, representing subjects connected with the history of America, beginning with the landing of Columbus. Two out of the eight represented incidents in the war of independence; one being the surrender of Lord Cornwallis, who seemed very sorry for himself. The view from the Capitol is fine; the gardens round it are kept in good order, and there being a great deal of maple in the woods, the redness of the leaf gave a brilliant effect to the scene.
From the Capitol we went to the Patent Office, in which are contained an endless variety of models. It is immediately opposite the Post Office, and both are splendid buildings of white marble. The Post Office is still unfinished, but it will be of great size. The Patent-Office is an enormous square building. The four sides, which are uniform, have large flights of stairs on the outside, leading to porticos of Corinthian pillars. We entered the building, and went into a large apartment, where we were lost in contemplation of the numerous models, which we admired exceedingly, though the shortness of the time we had to devote to them prevented our examining[Pg 133] them as minutely as they seemed to deserve. Papa, indeed, was disposed to be off when we had gone through this room, as we had still much to do, and he professed his belief that we must have seen the whole. I, having my wits more about me, could not conceive how this could well be the case, seeing we had only looked at one out of four sides. There is no one in these places to show them to strangers, so we asked a respectable-looking person if there were any more rooms, when he replied, "Oh, yes! you have only been looking at the rejected models." Whereupon we entered on the second side of the square; but, to confess the truth, the rejected and accepted ones seemed to us much of a piece, and we were not sorry, on arriving at the third side, to find it shut up and apparently empty, so we beat a retreat. We were told at Baltimore that the collection was a very fine one, and doubtless it may be very interesting to a person competent to judge of the details; but the models, besides being shut up in glass-cases, and consequently very inaccessible, were generally on too small a scale to be comprehended by ordinary observers, and in this respect, the collection was of much less interest to us than the exhibition we had lately seen in the unfortunate Crystal Palace at[Pg 134] New York, where the models exhibited were of the full size of the machines meant to be used, and consequently almost intelligible to an unprofessional person. Besides what may be strictly considered models, there were in the rooms some objects more suited to an ordinary museum. Such were various autographs, and many relics of Washington; and a case containing locks of the hair of all the presidents, from the time of Washington downwards.
When mentioning our visit to General Cass, I omitted to state the magnificence of the Treasury, which adjoins his official residence; an enormous structure, also of white marble. We counted thirty pillars in front, of the Ionic order, besides three more recently added on a wing, these three pillars of great height being cut out of single blocks of marble. We passed this building again in going from the Patent-Office to Lord Napier's, where we had an appointment with Mr. Erskine.
The noble mansion of England's representative is a cube of brick-work painted dark-brown, equal in size, and very much resembling in appearance, our own D. P. H.; but standing in a melancholy street, without the appendages of green-house, conservatory, and gate, as in that choice London man[Pg 135]sion. The Honourable Secretary's apartment was downstairs in the area, and the convenience of its proximity to the kitchen, with the thermometer at 85° in the shade, as it was to-day, was doubtless duly appreciated by him, he having just arrived from Turin. We found him waiting for us, and he accompanied us to the President's residence, called the White House. It is a handsome but unpretending building, not like its neighbours, of marble, but painted to look like stone; the public reception-rooms are alone shown, but a good-natured servant let us see the private rooms, and took us out on a sort of terrace behind, where we had a lovely view of the Potomac. The house is situated in a large garden, opposite to which, on the other side of the road, is a handsome, and well-kept square. The house has no pretensions about it, but would be considered a handsome country house in England; and the inside is quite in keeping, and well furnished. The furniture is always renewed when a new President takes possession; and as this is the case every four years, it cannot well become shabby.
In a line directly opposite the back of the house, and closing up the view at the end of the gardens, stands the monument which is being erected to Washington. This, when finished, is to be a cir[Pg 136]cular colonnaded building, 250 feet in diameter, and 100 feet high, from which is to spring an obelisk 70 feet wide at the base, and 500 feet high, so that, when completed, the whole will be as high as if our monument in London were placed on the top of St. Paul's. At present nothing but its ugly shaft is built, which has anything but a picturesque appearance, and it is apparently likely to remain in this condition, as it is not allowed to be touched by any but native republican hands, here a rather scarce commodity. It is being built of white stone, one of the many kinds found in this country. By the by, we omitted to state, in describing the Capitol, that the balustrades of the staircases, and a good deal of ornamental work about the building, are of marble, from a quarry lately discovered in Tennessee, of a beautiful darkish lilac ground, richly grained with a shade of its own colour; it is very valuable, costing seven dollars per cubic foot.
From the President's house we went to the Observatory, which, though unpretending in its external appearance, is said to be the finest in the world next to the one at St. Petersburgh; so at least says the Washington Guide Book, for I like to give our authority for what we ourselves should not have supposed to be the case. Mr. Erskine intro[Pg 137]duced himself, and then us, to Lieutenant Maury, who is at the head of it, and is well known as a writer on meteorological subjects. He is a most agreeable man, and we talked much about the comet, meteoric stones, &c.; we asked him what he thought of Professor Silliman's notion about the comet's tail being an electric phenomenon, but he seemed to think little was known on the subject. He said this comet had never been seen before, and might never return again, as its path seemed parabolic, and not elliptical; but he said that what was peculiarly remarkable about it was the extreme agitation observed in the tail, and even in the nucleus, the motion appearing to be vibratory. With regard to meteoric stones, he said the one we saw at New Haven, though of such a prodigious size, being 200 lbs. heavier than the one in the British Museum, was a fragment only of a larger stone. We asked permission to go to the top of the observatory, and at a hint from papa, I expressed the great desire I had to see Venus by daylight, through the great telescope; whereupon, he sent for Professor B——, and asked him to take us up to the observatory, and to direct the great telescope to Venus. We mounted accordingly, and I was some[Pg 138]what alarmed when the whole room in which we were placed, began to revolve upon its axis.
Setting the telescope takes some minutes, and the Professor ejected us from the room at the top of the building on to a balcony, from which we had a most lovely view of the neighbouring country. By means of a very good small telescope placed on a swivel, we could see most distinctly the Military Retreat (the Chelsea of America), beautifully situated upon a high hill about three miles off. We saw also through this telescope the Smithsonian Institute, which we were glad to be able to study in this way in detail, as we found we should not have time to go to it. It is a very large building of the architecture of the twelfth century, and the only attempt at Mediæval architecture which we have seen in the United States.
The view of the Potomac and of the hill and buildings of George Town was very extensive and remarkable; but before we had feasted our eyes sufficiently on it, we were summoned to see one of the most lovely sights I ever witnessed. Though it was mid-day, and the sun was shining most brilliantly, we saw the exquisitely sharp crescent of Venus in the pale sky, and about half the apparent size of the moon. The object-glass of the instrument was[Pg 139] divided into squares, and she passed rapidly across the field of the telescope, sailing, as it were, in ether; by the slightest motion of a tangent-screw of great length, we were able to bring her back as often as we liked, to the centre of the field. This mechanical process might, however, have been rendered unnecessary, had the machinery attached to the instrument been wound up; for when this is the case, if the telescope is directed to any star or point in the heavens, it continues to point to it for the whole twenty-four hours in succession, the machine revolving round in the plane to which it is set. The instrument is a very powerful one, and, like the smaller one we looked through before, was made by Fraunhofer, a famous optician at Munich. There are some other very wonderful instruments which we had not time to see, as we had to make desperate haste to get some dinner, and be off by the late train to Baltimore. But before I take leave of this subject, I must return for a minute or two to that most perfectly lovely creature Venus. She was a true crescent; we could imagine we saw the jagged edge of the inner side of the crescent, but the transition from the planet to the delicate sky was so gradual, that as far as this inner edge was concerned, this was probably only imagination. Her[Pg 140] colouring on this jagged side was of the most transparent silvery hue. The outer edge was very sharply defined against the sky, and her colour shaded off on this side to a pale golden yellow with a red or pink tint in it; this being the side she was presenting to the sun. No words can express her beauty. She is the planet that I told you lately looked so very large.
On our way to the station, and in our drives about the town, we had an opportunity of seeing the City of Washington. The town was originally laid out by Washington himself, and divided off into streets, or rather wide avenues, which are crossed by other streets of great breadth; but though the streets are named, in many of them no houses are yet built, and those that are have a mean appearance, owing to their being unsuited in height to the great width of the streets, which are in many cases, I should think, three times the width of Portland Place, and long in proportion. Notwithstanding, therefore, the beauty of the public buildings, the town greatly disappointed us.
On our arrival at Baltimore this evening, Mr. Garrett, the principal director of the Baltimore and Ohio Railway, called upon us and brought with him Mr. Henry Tyson, the chief engineer, or as he is[Pg 141] called, the master of machinery of the road, whom he was kind enough to appoint to go with us as far as Wheeling, the western terminus of the line.
This is the most remarkable railway in America for the greatness of the undertaking and the difficulties encountered in passing the Alleghanies, which the projectors of the road could only do by crossing the range at a height of 2700 feet, a project that most people looked upon as visionary. We are to start to-morrow morning at eight o'clock.
Wheeling, Oct. 21st.—We have accomplished the great feat of passing the Alleghanies, and Mr. Tyson has proved a Cicerone of unequalled excellence, from his great attention to us, added to his knowledge of the country, and his talents, which are of no ordinary kind. He is the engineer who has invented, or at least constructed on a new plan, the locomotives which are used upon this road: but besides being a very clever engineer, he is remarkably well read in general literature, and has a wonderful memory for poetry and a great knowledge of botany.
Though Mr. Garrett talked of the directors' car, we presumed it was only a common carriage such as we had been accustomed to, but appropriated to their use; instead of this we found a beautiful car, forty feet long by eight wide, of which the accom[Pg 142]panying diagram shows a plan drawn to scale. Outside: painted maroon, highly varnished with Canada balsam: the panels picked out with dark blue. Inside: painted pure white, also varnished. Ceiling the same, divided into small narrow panels, with excellent ventilators at each end. Round the car there were twenty-two windows, not shown in the plan, and three brilliant lamps in the sitting-room and hall, and one in the bed-room; these were lighted when passing through the tunnels. There were three hooks in the wall serving for hat pegs, and at the same time to support two flags for signals. A large map of the mountain pass from Cumberland to Wheeling hung over the sofa opposite the table. The table was covered with green baize stretched tightly over it. On the table were[Pg 143] placed a large blotting-book, ink, and pens, three or four daily newspapers which were changed each day, the yearly report of the railway, a peculiar time-table book, containing rules for the guidance of the station men, times of freight and passenger trains meeting and passing each other, &c. Papa has these. The sofas are covered with a pretty green Brussels carpet (small pattern) quilted like a mattress with green buttons, chairs covered with corded wollen stuff, not a speck or spot of ink or smut on anything. A neat carpet, not a speck or spot on it, a sheet of tin under and all round the stove. Pantry cupboard containing knives and forks, spoons, and mugs. Bed-room berths much higher and wider than in a ship. Red coloured cotton quilts, with a shawl pattern, two pillows to each bed, pillowcases of brilliant whiteness, sofa bed larger and longer than a German bed. White Venetian blinds occupied the places usually filled by the door panels and window shutters. Green Brussels carpet like the cover of the sofa; three chairs to match. The windows in the sitting-room had grey holland curtains running on wires with very neat little narrow strips of leather, and a black button to fasten them, and a button and well made button-hole below to keep them from blowing about when the window is open. Looking-glass in neat gilt frame, hung over[Pg 144] a semicircular console in the bed-room, another near the washhandstand, where a towel also hangs. Two drawers for clothes, &c. under berths. Table-cloth for meals, light drab varnished cloth, imitating leather, very clean and pretty, china plates, and two metal plates in case of breakages. Luncheon consisted of excellent cold corned beef, tongue, bread and butter, Bass's ale, beer, whiskey, champagne, all Mr. Tyson's. We supplied cold fowls, bread, and claret. The door at the end opens on a sort of platform or balcony, surrounded by a strong high iron railing, with the rails wide enough apart to admit a man to climb up between them into the car, which the workmen always do to speak to Mr. Tyson. Usual step entrance at the other end. The platform can hold three arm chairs easily, and we three sat there yesterday evening, talking and admiring the view. The door was always open and we were in and out constantly. Thrower and Gaspar, a capital German man-servant, sat in the hall. Carpet swept by Gaspar after dinner to remove crumbs. I wear neither bonnet nor shawl, but sit at the table and work, make mems., dry red leaves, and learn their names from Mr. Tyson. Papa is always moving about, and calling me out constantly to admire the view from the balcony. Yesterday on the lower[Pg 145] ground it was much too hot in the middle of the day to be there, and we were glad to be within the car, and to shade the glare of the sun by means of our pretty grey curtains, though it was cooler on the mountain.
But I must begin to describe our road more methodically. As we wished to get over the early part of it as expeditiously as possible, we started by the mail train at 8.30. It will be impossible to describe at length all the pretty places we passed, respecting each of which Mr. Tyson had always something to say. Soon after leaving the Washington junction, we came to a sweet spot called Ellicott's Mills, where he had spent his boyhood, and where every rock was familiar to him. The family of Ellicotts, who had resided there from the settlement of the country, were his mother's relations, and by his father's side he was descended from Lord Brooke, who was likewise one of the original settlers, the Warwick branch of the family having remained in England.
We first came in sight of the Blue Ridge at about forty miles from Baltimore. During the greater part of this distance we had been following up the Patapaco river; but soon after this, at the Point of Rocks, we came upon the Potomac. Here the[Pg 146] Baltimore and Ohio canal, a work of prodigious magnitude, and the railway run side by side between the river and very high cliffs, though the space apparently could afford room only for one of them. We reached Harper's Ferry a little after twelve, and the view is certainly splendid. Mr. Tyson had made arrangements to give the passengers a little extra time for dinner, that he might take us to see the view from the heights above without materially detaining the train; but the sun was so powerful that we were glad to limit our walk in order to see a little in detail the bridge over which we had just passed in the railway cars. It is a very wonderful work, but not so remarkable for its length as for its peculiar structure, the two ends of it being curved in opposite directions, assuming the form of the letter S. It passes not only over the river but over the canal, and before it reaches the western bank of the river it makes a fork, one road going straight on, and the other, which we went upon, forming the second bend of the S.
The curves in the railway are very sharp, and a speed of thirty-five miles an hour is kept up in going round those which have a radius of 600 feet. This, and repeatedly recurring ascents of a very steep grade, require engines which unite great[Pg 147] power with precision in the movements, and these are admirably combined in Mr. Tyson's engines; which, moreover, have the advantage of entirely consuming their own smoke, and we had neither sparks nor cinders to contend with. The common rate of travelling, where the road is level, is forty miles an hour, and at this rate each engine will take eighteen cars with 2600 passengers.
The difficulties they have to contend with on this road are greatly increased by the snow drifts in winter. Mr. Tyson told us that on one occasion the snow had accumulated in one night, by drifts, to fourteen feet in the cuts, and it required ten freight engines of 200-horse power each, or 2000-horse power altogether, to clear it away. Three hundred men were employed, and the wind being bitterly cold, hardly any escaped being frost-bitten. One of the tenders was completely crushed up by the force applied; and in the middle of the night, with the snow still driving, and in a piercing wind, they had to clear away the wreck: nineteen engines, called snow ploughs, are kept solely to clear away the snow.
At five o'clock we reached Cumberland, where we slept. After dinner we walked out in the most[Pg 148] lovely night possible to see the town, and the moon being nearly full, we saw the valley as distinctly almost as by daylight. There is a great gap here in the mountain, which forms a prominent feature in the landscape, and a church on the summit of a high hill rendered the picture almost perfect. We here saw the comet for the last time.
Next morning, the 20th October, we started early, in order to be able to take the mountain pass more leisurely, attached ourselves at 6.15 to the express train, and reached Piedmont at 7.30. During this part of our journey we continued to follow up the Potomac, but here we left it to follow up the Savage river, and for seventeen miles continued to ascend to Altamont, where we attained the summit level of 2700 feet above the sea. We cast ourselves off from the express at Piedmont, and afterwards tacked ourselves on to a train which left Piedmont at eight o'clock, and got to Altamont at 9.45; these seventeen miles occupied an hour and three quarters, the grade for eleven miles out of the seventeen being 116 feet per mile.
It is almost impossible to describe the beauty of the scenery here. The road goes in a zig-zag the whole way. We passed several substantial viaducts across the Savage river, often at a great height[Pg 149] above the valley, and on many occasions, when the road made one of its rapid turns, a vista of many miles up the gorges was obtained.
Of course the greatest skill is required in driving the engine up what is called the "Mountain Division." We mounted on the locomotive, to have a more perfect view of the ascent. This locomotive is very different to an English one, as the place where the driver sits is enclosed on three sides with glass, so as to shelter him and those with him from the weather. Mr. Tyson thought it necessary to drive a small part of the way himself; but after that, he resigned his position, as will be seen by the following certificate, to one equally qualified for an emergency, though hitherto his peculiar talent in that line had not been developed.
"Baltimore and Ohio Railway, Machinery Department.
"Baltimore, Oct. 21st, 1858."This is to certify that Mr. A. T. has occupied the position of 'Locomotive Engineer,' on the Mountain Division (3rd) of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad.
"The term of his occupation has been characterised by a close attention to his duties, and consequent freedom from accidents.
(Signed)
"Henry Tyson,
"Master of Machinery,
"Baltimore and Ohio R. R. Co."
[Pg 150]Papa, in fact, drove the engine a considerable way up the steepest part of the ascent, and as the driver must command an uninterrupted view of the road before him, he had a capital opportunity of seeing the country. Thrower and I sat on a seat behind him; but he alone had the full view, as the chimney of the engine rather obstructed ours in front, though on each side we saw perfectly. The whistle of the engine, when so close to our ears, was splendid, or perhaps you would have said, terrific.
From Altamont to Cranberry Summit, where the descent begins, there is a comparatively level country, called the Glades, which are beautiful natural meadows undulating and well cultivated, with high ranges of mountains, generally at no great distance from the road, but varying a good deal in this respect, so as sometimes to leave a considerable plain between it and the range. From these glades numerous valleys diverge, and, in looking down these, splendid vistas are obtained. The verdure even now is very bright, and the streams, which are everywhere to be seen, are remarkably clear and pure; so that although the interest of the road was less absorbing than when we were ascending the mountains, it was still very great. From Cranberry Summit the distant views to the westward were quite magnificent.[Pg 151]
We now entered on what is called the "Cheat River Region," and the descent to Grafton (a distance of thirty miles) is even more beautiful than the ascent to Altamont. To give you some slight idea of the nature of the road and of the scenery, I enclose a photograph of one of the bridges over the Cheat River. This is called the Tray Run Viaduct, and it is 640 feet long; the masonry is seventy-eight feet high, and the iron-work above that is eighty feet. The road here is about seven hundred feet above the river, which runs in the valley below. This river, the Cheat, is a dark, rapid, mountain stream, the waters of which are almost of a coffee-colour, owing, it is said, to its rising in forests of laurel and black spruce, with which the high lands here abound.
We passed hereabouts many curious-looking log houses, a photograph of one of which we enclose.[7] You will observe the man with a cradle by his side, and his whip, gun, bottle, jar, &c., also the chimney, which is a remarkable structure, consisting of a barrel above a heap of stones, showing the resources of the West.
Before reaching Grafton, we passed the Great[Pg 152] Kingwood tunnel, which is much thought of in America, being 4100 feet in length, though it is greatly beat by many of our tunnels in England; but tunnels are rare in America, as the roads generally run through the valleys.
We reached Grafton at four o'clock, and had a lovely afternoon to explore the beauties of the neighbourhood. We went into a number of cottages and log-huts, and were delighted with the people; but the details of our Grafton visit must be given to you vivâ voce on our return. The night was brilliant, and it was one o'clock in the morning before we took our last look of the moonlit valley, and of the rivers which here joined their streams almost under the windows of our rooms.
We may mention that in this day's journey, we passed the source of the Monongahela, the chief branch of what afterwards becomes the Ohio. It is here a tiny little clear stream, winding through the glades we have spoken of.
On Thursday morning, though it was past one before we went to bed, I was up at six, as soon as it was light, to make a sketch from our bed-room window, which will give you hereafter some notion of the scene, though neither description nor drawing can convey any real idea of it. After breakfast,[Pg 153] papa and I and Thrower went up a tolerably steep hill to the cottage of three old ladies, whose characters I had an opportunity of studying while papa went on with the guide to the Great National or State Turnpike Road, or "Pike Road" as they called it, which used to be the connecting link between Washington and Southern Virginia. Though much disused it is still well kept up. After going along it for some distance, papa struck up to the top of a high hill, from whence he had a magnificent view of the valleys on both sides of the ridge he was on, and he was surprised to find what large tracts of cultivated ground were visible, while to those below there seemed nothing but forest-covered mountains, but between these he could see extensive glades, where every patch was turned to account. This we afterwards saw from other parts of the road.
While papa was taking his hasty walk, Thrower and I sat down in the log-hut where these three old spinster sisters had lived all their lives. They were quite characters, and cultivated their land entirely with their own hands; though, when we asked their ages, two of them said they were "in fifty," and one "in sixty;" they were most intelligent and agreeable, and two looked very healthy; but the[Pg 154] third had just had a severe illness, and looked very ill. One was scraping the Indian corn grains off the cob, using another cob to assist her in the work; we watched the beautifully-productive plant, and admired its growth. Their cottage or hut looked quite comfortable, and there were substantial log stables and farm-buildings adjoining. When the weather permitted, they got down the hill to Grafton to the Methodist meeting. There is no Episcopal church there yet, excepting a Roman Catholic one, to which they will not go, though they speak with thankfulness of the kindness they have received from the priest.
They said their father used to tell them to read their Bible, do their duty, and learn their way to heaven, and this they wished to do. They were honest, straightforward good women, and ladies in their minds, though great curiosities to look at.
This walk, and our subsequent explorings in Grafton, occupied the whole forenoon, the temptation to pick the red leaves and shake the trees for hickory nuts being very great, and having greatly prolonged the time which our walk occupied. But the village itself, for it is no more, though, having a mayor, it calls itself a city, had great objects of interest, and is a curious instance of what a railway[Pg 155] will do in America to make a town; for it scarcely had any existence three years ago, and is now full of artificers and others employed in the railway works, all fully occupied, and earning excellent wages.
The people marry so early that the place was almost overflowing with children, who certainly bore evidence in their looks to the healthiness of the climate.
This being a slave state, there was a sprinkling of a black population; and among the slaves we were shocked by observing a little girl, with long red ringlets and a skin exquisitely fair, and yet of the proscribed race, which made the institution appear more revolting in our eyes than anything we have yet seen. The cook at the hotel was a noble-looking black, tall and well-made, and so famous for his skill at omelettes, that we begged him to give us a lesson on the subject, which he willingly did. I asked him if he were a slave, and he replied, making me a low bow, "No, ma'am, I belong to myself." The little red-haired girl was a slave of the mistress of the hotel.
We again linked ourselves on to a train which came up at about one o'clock, and at Benton's Ferry, about twenty miles from Grafton, we crossed the[Pg 156] Monongahela, over a viaduct 650 feet long; the iron bridge, which consists of three arches of 200 feet span each, being the longest iron bridge in America. Though the water was not very deep, owing to a recent drought, it was curious to see the little stream of yesterday changed into an already considerable river, almost beating any we can boast of in England.
We now began to wind our way down the ravine called Buffalo Creek, which we passed at Fairmont, over a suspension bridge 1000 feet long. The road still continued very beautiful, and was so all the way to this place, Wheeling, which we reached at about six o'clock. The last eleven miles was up the banks of the real Ohio, for the Monongahela, after we last left it, takes a long course northward, and after being joined at Pittsburg by the Alleghany, a river as large as itself, the two together there, form the Ohio. From Pittsburg to where we first saw it, it had come south more than 100 miles, and at Wheeling it is so broad and deep as to be covered with magnificent steamers; there were five in front of our hotel window, and most singular-looking they were, with their one huge wheel behind, scarcely touching the water, and their two tall funnels in front. They tower up to a great height, and are[Pg 157] certainly the most splendid-looking steamers we ever saw.
We here left our valued friend Mr. Tyson, who after calling on us at the hotel in the evening, was to return at ten o'clock to Baltimore. We certainly never enjoyed a journey more. He is the most entertaining man you can imagine, full of anecdotes and good stories; and, as we have said before, with such a marvellous memory, that he could repeat whole passages of poetry by heart. His knowledge too of botany was delightful, for there was not a plant or weed we passed of which he could not only tell the botanical and common name, but its history and use. He has travelled much, having been employed in mining business in the Brazils. He has also been in the West Indies, in England, Scotland, and Ireland, and on the Continent of Europe.
We had a pleasing variety in occasional visitors to the car; for not only the work-people on the road, as I have said, got up behind to speak to Mr. Tyson, and were always received by him in the most friendly manner, being men of high calibre in point of intelligence, but we had at different times a Dr. Orr, a physician and director of the railway, who was on the engine with us to set our bones, if papa had capsized us and the doctor had escaped;[Pg 158] also a Dr. Gerbard, a German surgeon, with a scar on his cheek from a duel at college in his youth. Dr. Orr was accompanied by a lady, with whom I conversed a good deal, and found she was the owner of many slaves; but I must write you a chapter on slavery another time. All the last day of our journey from Grafton to Wheeling, was through Virginia, and the rural population were chiefly slaves. The two doctors I have mentioned were our visitors yesterday. To-day, we had throughout with us Mr. Rennie (Mr. Tyson's assistant), and also Major Barry, an agent of the Company, and an officer in the United States service, who in the last Indian war captured with his own hand, Black Hawk, the great Indian Chief, in Illinois. He is an Irishman by birth, and had been in our service at the battle of Waterloo, but he left the British army, and entered the United States service in 1818. He was very intelligent and agreeable. Our last visitor was Colonel Moore, also an agent of the company; a most gentleman-like man. This will show you what a superior set of men are employed on American railways.
Among the men who spoke to us as we stood on our balcony, was a delightful character, a nigger.[Pg 159] I heard Mr. Tyson look over and say, "Jerry, why did you not tell me you were going to get married?" Up came Jerry, looking the very picture of a happy bridegroom, having been married the evening before to a dark widow considerably older than himself. He was quite a "get up" in his dress, with boots of a glistening blackness. He answered, "I sent you an invitation, Mr. Tyson, and left it at your office." He was nothing daunted by his interesting position in life, and had a week's holiday in honour of the event. He was, to use his own expression, a "'sponsible nigger," though he was actually only cleaner up, and carpet sweeper in the office, negroes never being allowed to have any charge in the working of the line, or a more "'sponsible" station than that connected with the office work, though in that they are often confidentially employed in carrying money to the bank, &c.
Columbus, Friday 22nd.—It began to rain last night, and continued to pour to-day till ten o'clock, so that we had no opportunity of seeing much of the town of Wheeling, but our rooms looked on to the Ohio, and were within a stone's throw of it. Another great steamer had come up in the night, so there were six now lying in front of the windows, looking like so many line-of-battle ships.[Pg 160]
We found that Jerry and his lady slept at our hotel, and I sent for them next morning to speak to us. She was smartly dressed in a dark silk, with a richly embroidered collar and pocket handkerchief, which she carefully displayed, and a large brooch. He wore a turn-down collar to his shirt, of the most fashionable cut; the shirt itself had a pale blue pattern on it, and a diamond (?) shirt pin, the shirt having a frill en jabot. His face was shining and glistening with cleanliness and happiness, and she looked up to him as if she were very proud of her young husband. He said he was very happy, and I complimented her on her dress, and asked her if she had bought much for the occasion, and she admitted that she had. I asked her where they went to church (all niggers are great worshippers somewhere, and generally are Methodists); and he said he went to the "Methodist Church," that his wife was a member, and I encouraged him to continue going regularly. He said he had married her for the purpose of doing so, and evidently looked up to her as a teacher in these matters. They said they could both read printed characters, but not writing, and that they read their Bibles. I asked him if there were any other cars on the line like Mr. Tyson's, and he said, "Yes, several,[Pg 161] miss." "Are they handsomer than his?" "Some are, they are all different in their fancy principle." He told us, of his own accord, that they had both been slaves. He bought his freedom for five hundred dollars. They both had been kindly treated as slaves, but he said, not only the hickory stick, but the "raw hide," was frequently used by unkind masters and mistresses; and, on my asking him whether slaves had any redress in such cases, he said their free friends may try to get some redress for them, but it does no good. This was his testimony on the subject, and I shall give you the testimony of every one as I gather it for you to put together, that you may be able to form your own deductions. Mr. Tyson had told us they had redress, though he is an enemy to the "institution" of slavery, as it is here called, but still maintains, what is no doubt the case, that they are oftener much happier in America than the free negro. Indeed he told us a well-treated slave will look down on a freeman, and say, "Ah! yes, he's only some poor free trash. He's a poor white free trash." It was curious to notice Jerry's sayings, only some of which I can remember. Mr. Tyson looked down the line from the balcony yesterday, and said, to Jerry, who had got out of a passenger car[Pg 162] for a minute, "Jerry, do you see the train coming?" "Yes, sir; it blowed right up there;" meaning it had whistled. I will write to you more at large ere long about slavery, when I have not topics pressing on time and pen.
We left our hotel this morning at eight o'clock, and even in the omnibus noticed the improved and very intelligent appearance of the men. They answered us quickly, cheerfully, and to the purpose; many wore large picturesque felt hats of various forms. It is true that, on starting, we were still in Virginia, of which Wheeling is one of the largest towns; but the bulk of our fellow-passengers were evidently from the West; they are chiefly descendants of the New Englanders, and partake of their character, with the exception of the nasal twang, which is worse in New England than anywhere else in America, and we are now losing the sound of it. The omnibus made a grand circuit of the town to pick up passengers, and thus gave us the only opportunity we had of seeing something of it. It rained in torrents, and this probably made it look more dismal than usual, but it certainly is much less picturesque and more English-looking than any town we have yet seen. The coal and iron, which constitute its chief trade, give it a very dirty appearance; but[Pg 163] its natural situation, stretching along the banks of the Ohio, which are here very high on both sides, is very beautiful. The omnibus at last crossed the river by a very fine suspension bridge, and, having left the slave states behind us, we found ourselves in the free State of Ohio.
On the opposite side of the river we entered the cars of the Ohio Central Railroad, but alas! we had no Mr. Tyson, and no sofas or tables or balconies, and were again simple members of the public, destined to enjoy all the tortures of the common cars. These however were in first-rate style, with velvet seats, and prettily painted, with brilliant white panelled ceilings; and we here fell in again, to my no small comfort, with the venders of fruit and literature, or "pedlaring," as it is called, which forms a pleasant break in the tedium of a long journey. I have been often told the reverse, but the literature sold in this way is, as far as we have seen, rather creditable than otherwise to the country, being generally of an instructive and useful character. Many works published quite recently in England, could be bought either in the cars or at the stores; and some of the better class of English novels are reprinted in America, and sold at the rate of two or three shillings a volume. The daily newspapers, sold on the[Pg 164] railways, are numerous; but these, with very few exceptions, are quite unworthy of the country. In general there are no articles worth reading, for they are filled with foolish and trashy anecdotes, written, apparently, by penny-a-liners of the lowest order of ability. The magazines, and some of the weekly illustrated papers, are a degree better, but a great deal of the wit in these is reproduced from "Punch."
The first eighty-two miles to Zanesville were through a pretty and hilly country. The hills were as usual covered with woods of every hue, so that though the scenery was inferior to what we had been passing through for the last few days, it was still very beautiful. Zanesville, which is a considerable town, is situated on the Muskingham river. This fine broad stream must add considerably to the waters of the Ohio, into which it falls soon after leaving Zanesville.
At Zanesville, after partaking of an excellent dinner, we were joined by an intelligent woman, returning home, with her little baby of ten weeks old, from a visit she had just been making to her mother. Her own home is in Missouri, and her husband being the owner of a farm of 500 acres, she was able to give us a good deal of information about the state of[Pg 165] agriculture in the Far West. I learnt much from her on various subjects, and was much surprised at the quick sharp answers she gave to all my questions. She was well dressed, something in the style of the English lady's maid, was evidently well to do, and was travelling night and day with her merry little baby. She possesses one slave of fourteen, for whom she gave four hundred dollars, whom she has had from infancy; she brings her up as her own, and this black girl is now taking care of her other children in her absence. I asked, "What do the slaves eat?" "Everything: corn-bread, that's the most." Papa said, "It is a great shame making Missouri a slave state."
Woman. "Ah yes; keeps it back."
Self. "Have you good health?"—many parts being said to be unhealthy.
Woman. A quick nod. "First-rate."
Self. "Did your mother give you the hickory stick?"
Woman. "No: the switch:—raised me on the rod of correction."
Self. "Had your husband the farm before you married?"
Woman. "His father had 'entered it,' and he gave my husband money, and my mother gave me[Pg 166] money, and then we married and 'entered it' ourselves."
All these answers came out with the utmost quickness and intelligence. She is an Irish Roman Catholic, her mother having brought her as a baby from Ireland, her husband is also Irish; but they are now Americans of the Far West in their manner and singular intelligence, beating even the clever Irish in this respect.
I said: "Do you pray much to the Virgin Mary in your part of America?"
Woman. "No: don't notice her much."
Self. "I am glad of that."
Woman. "We respect her as the mother of God."
She said the corn on the road-side we were then passing was far inferior to western produce, that it ought to be much taller, and that if it were so, the ear would be much larger and fuller. Our English wheat is never called corn, but simply wheat; and the other varieties oats, rye, &c., are called by their different names, but the generic term corn, in America, always means Indian corn. It is necessary to know this in order to prevent confusion in conversation. This woman's name was Margaret[Pg 167] M.; she was twenty-seven years of age, but looked younger; her husband, James M., was thirty-six.
I asked her whether he was tall or short. "Oh tall, of course. I wouldn't have had a poor short man." So we looked at papa, and laughed, and said our tastes were the same. She was a most agreeable companion. She noticed that I was reading a novel by the author of "John Halifax," which I had bought, the whole three volumes, for 1s. 6d., and said, "Ah! that's the sort of reading I like. That's a novel; but my priest tells me not to read that kind, that it fills me with silly thoughts; but to read something to make me more intelligent." I thought there seemed no deficiency in this respect, but agreed that the advice was good, and said that I had bought this for cheapness, and for being portable, it being in the pamphlet form; and that I was so interrupted with looking at the lovely scenery when travelling, that I could not take in anything deeper.
We wished each other good bye, and she wished me a happy meeting again with our children. And now papa says this must be closed, and it certainly has attained to no mean length, so I will not begin another sheet, and hope you will not be wearied with this long chapter.
[7] These photographs cannot be reproduced here, which I regret, as they were very well done.
JOURNEY FROM WHEELING TO COLUMBUS.— FIRE IN THE MOUNTAINS.— MR. TYSON'S STORIES.— COLUMBUS.— PENITENTIARY.— CAPITOL.— GOVERNOR CHASE.— CHARITABLE INSTITUTIONS.— ARRIVAL AT CINCINNATI.
Columbus, Oct. 23rd, 1858.
The letter which I sent you from this place this morning will have told you of our arrival here, but it was closed in such haste that I omitted many things which I ought to have mentioned. It, moreover, carried us only to Zanesville, and I ought to have told you that the view continued very pretty all the way to this place, and the day having cleared up at noon, we had a brilliant evening to explore this town.
Before describing Columbus, however, I shall go back to some omissions of a still older date; for I ought to have told you of a grand sight we saw the day we passed the Alleghany Ridge. On the preceding evening Mr. Tyson received a telegraphic message to say that an extensive fire was raging in the forest; it is supposed to have been caused by some people shooting in the woods. It must have been a[Pg 169] grand sight to the passengers by the train from which we had separated, and which went on during the night through the scene of the conflagration, for the fire was much more extensive than those which are constantly taking place, and which are passed by unheeded,—unhonoured with a telegraphic notice. When we passed by the place next morning it was still burning vigorously, but the daylight rendered the flames almost imperceptible. It was curious, however, to see the volumes of smoke, which we first perceived in a hollow. The fire was then travelling down the side of the mountain; and long after we passed the immediate spot we saw the fire winding about the mountains, spreading greatly, in the direction of the wind and making its way even against it, though it was blowing with considerable violence. The people in the neighbourhood were busily employed in trying to save their hayricks from destruction. Mr. Tyson said they would probably succeed in this, though the whole of the forest was likely to be burnt, as the fire would wind about among the mountains and pass from one to another for perhaps two months, unless a heavy rain put it out. This we hope has been the case, as it poured in torrents all the following night when we were at Wheeling.[Pg 170]
Another circumstance we ought to have mentioned was our passing through a very long tunnel, called the Board Tree Tunnel, about 340 miles from Baltimore. This tunnel, after having fallen in, has only been repaired within the last two months. The history of this catastrophe, and of the mode of remedying it, forms quite an incident in the history of the railway, and shows with what resolution difficulties in this country are overcome. To reopen the tunnel it was clear would be a work of time, so Mr. Tyson resolved to run a new temporary railway for three miles over the mountain which had been tunnelled, and this was accomplished by 3000 men in ten days. We saw the place where this road had passed, and the zig-zag line by which the mountain was crossed. The road seems positively to overhang the precipice, and reminded me of a mountain pass in Switzerland—as, indeed, the whole of the road here does. Mr. Tyson himself drove the first train over, and he said his heart was in his mouth when, having got to the top, he saw the descent before him, and the engine and train on a precipice where the least contretemps would have plunged the whole into the abyss below; but happily all went right, and till within the last two months this temporary road has been used.[Pg 171] It was really quite frightful to look up and think a train could pass over such a place, the grade being 420 feet in a mile, or 1 in 12½; but you will one day be able to form some idea of it, as a photograph was taken, and Mr. Tyson will give us a copy of it. This is certainly a wonderful country for great enterprises, and the Pennsylvania Central Railway, by which we contemplate recrossing the Alleghanies, is in some respects a still more remarkable undertaking, though the height at which the mountains are crossed on that line is not so great as that on the Baltimore and Ohio line, which, as I told you in my last, is at an elevation of 2700 feet. It was long supposed that such a feat could not be surpassed, but Mr. Tyson says that, encouraged by this, a railway now crosses the Tyrolean Alps at a somewhat higher level.
To return, however, to the Board Tree Tunnel: Mr. Tyson told us that the difficulty of restoring it to a safe condition was so great as almost to dishearten him till he had arched it completely over from one end to the other with solid stone masonry, which has rendered the recurrence of the accident impossible; but the disheartening circumstance, while the work was in progress, was the danger to which the men employed in the work were exposed, from the con[Pg 172]stant falling in of the roof. During its progress no less than forty-five men were killed, and about 400 severely wounded. They were chiefly Roman Catholics, and were it not for the encouragement given by an energetic Roman Catholic priest, he hardly thinks the men would have continued the work. The doctor, too, who attended the wounded, and whom we saw at breakfast at Grafton, was also most devoted to them. It was quite touching to hear the tender-hearted way in which Mr. Tyson spoke of the poor sufferers, for he was constantly there, and often saw them go in to almost certain death. He mentioned one poor widow to whom he had just sent three hundred dollars as a gift from the railway.
Before leaving the subject of Mr. Tyson, I must tell you one or two of his good stories. I had been telling him of the negro meeting, which I described to you in my last. In it I told you how the negroes had cried out "glory! glory!" from which it appears it is almost impossible that they can refrain. In corroboration of this he told us of a nigger woman who was sold from a Baptist to a Presbyterian family. In general slaves adopt, at once, the habits and doctrines of their new owners; but this poor woman could not restrain herself, and greatly disturbed the Presbyterian congregation, by shouting out[Pg 173] "glory! glory!" in the middle of the service. Next morning the minister sent for her and rebuked her for this unseemly interruption of his sermon; but she said doggedly, "Can't help it, sir; I'm all full of glory; must shout it out." Many of his amusing stories were about Irish labourers employed on the road. One of these, whose duty it was to show a light at the station as the train passed, failed one night to do so, and was seen asleep. The man who drove the engine threw a cinder at him as he passed, to awake him; but, instead of hitting him, the cinder broke his lamp glass. All this was told to Mr. Tyson, and also that the man was very angry at his lamp being broken. When Mr. T. went down the line next day, he stopped to lecture him, and the following colloquy ensued:—
Mr. Tyson. "Well, your lamp was broke, I hear, yesterday."
Irishman. "O, yes sir;" (terrified out of his life at the scolding he feared was coming, for he saw that Mr. Tyson knew all about it;) "but I forgive the blackguards intirely, sir, I quite forgive them."
Mr. T. kept his counsel, said nothing more, and the lamp has never failed since; but half the merit of this story depended on Mr. Tyson's way of telling it. He was deliciously graphic also, and full[Pg 174] of witty sayings of his own. When, for example, I showed him my photograph of your little brother, he exclaimed, "Well, he is a fine fellow; he don't mind if corn is five dollars a bushel." I think you will all appreciate this as a perfect description of the unconcern of a healthy intelligent-looking child, unconscious of the anxieties of those about him; but I must reserve his other good sayings and stories till we meet.
To-day we have been most busily employed, for Mr. Garrett, our railway friend at Baltimore, not only did us the good service of sending us by the car under Mr. Tyson's auspices, but gave us letters of introduction both to this place and to Cincinnati; and his letters here to Mr. Neil and Mr. Dennison have been of great use to us, as one or the other of them has been in attendance upon us since 11 o'clock this morning, together with a very pleasing person, a widow, niece of Mr. Neil, and they have shown us the town in first-rate style.
Columbus is built on the banks of the Sciota, about 90 miles from the point where it falls into the Ohio. It is the capital of the State, and its streets, like those of Washington, have been laid out with a view to its becoming one day a town of importance; but as the preparations for this,[Pg 175] though on a considerable scale, are not so great as at Washington, the non-completion of the plan in its full extent produces no disagreeable effect. In fact, the streets where finished are completely so, and the unfinished parts consist of an extension of these, in the shape of long avenues of trees. In the principal streets the houses are not continuous, but in detached villas, and, judging by the one in which Mr. Neil lives, appear to be very comfortable residences. He and his niece called upon us yesterday evening, and, although he is an elderly gentleman, he was here by appointment this morning at half-past 8, and took papa to call on Mr. Dennison, when they arranged together the programme for the day.
At 11 o'clock Mr. Dennison called, and took us to the Penitentiary, where nearly 700 prisoners are confined. I think he said 695, although it will hold the full number of 700 if need be. For the credit of the sex, I must say that only ten out of the whole are females. These ten are lodged each in a small room, for it can scarcely be called a cell, very well furnished, and opening into a large sitting-room, of which they all have the unrestrained use, although the presence of a matron puts a restraint on their tongues. They were employed in needlework. The cells of the men are arranged in tiers,[Pg 176] and are certainly very different looking habitations to those of the women, and greatly inferior in size and airiness to the cells at Philadelphia, where, in addition to the grating in front of the cell, there was a door behind leading into a small enclosure or court. Here the only opening in the cell is by a door into a long gallery, and the cells were much smaller than either at Philadelphia or at Kingston; but the prisoners only inhabit these cells at night, the solitary system not being adopted or approved of here.
The silent system, however, is practised here as at Kingston, and the prisoners are employed in large workshops, chiefly in making agricultural instruments, hoops for casks, saddles, carpenters' tools, and even rocking horses and toys, which must be rather heart-breaking work for those who have children. The men have certain tasks allotted them, and when the day's work is done, may devote the rest of their time to working on their own account, which most of them do; the chief warden told us that he had lately paid a man, on his leaving the prison, a hundred and twenty-five dollars for extra work done in this way. The warden told us that the men, when discharged, were always strongly urged to return to their own homes instead of seeking to retrieve their[Pg 177] characters elsewhere, and that their doing so was generally attended with a better result than when they went to a new place and had no check on their proceedings. This does away with the chief argument of our quaker friend at Philadelphia, in favour of the solitary system, which was, that the prisoner's return to his friends became more easy, when none of them knew that he had been in prison, of which they could not well be ignorant if he had mixed with other prisoners in a public jail. It must be borne in mind, however, that the great demand in this country for work renders it much more easy for a person so circumstanced to obtain employment, even with a damaged character, than in England, where our ticket-of-leave men find this almost impossible. There is also, we are told, a kinder feeling towards prisoners here on their leaving the jail than in England, and this saves them from the want and consequent temptation to which our English ticket-of-leave men are exposed; the result is that a much less proportion of those released in America are re-committed for new offences.
We visited the workshops, and afterwards went into a large court to see the men defile in gangs, and march into their dining hall, in which we afterwards saw them assembled at dinner, and a capital savoury[Pg 178] dinner it seemed to be. They have as much bread as they choose to eat, and meat twice a day; their drink is water, except when the doctor orders it otherwise. There are chaplains, called here Moral Instructors, who visit them and perform the service in the chapel, and evening schools are provided, at which the chaplains attend to teach reading, writing, and arithmetic. A library of books of general information is provided for the prisoner's use, and to each a Bible is given, and they are allowed to buy sound and useful books. They have each a gas lamp in their cell, which enables them to read there when their work is done, and they are allowed to see their friends in the presence of an officer. Sixty of the prisoners were Negroes, which is a large proportion when compared with the total numbers of the white and black population, especially as the blacks are often let off, owing to the leniency of the committing magistrates who have compassion on their inferior intelligence; and it is owing, it is said, to a like leniency that there are so few females, though certainly not for the same reason. There are a large number of Irish in the prison.
Our next visit, still under Mr. Dennison's escort, was to the Capitol or State House, a very fine building of white limestone. The façade is more than[Pg 179] 300 feet long, and the height nearly 160 feet to the top of the dome. This however has not yet been completed. The architecture is Grecian. Here, as at Washington, are Halls for the Senate and House of Representatives, in equally good taste and somewhat similarly arranged. Mr. Dennison, who had once been a member of the Senate, was repudiating the accounts so commonly given of the behaviour of the senators, when Mr. Niel came in, and over-hearing what he was saying, begged to remark that when they "went to work" they usually divested themselves of their coats without substituting any senatorial garment in its place; and putting his legs on the desk before the chair, he declared that such was the usual posture in which they listened to the oratory of the place.[8]
We afterwards went through the apartments appropriated to the Treasurer and Auditor of the State, the two chief officers of the Government, which are very capacious and well fitted up—and we[Pg 180] were specially introduced to both these functionaries; Mr. Neil, who is somewhat of a wag, was rather jocose with them, and high as their position here is, they very cordially retaliated on him. We next went to those appropriated to the Governor of the State, General Chase, in order that we might be introduced to him, but he was out, which we regretted. He is a candidate to succeed Mr. Buchanan as President. The remainder of the building was occupied by numerous committee-rooms, by the courts of law, the judges' apartments, a law library, and a beautiful room intended for a general library, but in which the collection of books at present is very small. On the whole the building and its contents are very creditable to this, the largest and wealthiest of the States in the West, considering that forty years ago the country here was a wild forest region where no tree had been cut down.
25th October.—We have seen Columbus well, and it has much to attract attention. On Saturday we went from the Capitol to the Lunatic Asylum, but excepting in its being more pleasingly arranged than the one at Utica, there was nothing very striking in its appearance. The galleries in which the patients were walking were prettily decorated with flowers cut out in paper, giving it a very[Pg 181] gay appearance; and when the patients become desponding, they have a dance in the great hall, to revive them. The matron who went round with us said that the men and women conduct themselves on these occasions with perfect propriety. The men and women are otherwise so entirely separated in this Asylum that papa went round to the men's wards with the doctor, while I was taken round by the matron to those appropriated to the women. We thought it a pleasant, cheerful-looking place, considering the melancholy object to which it is devoted.
The next sight we saw was, the Asylum for the Deaf and Dumb: being Saturday, we could not see the mode of tuition, but we have gone through it this morning, and yesterday we attended the afternoon service there, so that in our three visits we have been able to form a pretty good idea of the system carried out. They have an alphabet by which they can spell words, which they do by using one hand only. They speak thus with considerable rapidity, but this method is confined almost entirely to express proper names and words of uncommon use, as the whole conversation is carried on in general by signs, and it was most beautiful to see the graceful manner in which the matron spoke to them.[Pg 182] As this system of signs does not represent words, but things and ideas, it has the great advantage of being universally understood when taught, and as the same system is adopted in several countries of Europe, in Norway and Sweden for example, a Norwegian and American child can converse easily together without either knowing a syllable of the other's language. It seems quite as rapid as talking.
We were present at the afternoon sermon, which lasted about half an hour, the subject being that of Simeon in the Temple, and except to express Simeon's name, there was no use at all made of the fingers. Dr. Stone, the principal, had preached in the morning on the subject of Daniel's interpretation of Nebuchadnezzar's dream, and when we went, the children were being examined on the subject of this lecture. We saw a number of questions asked, but in this case the words were spelled in order that Dr. Stone, who was teaching them, might be satisfied that they understood the full meaning of the question in its grammatical sense, as well as its general signification, and the answers were all written down on large black boards. They wrote with prodigious rapidity in large distinct writing—and the answers, which were all different and showed they were not got up by rote, were in most cases very good.[Pg 183] This was being done by the eldest class, and some of the elder boys and girls seemed full of intelligence. We saw minutely only what was going on in this and in the youngest class, which was no less remarkable, considering that some of the children had not been more than two or three months in the Asylum, and when they came there had no idea of either reading or writing.
When I say the youngest class, it is not with reference to the age of the pupils, but to the recent period of their admission, for some of them were as old in years as in the first class, while others were very young; one of them, a very pretty little Jewish girl with sparkling intelligent eyes, was indeed a mere child. We had on Sunday seen this little girl being taught her lesson, which consisted of the simple words, "I must be kind," and it was very pretty to see the way in which the notion of kindness was conveyed by signs. This morning she was writing this on the slate, and she afterwards wrote in a very neat handwriting a number of short words—cat, dog, horse, &c.—which were dictated to her by signs which were of so simple a nature that we could understand many of them; a goat, for example, was represented by the fingers being stuck on each side of the head as[Pg 184] horns, and then by the man drawing his hand down from his chin to indicate the beard. They thus became acquainted by signs with almost every object in the first instance, and are led on by degrees to complex ideas of every kind. Dr. Stone says that the use of signs is known in England, but he believes is never practised to any extent, and certainly not in giving religious instruction. No attempt is made here, as in England, to teach them to articulate, as he considered the attempt to do this to be a great mistake, it being a painful effort to the child, which never leads to any good practical result. In some cases where deafness has been accidentally brought on after children have learned to speak, it is then as far as possible kept up; but even then the effort, as we saw, was very painful.
Our next visit was to the Blind Institution, but here there was nothing very remarkable, though owing to the children not being in school we saw the Institution very imperfectly. Raised characters are used here, as I believe everywhere else; one little girl who was called up read and pronounced very well; we also heard some of them sing and play for a considerable time. The bulk of the children, or rather young people, for they keep them here till they are one or two and twenty, were[Pg 185] walking about the gardens invariably in pairs, which seems an excellent preservative against accidents: this they do of their own accord.
We next went to the Idiot Asylum, but the children being, as usual on Saturday, out of doors, we merely took a general look at the place, and returned there this morning to see the system pursued for them more in detail. Dr. Patterson, the superintendent, is a man of wonderful energy; and two young women and a matron, the two young teachers especially, must be exemplary characters, for they appear to devote themselves to their work with an energy and kindness which is perfectly marvellous, considering the apparently hopeless task they are engaged in. However, when taken young, from six to seven years of age, the capabilities of these poor children for improvement seem in general great, unless the infirmity is occasioned by epileptic fits, when the cure is considered almost hopeless. We were entertained by a story told by Dr. Patterson of a boy brought to him by the Mayor of C., who told him it was a bad case, but that he would be satisfied if he could fit him to be a missionary. Dr. P. replied that he could not answer for that, but that he could at all events fit him to be Mayor of C.[Pg 186]
The great means resorted to for improvement is constant occupation, changed every quarter of an hour through out the day. By this means their physical power at night is nearly exhausted, and they invariably sleep well; where no greater improvement is arrived at, they can in all cases gain cleanly habits, and get entirely rid of that repulsive appearance which an idiot left to himself is almost sure at last to acquire. Active exercises are what they resort to in the first instance; they have a large school-room fitted up with ladders and gymnastic apparatus of all kinds. We saw little boys, who shortly before were scarcely able to stand alone, climbing places which made me tremble for their safety, but it was curious to observe with what caution they did it.
When we entered the room the youngest class were all standing round a piano, at which one of the teachers was playing, whilst she and the other teacher were leading them on in singing a cheerful song, and it was really quite touching to hear and see them; they sang very fairly, not worse than children usually do at that age. After a quarter of an hour of this they went through their Calisthenic exercises, marching in perfect time, clapping their hands, and going through different[Pg 187] gestures with great accuracy, and these poor children a very few months ago had hardly any control over their actions.
Another thing taught is, to distinguish colour and form—for which purpose they have cards cut out into circles, squares, and octagons—and other marked shapes, of every variety and shade of colour. Five or six of these of different sorts were spread on the table, and a large unsorted pack was placed before a little boy five or six years old, and it was quite interesting to see him proceed to sort them by placing each one on the top of the counterpart which had been placed at first on the table. As there were many more kinds in the pack than those spread out on the table, when he came to a new one he first placed it in contact with the others to see if it suited, and after going round them all and seeing that none were the same, he appeared puzzled, and at last set it down in a place by itself. Although there was a certain degree of vacancy in the expression of the child, it seemed quite to brighten up at each successive step, and the occupation was evidently a source of considerable enjoyment to him. This little fellow had been a very short time in the Asylum, and when admitted had not the slightest idea of form, colour, or size.[Pg 188]
Another mode adopted is, to take little blocks of wood of different sizes and forms, which the child is required to fit into corresponding holes cut out in a board. All this is for the least advanced pupils. They learn afterwards to read and write, and some of the very little ones traced lines upon a board as well as most children could do with all their senses about them. The elder ones could write short words and read easy books; they are taught to read by having short words like cow, dog, ox, printed on cards, and are then shown by a picture what the words represent, and they are not taught their letters or to spell words till they begin to learn to write; the elementary books therefore consist chiefly of words representing ideas quite independently of the letters of which the words are formed. Many, however, can never fully obtain the power of speech, and that without any physical defect in their organs, and without the accompaniment of deafness, for they hear perfectly. In these instances to teach them to speak is very difficult, and sometimes hopeless. The poor little boy whom we saw sorting his cards, was one of those cases in which no articulate sound had ever been uttered, or could be produced by any teaching. At the same time the development of his head, and that of many others,[Pg 189] was almost perfect and quite a beau ideal of what a head should be.
I forgot in speaking of the deaf and dumb to mention that their crying and laughter were quite like those of other children, and it appears to be the same with the idiots, even though they cannot speak. There was among the idiots one boy in irons to support his legs, which were otherwise quite without power, and he seemed under this treatment to be rapidly improving. They all have meat twice a day, and great care is taken to feed them generously. The only other sight in Columbus is the Medical College, which, however, we had no time to go over. We must, however, except the Governor's house, not forgetting its inmates, Governor Chase himself, and his interesting daughter. We had been introduced to the Governor by Mr. Dennison, after missing him on Saturday at the Capitol, and he most kindly asked us to drink tea and spend the evening with him, apologising for time not permitting his daughter to call upon us. He is Governor of the State of Ohio, an office that is held for two years. He is a first-rate man in talent and character,—a strong abolitionist, and a thorough gentleman in his appearance—showing that the active and adventurous habits of his nation[Pg 190] are quite consistent with the highest polish and refinement. He is deeply involved in the politics of his country, and, as I said before, is a candidate for the next presidentship. His strong views on the question of slavery will probably be a bar to his success, but unfortunately another hindrance may be that very high social character for which he is so remarkable. To judge at least by the treatment of such men as Henry Clay, and others of his stamp, it would appear as if real merit were a hindrance rather than a help to the attainment of the highest offices in America.[9]
The Governor's house looked externally something like an English rectory standing in a little garden, and we were at first shown into a small sitting-room. It seems the fashion all over America, as it is abroad, to leave the space open in the middle of the room, and the chairs and sofas arranged round the walls, but there is always a good carpet of lively colours or a matting in summer, and not the bare floor so constantly seen in France and Germany. The little[Pg 191] gathering consisted of the Governor, his two daughters (his only children), his niece, and his sister, Mr. Dennison, and Mr. Barnay, a clever New York lawyer, with whom we had crossed the Atlantic. But if the Governor recommended himself to us as a gentleman, what am I to say of his daughter? Papa has gone out and has left her description to me, whereas he could give a much more lively one, as he at once lost his heart to her. Her figure is tall and slight, but at the same time beautifully rounded; her neck long and graceful, with a sweet pretty brunette face. I seldom have seen such lovely eyes and dark eyelashes; she has rich dark hair in great profusion, but her style and dress were of the utmost simplicity and grace, and I almost forgave papa for at once falling in love with her. Her father has been three times a widower, though not older-looking than papa, and with good reason he worships his daughter. She has been at the head of her father's house for the last six months, and the naïve importance she attached to her office gave an additional attraction to her manners. While we sat talking in the little room the Governor handed me a white and red rose as being the last of the season. He had placed them ready for me in a glass, and I have dried them as a memorial of that pleasant evening. We soon went[Pg 192] into the dining-room, where tea and coffee were laid out on a light oak table, with an excellent compôte of apples, a silver basket full of sweet cakes, of which the Americans are very fond: bread—alas! always cut in slices whether at the hotels or in private, fresh butter,—an improvement on the usual salt butter of the country, and served, as it generally is, in silver perforated dishes to allow of the water from the ice to drain through, and a large tureen of cream toast. This is also a common dish, being simply slices of toast soaked in milk or cream and served hot. It often appears at the hotels, but there it is milk toast, and is not so good. I thought the cream toast excellent, and a great improvement on our bread and milk in England, but papa did not like it. The Governor and his fair daughter presided at the table, the Governor first saying grace very reverently, and we had a very pleasant repast.
After this we were conducted to the drawing-room. Such a bijou of a room! The size was about twenty feet by eighteen, and the walls and ceiling, including doors, window-frames, and shutters—there were no curtains, might have been all made of the purest white china. It is a most peculiar and desirable varnish which is used on their wood-work that[Pg 193] gives this effect. Mr. Tyson told us that it is made of Canada balsam, and that it comes therefore from our own territory, so that it is very stupid of Cubitt and others not to make use of it. The effect is like what the white wood-work of our drawing-room was when it was first finished, and you may imagine the appearance of the whole room being done with this fine white polish everywhere. We see it in all the hotels and railway carriages, so that it cannot be expensive. The windows were pointed, and the shutters were made to slide into the walls. They were shut on that evening, and were made, as they often are, with a small piece of Venetian blind-work let into them, also painted white. If we had called in the morning we should probably have found the room in nearly total darkness, as we found to be the case at Mr. Neil's, for the dear Americans seem too much afraid of their sun. There was a white marble table in the centre of this drawing-room, and the room was well lighted with gas. The only ornament was a most lovely ideal head in marble by Power, the sculptor of the Greek slave. The simplicity and beauty of the room could not be surpassed, and we spent a most interesting evening.
The father and daughter we found to be full of intelligence and knowledge of our best authors,[Pg 194] though neither of them has ever been in England. Miss Chase is much interested in a new conservatory, took me over it, and gave me several very pretty things to dry. I shall endeavour to get cuttings or seeds of them. I was generous enough to allow papa afterwards to go over the conservatory alone with her. She is longing to come and see England, but her father is too busy at present to leave the country. She expressed such sorrow not to know more of us, that we promised to call this morning after our "asylum" work was done, when she showed us over the house, which is very pretty, and nicely arranged throughout.
I think I have nothing more to say of Columbus, except that we heard two sermons and saw one on Sunday; for, besides the morning sermon at the Episcopal Church, and the sign one to the deaf and dumb, we looked in at another where a negro was preaching to his fellow niggers with great energy and life; but the ladies were quiet, and restrained their agonies and their "glory."
Cincinnati, Oct. 27th.—We left Columbus at forty minutes past twelve yesterday. Mr. Dennison and Mr. Neil's son met us at the station, and Mr. Neil gave me some dried red leaves he had promised me, which have kept their colour tolerably well. Mr. D. is president[Pg 195] of the railroad on which we were about to travel, and wished to give us free tickets to this place, but papa declined with many thanks. Papa has no sort of claim or connection with this railway, and I only mention the circumstance to show the extreme kindness and liberality of these gentlemen, who knew nothing of us, and probably had never heard our names until they had received letters of introduction about us from others, who were themselves equally strangers to us a few days ago. They introduced us to the freight agent of the Ohio and Mississippi Railway, who travelled with us, as did also a clever handsome widow. She seemed to be well connected, being related to General Cass and other people of note. She reminds me a little of Mrs. B. in style and manner, and it is pleasant to have some one to talk to, for we do not find people in general communicative in travelling, though papa says the fault may be ours.
There was nothing particularly pretty on the road, as the trees are, I grieve to say, losing their leaves in this neighbourhood; but on approaching this great city, "the Queen of the West," we came again on the Ohio. The water is now very low, but the bed of the river shows how great its width is when full; and even now there is a perfect navy of[Pg 196] splendid steamers floating on its waters, many of which we saw as our train drove through the suburban streets of the city. Unhappily the rain poured down upon us as we got into the omnibus, but we were soon consoled by finding ourselves in this most magnificent hotel, the finest I have yet seen. The drawing room, is I should think, unsurpassed in beauty by any hotel anywhere, and I shall endeavour to make a drawing of it before I leave. The hotel at Columbus was tolerably large, as you may suppose, when I tell you that our dining room there was about ninety feet by thirty. This one, however, has two dining rooms of at least equal dimensions, which together can dine 1000 persons, and it makes up 600 beds. We sat in the drawing room yesterday evening, for we could not reconcile ourselves to leave it, even to write this journal. There were various ladies and gentlemen laughing and talking together, but no evening dresses, and nothing of any importance to remark about them. One young lady only was rather grandly dressed in a drab silk; she afterwards sat down to the piano, and began the usual American jingle, for I cannot call it music; and I have since been told she was the daughter of the master of the house. "Egalité" is certainly the order of the day here, and this young lady was[Pg 197] treated quite on an equality with the other ladies in the room. The food is excellent, and we are very thankful to have so luxurious a resting place if we are at all detained here. We have several friends in the hotel, who are here to meet papa on business.
This morning we have had a visit from Mr. Mitchell, the astronomer, and author of the work on Astronomy, which I remember reading with pleasure just before I left England. His daughter is to call on me and drive us out, and we are to pay a visit to his observatory. We went this afternoon to leave some letters, which Mr. Dennison had given us for Mr. Rufus King and Mr. Lars Anderson. We found Mrs. King at home; her husband is much devoted to educational subjects and to the fine arts. There were some very good pictures and engravings in the drawing room, and amongst the latter two of Sir Robert Strange's performances. We found both Mr. and Mrs. Anderson at home; they live in a splendid house, but as it was getting dark we could not see the details. We sent in our cards with our letter, and the room being full of people, Mr. Anderson introduced papa to each one separately, and me as Mrs. S——. As these guests went out others came in, and fresh introductions took place,[Pg 198] but still always Mr. T—— and Mrs. S——, and he so addressed me during the visit. As we were going away papa said that he was making some strange mistake about my name, but he insisted upon it that we had so announced it; and on looking at our cards I found the card of a very vulgar lady at New York, which I had given by mistake as my own.
As we were leaving the room, a very amiable and pleasing person asked me if I would not call upon Mr. Longworth, the most celebrated character in this country, who she said was her father and the father of Mrs. Anderson. I said that we had letters to him from Mr. Jared Sparks, and that we had meant to call on him the next day, but she said we had better return with her then. We accordingly accompanied her through Mr. Anderson's garden, and through an adjoining one which led to her father's house, likewise a very large one, though not presenting such an architectural appearance as Mr. Anderson's. The old gentleman soon made his appearance, and afterwards Mrs. Longworth. They were a most venerable couple, who had a twelve-month ago celebrated their golden marriage, or fiftieth anniversary of their wedding day. We were invited to stay and drink tea, which we did, and met a large assemblage of children and grand[Pg 199]-children; a great-grand-child who had been present at the golden wedding, was in its nursery.
Mr. Longworth, among other things remarkable about him, is the proprietor of the vineyards from which the sparkling champagne is produced, known, from the name of the grape, as the sparkling Catawba; but he seems no less remarkable from the immense extent of his strawberry beds, which cover, I think he said, 60 acres of ground. He told us the number of bushels of fruit they daily produce in the season; but the number is legion, and I dare not set it down from memory. He showed papa a book he had written about his grapes and strawberries, and is very incredulous as to any in the world being better than his. This led to a discussion upon the relative size of trees and plants on the two sides of the Atlantic; and in speaking of the Indian corn, he tells us he has seen it standing, in Ohio, eighteen feet high, and he says it has been known, in Kentucky, to reach as high as twenty-five feet, and the ear eighteen inches long.
The old gentleman is a diminutive-looking person, with a coat so shabby that one would be tempted to offer him a sixpence if we met him in the streets; indeed a story is told of a stranger, who,[Pg 200] going into his garden, and being shown round it by Mr. Longworth, gave him a dollar, which the latter good-humouredly put into his pocket, and it was not till he was asked to go into the house that the stranger discovered him to be the owner.[10] He is, however, delightfully vivacious, and full of agricultural hobbies. His wife is a very pleasing, primitive-looking person. We tasted at their house some of the ham for which this city, called by the wits Porkopolis, is so remarkable. The maple sugar is used in curing it, and improves the flavour very much.
October 28th.—I must bring this letter to a rapid close, for it must be posted a day earlier than we expected. We intend to start in two days for St. Louis, and there I will finish my account of Cincinnati. To-day we have seen a great many schools, which have given us considerable insight into the state of education in America. My next[Pg 201] letter will probably bring us to our most western point, though we have not yet quite settled whether we shall go to the Falls of St. Anthony, or to Chicago. Papa says I must close, and I must obey.
[8] Though this description of the Senate was meant as a good-humoured satire on the absence of etiquette in their assemblies, it is probably no very exaggerated account of what is sometimes seen there; but it would be most unfair to draw any conclusion from this as to the behaviour in general society of well-educated gentlemen in America, there being as much real courtesy among these as is found in any other country, though certainly not always accompanied by the refinements of polished society in Europe.
[9] It is not meant here to obtrude special views of politics, or to maintain that democratic principles have naturally this tendency; but it may help to explain why so little is heard or known in England of the better class of Americans. Their unobtrusive mode of life entirely accounts for this, and it is to be regretted that it is the noisy demagogue who forms the type of the American as known to the generality of the European public.
[10] I should not have taken the liberty of printing this account of Mr. Longworth were he not, in a manner, a public character, well known throughout the length and breadth of the land, and his eccentricities are as familiar to every one at Cincinnati as his goodness of heart. In speaking, too, of his family, it is most gratifying to be able to record the patriarchal way in which we found him and Mrs. Longworth, surrounded by their descendants to the third generation.
If any apology is required, the same excuse—of his being a well-known public character—may be made for saying so much of Governor Chase and of his family.
CINCINNATI.—MR. LONGWORTH.—GERMAN POPULATION—-"OVER THE RHINE."—ENVIRONS OF CINCINNATI.—GARDENS.—FRUITS.—COMMON SCHOOLS.—JOURNEY TO ST. LOUIS.
Vincennes, Indiana, Nov. 1st, 1858.
My last letter brought us up to our arrival at Cincinnati, and our passing the evening at Mr. Longworth's on the following day. Next day, Wednesday the 27th, Mrs. Anderson, Mr. Longworth's daughter, called and asked us to spend that evening also at her mother's house. She took me out in her carriage in the morning to see some of the best shops, which were equal to some of our best London ones in extent and in the value of the goods; and in the course of the day we called at Monsieur Raschig's; he not being at home, we made an appointment to call there late in the evening.
The party at the Longworths was confined to the[Pg 203] members of their large family, all of whom are very agreeable. There were two married daughters, Mrs. Flagg and Mrs. Anderson, and the grandson and his wife, Mr. and Mrs. Stettinius; and we also saw the little great-grand-daughter, who is a pretty child of eighteen months. The dining-room not being long enough to accommodate us all at tea, the table was placed diagonally across the room, and it was surprising to see Mrs. Longworth pouring out tea and coffee for the whole party as vigorously as if she were eighteen years old, her age being seventy-two. She is remarkably pretty, with a fair complexion, and a very attractive and gentle manner and face.
We had quails and Cincinnati hams, also oysters served in three different ways—stewed, fried in butter, and in their natural state, but taken out of their shells and served en masse in a large dish. Our friends were astonished that we did not like these famous oysters of theirs in any form, which we did not, they being very huge in size and strong in flavour. We said, too, we did not like making two bites of an oyster; they pitied our want of taste, and lamented over our miserably small ones in England. After tea we saw some sea-weed and autumnal leaves beautifully dried and[Pg 204] preserved by Mrs. Flagg, and we also looked over an illustrated poem on the subject of Mr. and Mrs. Longworth's golden wedding, the poem being the composition of Mr. Flagg. Towards ten o'clock a table was laid out in the drawing-room with their Catawba champagne, which was handed round in tumblers, followed by piles of Vanilla ice a foot and a half high. There were two of these towers of Babel on the table, and each person was given a supply that would have served for half a dozen in England; the cream however is so light in this country that a great deal more can be taken of it than in England; ices are extremely good and cheap all over America; even in very small towns they are to be had as good as in the large ones. Water ices or fruit ices are rare; they are almost always of Vanilla cream. In summer a stewed peach is sometimes added.
We left the Longworths that evening in a down pour of rain, so that papa only got out for a minute at the door of Miss Raschig's uncle, and asked him to breakfast with us next morning. He accordingly came; we found him a most quick, lively, and excellent man, full of intelligence, and he received us with the warmth and ardour of an old friend, having during the twenty-five years he has been[Pg 205] in America scarcely ever seen any one who knew any of his relatives. He is a Lutheran minister, and has a large congregation of Germans. He said a good deal had been going on during the revivals at Cincinnati, and he thought the feeling shown was of a satisfactory kind; there had been preaching in tents opposite his church.
The part of the town where he resides beyond the Miami Canal, which divides it into two portions, is known by the name of "Over the Rhine," and is inhabited almost entirely by Germans, of whom there are no less than 60,000 in the town. Mr. Raschig's own family consists of nine sons and one daughter, the youngest child being a fortnight old. We went to see them before we left the place, and found the mother as excellent and agreeable as himself, with her fine little baby in her arms. She said that boys were much easier disposed of than girls in this country, and their three eldest sons are already getting their livelihood, the eldest of all being married. We saw the third son, a very intelligent youth, who is a teacher in one of the schools in the town, and the daughter, a pleasing girl of fourteen, sung to us. She promises to have a good voice, though it will never equal her cousin's.
On the evening of the 28th we went by invitation[Pg 206] to Mr. and Mrs. King's. He is a lawyer, and they are connected by marriage with the Neils of Columbus and with the Longworths. The Andersons were there, and we again had a liberal supply of ices. The following evening, the 29th, we went to the Andersons, where there was a large party consisting of the Directors of the Ohio and Mississippi Railway, with whom, by the bye, I had dined that day at the hotel, there being ten gentlemen and myself, the only lady, at table. The party at the Andersons was also an assemblage of some of the beau monde of Cincinnati. The ladies were all dressed in high silk dresses remarkably well made, and looking as if they all had come straight from Paris. I never saw a large party of prettier or better chosen toilettes. The dresses were generally of rich brocaded silk, but there was nothing to criticise, and all were in perfect taste. We assembled in a long drawing-room carpeted, and sufficiently supplied with chairs, but there being neither tables nor curtains, the room had rather a bare appearance, though it was well lighted and looked brilliant. Towards ten o'clock we were handed into the dining-room, where there was a standing supper of oysters,—the "institution" of oysters as they justly call it,—hot quails, ham, ices, and most[Pg 207] copious supplies of their beloved Catawba champagne, which we do not love, for it tastes, to our uninitiated palates, little better than cider. It was served in a large red punch-bowl of Bohemian glass in the form of Catawba cobbler, which I thought improved it; but between the wine and the quails, which, from over hospitable kindness, were forced on poor papa, he awoke the next morning with a bad headache, and did not get rid of it all day.
The weather during our stay at Cincinnati was so wet that, with the exception of a drive which Mr. Anderson took us to some little distance on the heights above, and a long visit which we paid to the school under Mr. King's auspices, we had little out-door work to occupy us. I once, however, and papa twice, crossed the Ohio in a steamboat, and took a walk in the opposite slave state of Kentucky. The view thence of the town and its fleet of steamboats is very striking. The opposite hills, with the observatory perched on the highest summit, were very fine.
Mr. Anderson one day took us a long drive to the top of these hills; the whole country, especially near a village called Clifton, about six miles from the town, is studded with villas. We drove through[Pg 208] the grounds of two which overlooked splendid views of the neighbouring country; each of them being situated at the end of a sort of natural terrace projecting into the valley, and thus commanding a panoramic view all round.
The grounds attached to these villas are of considerable extent, but nothing has surprised us more than the poverty of the gardens in America. It may, however, be accounted for by the difficulty and expense of obtaining labour in this country, and by the consequent facility with which men who show any talent, and are really industrious, can advance themselves. A scientific gardener, therefore, if any such there be, would not long remain in that capacity. One of the houses had a really fine-looking conservatory attached to it, but, like others we have seen in the course of our travels, it was almost entirely given up to rockery and ferns. This is a degree better than when the owners indulge in statuary. We were made by the driver on another occasion to stop at a garden ornamented in this way, but certainly Hiram Power's talents had not been called into request, and the statues were of the most common-place order.
It is not only in their gardens, however, but in the general ornamental cultivation of their grounds,[Pg 209] that the Americans are deficient, for even at Newport, where we greatly admired, as I think I mentioned, the greenness of the grass, it was coarse in quality, and bore no sort of resemblance to a well-trimmed English lawn. Nor have we ever seen any fruit, with the exception of their apples, to compare to ours in England. These are certainly very fine. I hardly know the weight of an English apple, but at Columbus we got some which were brought from the borders of Lake Erie which are called the twenty-ounce apple. The one we ate weighed about sixteen ounces, and measured thirteen inches round. They are said to weigh sometimes as much as twenty-seven ounces. It is what they call a "fall," meaning an autumnal, apple.[11]
Next to their apples their pears deserve notice; but, though better than ours, they are not superior to those produced in France. The quantity of fruit, however, is certainly great, for the peaches are standard and grown in orchards; but they are quite uncultivated, and the greater part that we met with were hardly fit to eat. They are, notwithstand[Pg 210]ing, very proud of their fruit, especially of these said peaches and of their grapes, which, to our minds, were just as objectionable productions. There is one kind called the Isabella, which we thought most disagreeable to eat, for the moment the skin is broken by the teeth and the grape squeezed the whole inner part pops out in a solid mass into the mouth. We are past the season of wild flowers; but these must make the country very beautiful in the early spring, to judge from the profusion of rhododendron and other shrubs, which were most luxuriant, especially where we crossed the Alleghanies and along the banks of the Connecticut. To return, however, to our drive.
After visiting these villas we passed a great number of charitable institutions for the relief of the poor, who are remarkably well looked after in this country. One of these institutions was the Reformatory, a large building, where young boys are sent at whatever age they may prove delinquents, and are kept and well educated till they are twenty-one. But the grand mode in which the state provides against crime of all kinds is the system of education for all classes.
I have said we went under Mr. King's guidance to see the common schools of Cincinnati. These are[Pg 211] divided into three classes, called the district schools, the intermediate schools, and the high schools; we went through each grade, and were much pleased with the proficiency of the pupils. The examinations they went through in mental arithmetic were very remarkable, and the questions put to the boys of the intermediate class, who were generally from eleven to thirteen years old, were answered in a very creditable manner.
In the high school, the teaching is carried on till the pupils reach the age of sixteen or seventeen, and even eighteen, after which they either leave school altogether or go to college. They are generally the children of artisans or mechanics, but boys of all ranks are admitted, and are moved on from one grade to another. The schools are entirely free, and girls are admitted as well as boys, and in about equal numbers. The girls and boys are taught, for the most part, in separate rooms, but repeat their lessons and are examined together, so that there is a constant passing in and out from one class-room to another, but still great order is preserved. This assembling together, however, of large numbers of boys and girls, for so considerable a portion of the day, did not strike us as so desirable as it is there said to be. The advocates of the system say it[Pg 212] refines the rough manners of the boys; but it is more than questionable if the characters of the girls are improved by it, and if the practice, in its general results, can be beneficial.
The subjects taught to both boys and girls are invariably the same; and it was curious to hear girls translating Cicero into excellent English, and parsing most complicated sentences, just like the boys, and very often in better style, for they often answered when the boys could not. They seemed chiefly girls from sixteen to eighteen. They answered, also, most difficult questions in logic, and they learn a good deal of astronomy, chemistry, &c., and have beautiful laboratories and instruments. Music is also taught in a very scientific way, so as to afford a knowledge of the transpositions of the keys, but in spite of this, their music and singing are very American. German and French are also taught in the schools when required.
The teachers, both men and women, have very good salaries; the youngest women beginning with 60l. and rising to 120l. a year, while the men's salaries rise up to 260l. a year, and that in the intermediate or second class schools. This style of education may appear too advanced for girls in their rank of life, but in this country, where they[Pg 213] get dispersed, and may attain a good position in a distant district, the tone thus given by education to the people, is of great importance. The educating of the females in this way must give them great powers, and open to them a field of great usefulness in becoming teachers themselves hereafter. The education given is altogether secular, and they profess to try and govern "by appeals to the nobler principles of their nature," as we gather from a report which was put into our hands at leaving.
This is but a weak basis for a sound education, and I cannot but think its insufficiency is even here practically, and perhaps unconsciously, acknowledged; for, though no direct religious instruction is professedly given, a religious tone is nevertheless attempted to be conveyed in the lessons. At the opening of the school, a portion of the Bible is read daily in each class; and the pupils are allowed to read such versions of the Scriptures as their parents may prefer, but no marginal readings are allowed, nor may any comments be made by the teachers.[12]
[Pg 214]We left Cincinnati this morning in the car appropriated to the use of the Directors of the Ohio and Mississippi Railway, on which line we are travelling. It is neatly fitted up with little "state" rooms, with sofas all round. There were four of these, besides a general saloon in the middle; but the whole was greatly inferior to the elegance of Mr. Tyson's car on the Baltimore and Ohio Railway. Our party consisted of about thirty persons, of whom four were judges, and about a third of the number were ladies, accompanying their liege lords, and chiefly asked in honour of me, to prevent my being "an unprotected female" among such a host of gentlemen. An ordinary car was attached to that of the Directors, for the use of any smokers of the party. We left Cincinnati at half-past eight, and reached this place, Vincennes, where we are to sleep, at about six o'clock. The road was very pretty, though the leaves were nearly all off the trees; the forms[Pg 215] of the trees were, however, lovely, and it was quite a new description of country to us, the clearings being recent and still very rough in appearance, and the log-houses, in most places, of a most primitive kind. Vincennes, where we are to sleep, is an old town of French origin, prettily situated on the river Wabash, which we can see from our windows.
St. Louis, November 4th.—We came on here on the 2nd instant, and soon after leaving Vincennes found ourselves in a prairie, but it was not till after sixty miles that we got to the Grand Prairie, which we traversed for about sixty more. The vastness, however, of this prairie, consists in its length from north to south, in which it stretches through nearly the whole length of the State. These prairies are enormous plains of country, covered, at this time, by a long brown grass, in which are the seed-vessels and remains of innumerable flowers, which are said to be most lovely in their form and colour in the spring. It was disappointing only to see the dark remains of what must have been such a rich parterre of flowers. One of our party, Colonel Reilly, of Texas, who had seen our Crystal Palace gardens at Sydenham, in full flower, said that they reminded him of the prairies in the spring. The ground is so level, that the woods on the hori[Pg 216]zon had the effect that the first sight of the dark line of land has at sea. In many places near the road on each side, small farms were established, and good-sized fields of Indian corn were growing; and wherever there was a railway station, a town, or even a "city" with one or two churches, and an hotel, besides grocery stores and wooden buildings of various kinds, were in progress in this immense wilderness.
The rain poured down incessantly, giving the country a melancholy and forlorn appearance. Towards the latter part of our journey, we descended into and traversed the great valley of the Mississippi. We passed several coal-mines, and here, where the vein of coal is eight feet thick, the land, including the coal, may be bought for one pound an acre. The country soon assumed the appearance of a great swamp, and is most unhealthy, being full of fever and ague.
At length our train stopped, and we were ushered into omnibuses of enormous length, drawn by four horses, and two of these caterpillar-like looking vehicles were driven on to the steam-ferry, and in this unromantic way we steamed across the great Father of Waters, and a most unpoetic and unromantic river it appeared to be. There is nothing[Pg 217] in its width here to strike the eye or the imagination, though its depth is very great, and it has risen ten feet within the last week. But it appeared to us ugly and inconsiderable after the wide, rapid, clear, and magnificent St. Lawrence. We were driven through a sea of mud and mire to this large and comfortable hotel, and were shortly afterwards seated at table with the rest of our party.
I forgot to mention that, at Vincennes, seven sportsmen had been out all day, before we arrived, to procure game for us, and were much disappointed at not being able to get us any prairie hens, which are a humble imitation of grouse, though Americans are pleased to consider them better than that best of birds; but "comparisons are odious," and the prairie-hens are very praiseworthy and good in their way. We had, however, abundance of venison and quails, and the same fare met us here, with large libations of champagne. The owner of our hotel at Cincinnati travelled with us, and looked as much like a gentleman as the rest of the party; and we have been joined here in our private drawing-room by the landlord and landlady of this hotel. Not knowing at first who they were, papa turned round to the former, and asked him if he knew St. Louis, and had been long here, to which our friend replied,[Pg 218] "Yes, sir; I have lived here eighteen years, and am the master of this hotel." Yesterday our dinner was even better than on the day of our arrival, closing with four or five omelettes soufflées, worthy of Paris, and the same number of pyramids of Vanilla ice. So much for the progress of civilisation across the Mississippi.
We paddled about in the muddy streets yesterday, and looked in at the shop-windows. We found even here plenty of hoop petticoats, and of tempting-looking bookseller's shops. Our hotel is close to the Court-house, a handsome building of limestone, with a portico and a cupola in process of building, being a humble imitation of the one at Washington. Yesterday evening, one or two of the gentlemen amused us after dinner with some nigger songs, ending, I suppose out of compliment to us, with "God save the Queen." I studied the toilette of one of our party this morning—the only young unmarried lady among us. I had often seen the same sort of dress at the hotels, but never such a good specimen as this. It is called here the French morning robe or wrapper, and this one was made of crimson merino, with a wide shawl bordering half-way up the depth of the skirt. The skirt is quite open in front, displaying a white petticoat with an embroidered bor[Pg 219]dering. The body of the wrapper was formed in the old-fashioned way, with a neck-piece, with trimmings of narrow shawl borderings; there was no collar at all, the crimson merino coming against the neck without any break of even a frill of white. The sleeves were very large, of the latest fashion, with white under sleeves, and the waist was very short, confined with a red band of merino. These dresses are very common in the morning, and are, I believe, thought to be very elegant. They are frequently made like this, of some violent coloured merino, and often of silk, with trimmings of another coloured ribbon.
Having digressed so far from my account of St. Louis, I will go back for a few minutes to Cincinnati, to describe the grand fire-engines we saw there, with horses all ready harnessed. One particular engine, in which the water was forced up by steam, could have its steam up and be ready for action in three minutes from its time of starting, and long, therefore, in all probability before it reached the place where its services were required. These engines all had stags' horns placed in a prominent position in front, as a sign of swiftness, and on this particular one there was printed under the horns, "Sure Thing, 287 feet," meaning that it could throw[Pg 220] the water that height. Another had on it, "243 feet. Beat that!" the Americans being very laconic in all their public communications. The regular plan on which most of the American towns are built and the division into wards, give great facilities for showing where a fire takes place; balls are shown from the top of a high tower to direct the engines where to go, the number of balls pointing out the ward where the fire exists.
Another grand invention, which we found here as well as everywhere else, is their sewing machine. These sewing machines wearied us very much when we landed at New York, for they seemed to be the one idea of the whole country; and I am afraid we formed some secret intentions to have nothing to do with them. I had seen them in a shop window in the City, in London, but knowing nothing of their merits, almost settled in my own mind they had none. At last I found how blind I had been, and what wonderful machines they are. There are numbers of them of various degrees of excellence. They are so rapid in their work, that if a dress without flounces is tacked together, it can be made easily by the machine in a morning: a lady here showed me how the machine is used; she told me it is so fascinating that she should like[Pg 221] to sit at it all day. She works for her family, consisting of a husband and nine sons, and takes the greatest pleasure in making all their under clothing; and working as she does, not very constantly, she can easily do as much as six sempstresses, while the machine, constantly worked, could do as much as twelve. The work is most true and beautiful and rapid, and the machine must be an invaluable aid where there is a large family. It is much used also by tailors and shoemakers, for it can be used with all qualities of materials, whether fine or thick. The price of one is from 15l. to 25l. It requires a little practice to work at it, but most American ladies who have large families possess one, and dressmakers use them a great deal.
November 4th.—To return to this town of mud and mire, we have been nearly up to our knees in both to-day, and went on board one of the large steamers, but found it was not nearly so grandly fitted up as the one in which we went from New York to Newport. There is an enormous fleet of steamers here, but the Mississippi still looked most dingy, muddy, and melancholy. We were given tickets this evening, to hear a recitation by a poet named Saxe, of a poem of his own, on the Press, and we soon found ourselves in an enormous hall[Pg 222] about 100 feet by 80, nearly filled by a very intelligent-looking audience. A man near us told us that Mr. Saxe had a European reputation, which made us feel much ashamed of our ignorance, in never having heard of him before, and, unhappily, we came away no wiser than we went as regards the merits of his poetry; for though our seats were near him, there was something either in the form of the hall, or in the nature of his voice and pronunciation, which made us unable to hear what he said. There were bursts of laughter and applause at times from the audience, but we took the first opportunity of leaving.
As we walked home, we passed a brilliantly-lighted confectioner's shop, where we each had an ice, but they were too sweet, and after eating and criticising them, we came to another confectioner's, when papa insisted upon going in, and ordered two more ices, which were very good. We were presented here with filtered water, the usual drinking water in this town being something of the colour of dingy lemonade, though its taste is good.
We purpose going to-morrow.... I turn to ask papa where—and he shakes his head, and says he does not know. On my pressing for a more distinct answer, he says, "Up the Missouri at all events."[Pg 223] This sounds vague, but I believe before night we shall be on our way to Chicago, and shall thus have taken leave of the "far west." And now I must take my leave of you for the present, though I fear this is but a dull chapter of the journal.
[11] As an instance of the ingenious devices used to save labour in this country, we may mention a machine for paring apples, which we bought in the streets at Boston for twenty cents, or about 10d. English. By turning a handle it can perform, simultaneously, the operations of peeling the apple, cutting out the core, and slicing it.
[12] For fear that we may have misinterpreted what is said above, we think it advisable, as the matter is a most important one, and one that may interest others, to extract from the report the passage on which these observations were founded; for it is not a clear specimen of American composition, and might, therefore, easily become a subject of misrepresentation:—
"The Opening Exercises in every Department shall commence by the reading of a portion of the Bible, by or under the direction of the teacher, and appropriate singing by the pupils.
"The pupils of the Common Schools may read such version of the Sacred Scriptures as their parents or guardians may prefer, provided that such preference of any version except the one now in use be communicated by the parents or guardians to the Principal Teachers, and that no notes or marginal readings be read in the school, or comments made by the Teachers on the text of any version that is or may be introduced."
ST. LOUIS.— JEFFERSON CITY.— RETURN TO ST. LOUIS.— ALTON.— SPRINGFIELD.— FIRES ON THE PRAIRIES.— CHICAGO.— GRANARIES.— PACKING HOUSES.— LAKE MICHIGAN.— ARRIVAL AT INDIANAPOLIS.
Jefferson City, on the Missouri,
Nov. 6th, 1858.
Here we are really in the Far West, more than 150 miles from the junction of the Missouri with the Mississippi, though still 2950 from the source of this great-grandfather of waters—for I can give it a no less venerable name. We first caught sight of it, or struck the river, as the phrase is here, about 98 miles below this city, and for a long time we followed its banks so closely, that we could at any point have thrown a stone from the car into the river. At Hermann, a little German settlement on its banks, we stopped and had an excellent dinner, but it was so late before we left St. Louis, that we passed the greater part of what seemed very pretty scenery in the dark, so that I shall defer any further[Pg 225] description of it till we return over the ground on Monday.
We were most unfortunate in our weather during our stay at St. Louis, and I had no opportunity of seeing the beauties of the neighbourhood, which we hear much extolled, but respecting which we are rather sceptical. The only drive we took, was to a new park being made outside the town, called Lafayette Park, which gave us anything but a pleasant impression of the entourage of St. Louis; we must admit, however, that a very short distance by railway brought us into a very pretty country, and no doubt the dismal weather and bad roads made our drive very different to what it might have been on a fine day. Still, with the impression fresh in our memory of our drive in the neighbourhood of Cincinnati in much the same sort of weather, we are compelled to think that the country about the Queen of the West and the banks of the Ohio greatly surpasses in beauty St. Louis and the muddy river which has so great a reputation in the world.
Springfield, Illinois, November 9th.—Although our damp disagreeable weather has not left us, we have contrived to see a good deal of Jefferson City. We made a dash a short way up the Missouri in a steamboat, and landed and took a walk on the[Pg 226] northern side of the river, and as we exchanged a mud for a sandy soil, it was less disagreeable than on the south side. The northern shore, which from the opposite side seemed hilly and well wooded, is very pretty, but on landing the hills had receded to a distance, and we found a considerable plain between them and the river. Up to the water's edge, however, the country is well wooded. On the spot where we landed we saw a large tree, at least ten feet in diameter, burnt almost to its centre, and its fine head destroyed by fire; and on asking some bystanders if any one had intended to burn it down, they said, "Oh, no, some one has merely made a fire there to warm himself;" a strong proof of the little value put here on fine timber.
The view of Jefferson City from the opposite bank, looking down the river, is very striking. Being the capital of the state of Missouri, there was the usual Capitol or state-house, and, unlike most others that we have seen, the building with its large dome was completed. It is a fine edifice of white stone, standing at a great height above the river, on what is here called a bluff, namely, a rock rising perpendicularly from the water's edge. The principal part of the town is built along the heights, but the ground slopes in places, and the houses are then[Pg 227] carried down to the river side. The railway runs under the cliff, and can be seen winding along up and down the river, for some distance each way; it has not yet been carried much further, as this is the last large town to which railways in the west reach; but, as its name, the Pacific Railway, implies, it is intended ultimately to be carried "right away" west till it joins the ocean. We went on Sunday to the Episcopal church. There was the Communion service, and a very good sermon on the subject of that ordinance.
We yesterday returned to St. Louis, and after a brief halt came on here. As our journey back to St. Louis was in the daytime, we had an opportunity of seeing the very interesting country which we passed on Saturday in the dark. The most remarkable feature of the road was crossing the Osage within 200 or 300 yards of its confluence with the Missouri. It is about 1,200 feet broad, and we saw in it one of those beautiful steamboats which give so much character here to the rivers. The Osage is navigable for these large boats for 200 miles above this place. We passed various other rivers, among others the Gasconade, at a spot memorable for a terrible catastrophe which happened on the day of the opening of the railway,[Pg 228] when the first bridge which crossed it gave way as the train was passing, and nine out of thirteen cars were precipitated into the bed of the river; thirty people, chiefly leading characters of St. Louis, were killed, and many hundreds desperately hurt.
We have little more to say of St. Louis, as the museum was the only public building we visited. The great curiosity there is the largest known specimen of the mastodon. It is almost entire from the tip of its nose to the tip of its tail, and measures ninety-six feet in length. We left St. Louis, and were glad to escape for a time at least out of a slave state. The "institution" was brought more prominently before us there than it has yet been, as St. Louis is the first town where we have seen it proclaimed in gold letters on a large board in the street, "Negroes bought and sold here." In the papers, also, yesterday, we saw an advertisement of a "fine young man" to be sold, to pay a debt.
We took our departure in the Alton steamboat, in order to see the first twenty-four miles of the Upper Mississippi, and the junction of that river and the Missouri, which takes place about six miles below Alton; both rivers, however, are very tame and monotonous, and it was only as we were reaching[Pg 229] Alton, that the banks of the Mississippi assumed anything like height. Alton itself stands very high, and as it was getting dark when we arrived, the lights along the hills had a fine effect. We are told it is a pretty town, but it was dark when we landed, and we had to hurry into the train that brought us to this place. The steamboat in which we went up the river was a very fine one, but not at all fitted up in the sumptuous manner of our Newport boat. Papa paced the cabin, and made it 276 feet long, beyond which there was an outside smoking cabin, and then the forecastle.
Springfield is in the midst of the Grand Prairie, and, as we are not to leave it till the afternoon, we have been exploring the town, and, as far as we could, the prairie which comes close up to it; but the moment the plank pavement ceased, it was hopeless to get further, owing to the dreadfully muddy state of the road. This mud must be a great drawback to residing in a prairie town, as the streets are rendered impassable for pedestrians, unless at the plank crossings. On our way back to the hotel, we accosted a man standing at his door, whose strong Scotch accent, in reply to a question, told us at once where he came from. He asked us into his house, and gave us a good deal[Pg 230] of information about the state of the country. He was originally a blacksmith at Inverary, and had after that pursued his calling in a very humble way in Fife and in Edinburgh, and came out here penniless twenty-six years ago, when there were only a few huts in the place; but he has turned his trade to better account here, for he lives in a comfortable house, and has $50,000, or 10,000l. invested in the country. He seemed very pleased to see us, and talked of the Duke of Argyle's family, as well as of the Durhams, Bethunes, Anstruthers, &c. Having lived when in Fife, at Largo, he seemed quite familiar with the Durhams, with the General's little wife, and with Sir Philip's adventures, from the time of the loss of the Royal George downwards.
This is the capital of Illinois, and the state-house here, too, is finished, and is a fine building. The governor has a state residence, which is really a large and handsome building, but is altogether surpassed by the private residence of an ex-governor, who lives in a sumptuous house, to judge from its external accompaniments of conservatory, &c.; it is nearly opposite our Scotch friend's abode, but the ex-governor dealt in "lumber" instead of iron, and from being a chopper of wood, has raised himself to his present position.[Pg 231]
Chicago, Nov. 10th.—We did not reach Chicago last night till 12 o'clock, our train, for the first time since we have been in America, having failed to reach its destination at the proper time; but the delay of two hours on this occasion was fairly accounted for by the bad state of the rails, owing to the late rains. Before it became dark we saw one or two wonderful specimens of towns growing up in this wilderness of prairie. The houses, always of wood and painted white, are neat, clean, and well-built. There is, generally, a good-looking hotel, and invariably a church, and often several of these, for although one would probably contain all the inhabitants, yet they are usually of many denominations, and then each one has its own church. About twenty or thirty miles from Chicago, we saw a very extensive tract of prairie on fire, which quite illuminated the sky, and, as the night was very dark, showed distinctly the distant trees and houses, clearly defining their outline against the horizon. On the other side of us, there was a smaller fire, but so close as to allow us to see the flames travelling along the surface of the ground. These fires are very common; we saw no less than five that night in the course of our journey.
We have been busily employed to-day in going[Pg 232] over Chicago. The streets are wide and fine, but partake too abundantly of prairie mud to make walking agreeable: some of the shops are very large; a bookseller's shop, to which papa and I made our way, professes to be the largest in the world, and it is certainly one of the best supplied I ever saw with all kinds of children's books. From the bookseller's we went to papa's bankers, Messrs. Swift and Co.; Mr. Swift took us to the top of the Court-house, a wonderful achievement for me, but well worth the trouble, as the view of the town was very surprising. We went afterwards to call on William's friend, Mr. Wilkins, the consul, where we met Lord Radstock. Mr. Wilkins kindly took us to see Mr. Sturge's great granary; there are several of these in the town, but this, and a neighbouring one, capable of holding between them four or five million bushels of corn, are the two largest. The grain is brought into the warehouse, without leaving the railway, the rails running into the building. It is then carried to the top of the warehouse "in bulk," by means of hollow cylinders arranged on an endless chain. The warehouse is built by the side of the river, so that the vessels which are to carry the corn to England or elsewhere, come close under the walls,[Pg 233] and the grain is discharged into the vessels by means of large wooden pipes or troughs, through which it is shot at once into the hold. Mr. Wilkins has seen 80,000 bushels discharged in this manner, in one day.
We afterwards drove about six miles into the country, through oceans of mud, to see one of the great slaughter and packing-houses. I did not venture out of the carriage, but the proprietor took Mr. Wilkins, Lord Radstock, and papa through every part of the building. In a yard below were a prodigious number of immense oxen, and the first process was to see one of these brought into the inside of the building by means of a windlass; which drew it along by a rope attached to its horns and passing through a ring on the floor.
The beast, by means of men belabouring it from behind, and this rope dragging it in front, was brought in and its head drawn down towards the ring, when a man with a sledge-hammer felled it instantaneously to the ground; and without a struggle it was turned over on its back by the side of eight or ten of its predecessors who had just shared the same fate, and were already undergoing the various processes to which they had afterwards to be subjected. The first of these was to rip up and remove the intestines of[Pg 234] the poor beast, and it was then skinned and cut lengthways into two parts, when the still reeking body was hung up to cool. The immense room was hung with some hundreds of carcases of these huge animals thus skinned and cleft in two. The process, from the time the animal leaves the yard alive till the time it is split and hung up in two pieces, occupied less than a quarter of an hour. At the end of two days they are dismembered, salted, packed in casks, the best parts to be shipped to England, and the inferior parts to be eaten by the free and enlightened citizens of this great continent. The greater number of these beasts come from Texas, and have splendid horns, sometimes three feet long.
The next thing they saw was the somewhat similar treatment of the poor pigs; but these are animals, of which for size there is nothing similar to be seen in England, excepting, perhaps, at the cattle show. At least, one which papa saw hanging up weighed 400 lbs., and looked like a young elephant. In the yard below there was a vast herd of these, 1500 having arrived by railway the night before; the number killed and cut up daily averages about 500. It takes a very few minutes only from the time the pig leaves the pen to its being hung up, preparatory to its being cut up and salted. They[Pg 235] first get a knock on the head like the more noble beasts already mentioned; they are then stuck, in order to be thoroughly bled; after this they are plunged headlong into a long trough of boiling water, in which they lie side by side in a quiescent state, very different to the one they were in a few minutes before, when they were quarrelling in a most unmannerly manner in the yard below. From this trough the one first put in is, by a most ingenious machine, taken up from underneath, and tossed over into an empty trough, where in less than a minute he is entirely denuded of his bristles, and passed over to be cleft and hung up. The trough holds about eight or ten thus lying side by side, and the moment one is taken out at one end, another is put in at the other, and they thus all float through the length of the trough, and are taken out in order; but so rapid is the process, that no one pig is long in; in fact, the whole business occupies only a very few minutes per pig. Every part is turned to account, the mass of bristles being converted into tooth brushes, &c. In the huge larder, in the story next above the oxen, there were about 1500 unhappy pigs hung up to cool, before being cut up, salted, packed, and sent off. There are several establishments of this nature in Chicago, but only[Pg 236] one of equal extent to the one papa saw. About 400,000 pigs are shipped every year from Chicago. I do not know the total number of cattle, but this house alone slaughters and sends away 10,000. There were places on an enormous scale for preparing tallow and lard, and there were many other details equally surprising, which I have not now time to describe; but papa says that the smells were most offensive, and that it was altogether a very horrible sight, and it was one I was well pleased to escape.
Among the other wonders of Chicago, I must do honour to its hotel, which I should say was as good as any we have yet seen in America. These American hotels are certainly marvellous "institutions," though we were getting beyond the limits of the good ones when we reached Jefferson City. That, however, at St. Louis is a very fair sample of a good one.
Indianapolis, Nov. 11th.—We arrived here late this afternoon, and have not been able as yet to see anything of the town, I shall therefore defer a description of it to my next. The road from Chicago was not without its interest, though we are becoming very tired of the prairies. At first starting we went for many miles along the borders of Lake Michigan, which we again came upon at a very[Pg 237] remarkable spot, Michigan city, about sixty miles from Chicago. Along the first part of the lake, in the neighbourhood of Chicago, the shore consists of fine sand, in strips of considerable width, and flat like an ordinary sea beach; but at Michigan city the deep sand reached to a considerable distance inland, and then rose into high dunes, precisely like those on the French coast. As we had to wait an hour there, papa and I scrambled up one of these, and although below there was deep loose sand, yet above it was hard and solid, and bound together with little shrubs like the French dunes. The view of the lake from the top was very pretty, and boundless towards the north, we being at the southern extremity. I picked up a few stones on the beach as a memorial of this splendid lake. We were very much tempted, when at Chicago, to see more of it, and to go to Milwaukee and Madison, but we were strongly advised by Mr. Wilkins not to go further north at this season. The wreaths of snow which during the night have fallen in patches along the road, and greeted our eyes this morning, confirmed us in the wisdom of this advice, and we are now bending our steps once more towards the south. We are still here in the midst of prairie, but more wooded than in our journey of Tuesday. We[Pg 238] crossed to-day, at Lafayette, the Wabash, which we had crossed previously at Vincennes, and here, as there, it is a very noble river. This must end my journal for the present.
INDIANAPOLIS.— LOUISVILLE.— LOUISVILLE AND PORTLAND CANAL.— PORTLAND.— THE PACIFIC STEAMER.— JOURNEY TO LEXINGTON.— ASHLAND.— SLAVE PENS AT LEXINGTON.— RETURN TO CINCINNATI.— PENNSYLVANIA CENTRAL RAILWAY.— RETURN TO NEW YORK.
Lexington, Kentucky, Nov. 13th, 1858.
My last letter was closed at Indianapolis, but despatched from Louisville. On the morning after I wrote we had time, before starting for Louisville, to take a walk through the principal streets of Indianapolis. The Capitol or state-house is the only remarkable building; and here, as in most other towns in America, we were struck by the breadth of the streets. In the centre of Indianapolis there is a large square, from which the four principal streets diverge, and from the centre of this, down these streets, there are views of the distant country which on all sides bounds the prospect. This has a fine effect, but all these capital cities of states have an unfinished appearance: great cities have been planned, but the plans have never been adequately[Pg 240] carried out. The fact is, they have all a political, and not a commercial origin, and they want the stimulus of commercial enterprise to render them flourishing towns, or to give them the finished appearance of cities of much more recent date, such as Chicago and others.
We left Indianapolis at about half-past ten, and reached Jeffersonville, on the north side of the Ohio at four. The country at first was entirely prairie, but became a good deal wooded as we journeyed south. It is much more peopled than the wide tracts which we have been lately traversing, for neat towns with white wooden houses and white wooden churches here succeeded each other at very short distances; we crossed several large rivers, tributaries of the Wabash; one, the White river, was of considerable size, and the banks were very prettily wooded. At Jeffersonville we got into a grand omnibus with four splendid white horses, and drove rapidly down a steepish hill, straight on board the steamboat which was to carry us across the Ohio. The horses went as quietly as on dry land, and had to make a circuit on the deck, as we were immediately followed by another similar equipage, four in hand, for which ours had to make room. This was followed by two large baggage waggons and a[Pg 241] private vehicle; and all these carriages were on one side of the engine-room. At the other end there was space for as many more, had there been any need for it; and all this on a tiny little steamboat compared with the Leviathans that were lying in the river.
On reaching Louisville we were comfortably established in a large handsome hotel. As there was still daylight, we took a walk through the principal streets, and found ourselves, as usual, in a bookseller's shop; for not only are these favourite lounges of papa's, but we generally find the booksellers intelligent and civil people, from whom we can learn what is best worth seeing in the town. The one at Louisville lauded very much the pork packing establishments in this town, and said those at Chicago, and even those of Cincinnati, are not to be compared with them; but without better statistics we must leave this question undecided, for papa saw quite enough at Chicago to deter him from wishing to go through the same sight at Louisville; we, however, availed ourselves of the address he gave us of the largest slave-dealer, and went to-day to see a slave-pen.
We have lately been reading a most harrowing work, called the "Autobiography of a Female Slave," whose experience was entirely confined to[Pg 242] Kentucky—indeed, to Louisville and the adjoining country within a few miles of the Ohio. She describes Kentucky as offering the worst specimen of a slave's life, and gives a horrid account of the barbarity of the masters, and of the almost diabolical character of the slave-dealers, and of those who hold subordinate situations under them. We were hardly prepared, therefore, on reaching this pen to be received, in the absence of the master, by a good-looking coloured housekeeper, with a face as full of kindness and benevolence as one could wish to see, but "the pen" had yesterday been cleared out, with the exception of one woman with her six little children, the youngest only a year old, and two young brothers, neither of whom the dealer had sold, as he had been unable to find a purchaser who would take them without separating them, and he was determined not to sell them till he could. In the case both of the woman and of the two boys, their sale to the dealer had been caused by the bankruptcy of the owner. The woman had a husband, but having a different master, he retained his place, and his master promised that when his wife got a new home he would send him to join her.
No doubt this separation of families is a crying evil, and perhaps the greatest practical one, as respects[Pg 243] hardship, to which the system is necessarily subject; but certainly, from what we have seen and heard to-day, it does not seem to be harshly done, and pains are taken to avoid it: the woman said she had been always kindly treated, and there was not the slightest difficulty made by the dark duenna to our conversing with the slaves as freely as we liked, and she left us with the whole group. The woman took us to see her baby, and we found it in a large and well ventilated room, and she said they had always as much and as good food as they could wish. She said she was forty-five years old, and had ten children living, but the four eldest were grown up. The eldest of those she had with her was a little girl of about thirteen; she said, in answer to a question from papa, that the children had made a great piece of work at parting with their father, but the woman herself seemed quite cheerful and satisfied with her prospects.
On our journey here there were a great many slaves in the car with us, coming to pass their Sunday at Lexington. They seemed exceedingly merry, and one, whom papa sat next, said he had accumulated $950, and that when he got $1900, he would be able to purchase his freedom. He said his master was a rich man, having $300,000, and that[Pg 244] he was very well treated; but that some masters did behave very badly to their slaves, and often beat them whether they deserved it or not. From the specimen we had of those in the cars, they seemed well-conditioned men, and all paid the same fare that we did, and were treated with quite as much attention. They seem to get some sort of extra wages from their masters besides their food and raiment, out of which they can lay by if they are provident, so as to be able to purchase their freedom in time; but they do not seem always to care about this, as one man here has $4000, which would much more than suffice to buy his freedom; but he prefers remaining a slave. We shall probably see a good deal more of the condition of the slaves within the next few days, so I shall say no more upon the subject at present, excepting that all this does not alter the view which we cannot help taking of the vileness of the institution, though it certainly does not appear so very cruel in practice as it is often represented to be by the anti-slavery party.
There are only two great sights to be seen at Louisville. One, the famous artesian well, 2086 feet deep, bored to reach a horrid sulphur spring, which is, however, a very strong one as there are upwards of 200 grains of sulphates of soda and[Pg 245] magnesia in each gallon of water, and upwards of 700 grains of chlorides of sulphur and magnesia. There is a fountain over the well, in which the water rises 200 feet, but whether by external pressure or by the natural force of the water, the deponent sayeth not. It comes out in all sorts of forms, sometimes imitating flowers, and sometimes a shower of snow, on which the negro who showed it to us expatiated with great delight. When I said there were only two sights to see, I alluded to this well, and to the magnificent steam vessel, the "Pacific," which was lying at Portland, about three miles down the Ohio, below the Falls; but I forgot altogether the Falls themselves, and the splendid canal described in papa's book, through which vessels are obliged to pass to get round them, which I ought not to pass without some notice. The river here is upwards of a mile wide, but the falls are most insignificant; and though the Guide Book describes them as "picturesque in appearance," and that the islands give the Ohio here "the appearance of a great many broken rivers of foam, making their way over the falls, while the fine islands add greatly to the beauty of the scene;" neither papa with his spectacles, nor I with my keen optics, could see more than a ripple on the surface of the water.[Pg 246] These falls, however, are sufficient to prevent vessels of any great burden ascending or descending beyond this point of the river, and hence the necessity of the canal: but this splendid work, about which papa's interest was very great, in consequence of what he had written about it, proved as great a disappointment as the falls themselves. It must, however, have been a work of great difficulty, as it is cut through a solid bed of rock.[13] The locks are suffi[Pg 247]ciently capacious to allow of the passage of steamers 180 feet long by 40 feet in breadth, one of which we saw in the lock, and there were three others waiting to pass through.
These, to our eyes, seemed large and beautiful vessels; but they were altogether eclipsed and their beauty forgotten, when we found ourselves on board the "Pacific." This vessel was to sail in the evening, and is one of the most splendid steamers on the river; certainly nothing could exceed her comfort, infinitely beyond that of the Newport boat, as the saloon was one long room, unbroken by steam-engine or anything else, to obstruct the view from one end to the other. Brilliant fires were burning in two large open stoves, at equal distances from either end, and little tables were set all down the middle of the room, at which parties of six each could sit and dine comfortably. The vessel was upwards of 300 feet long, the cabin alone being about that length. On each side of the cabin were large, comfortable sleeping berths, and on the deck below, adjoining the servants' room, was a sweet little nursery, containing, besides the beds and usual[Pg 248] washing apparatus, four or five pretty little rocking-chairs, for the children. We were shown over the kitchen, and everything looked so complete and comfortable that we longed to go down in her to New Orleans, whither she is bound, and which she will reach in six days. Everything was exquisitely clean, the roof and sides of the cabin being of that beautiful white varnish paint which I have before described, which always looks so pure and lovely. There was not much ornament, but all was in good taste.
On leaving the "Pacific," we drove to the inn at Portland. The Kentuckians are a fine tall race of men; but, tall as they are in general, the landlord, Mr. Jim Porter, surpassed them all in height, standing 7 feet 9 inches without his shoes. This is the same individual of whom Dickens gave an amusing account in his American notes fifteen years ago.
We left Louisville at two o'clock, and came on to Lexington this afternoon. The country is much more like England than anything we have yet seen, being chiefly pasture land. The grass is that known here, and very celebrated as the "blue grass" of Kentucky; though why or wherefore it is so called we cannot discover. It is of prodigiously strong growth, sometimes attaining two feet in height; but it is[Pg 249] generally kept low, either by cropping or cutting, and is cut sometimes five times a year. The stock raised upon it is said to be very fine, and the animals are very large and fine looking; but either from the meat not being kept long enough, or from some cause which we cannot assign, the beef, when brought to table, is very inferior to the good roast beef of Old England.
The road from Louisville to this place is pretty throughout, and seemed quite lovely as we approached Frankfort, though it was getting too dark as we passed that town to appreciate its beauties thoroughly. For some miles before reaching it, the road passes through a hilly country, with beautiful rounded knolls at a very short distance. The town is situated on the Kentucky river, the most beautiful, perhaps, in America. In crossing the long bridge, we had a fine view down its steep banks, with the lights of the town close on its margin. The state Capitol which we passed, is close to the railway, and is a marble building, with a handsome portico. We were very sorry not to have stopped to pass to-morrow, Sunday, at this place, but we were anxious to reach Lexington, in order to get our letters. We have no great prospects here, as the hotel, excepting the one[Pg 250] at Jefferson City, is the worst we have found in America. We had hardly set foot in it, when General Leslie Combe called upon us, having been on the look-out for our arrival. He claimed cousin-ship, having married a Miss T——, but we must leave it to Uncle Harry to determine to which branch of the T—— family she can claim kindred.
November 15th.—The weather has been unpropitious, and instead of starting to explore the Upper Kentucky, which we had meant to do, we are returning this afternoon to Cincinnati. We have, however, been able to see all the sights here that are worth seeing, besides having been edified yesterday by a nigger sermon, remarkable, even among nigger sermons, for the wonderful stentorian powers of the preacher. The great object of interest here is Ashland, so called from the ash timber with which the place abounds. This was the residence of Henry Clay, the great American statesman. General Combe gave us a letter of introduction to Mr. James B. Clay, his eldest son, who is the present proprietor of the "location." The house is very prettily "fixed up," to use another American phrase; but we were disappointed with the 200 acres of park, which Lord Morpeth, who passed a week at Ashland, is said to extol as being like an English one. We saw[Pg 251] nothing, either of the "locust cypress, cedar, and other rare trees, with the rose, the jasmine, and the ivy, clambering about them," which the handbook beautifully describes. The fact is, the Americans, as I have before observed, have not the slightest idea of a garden; and on papa's venturing to insinuate this to Mr. Clay, he admitted it, and ascribed it to its undoubted cause, the expense of labour in this country.
From Ashland we went to what is really a Kentucky sight, the Fair Ground. On an eminence at about a mile from the town, surrounded by beautiful green pastures, there stands a large amphitheatre, capable of holding conveniently 12,000 spectators. In the centre is a large grass area, where the annual cattle show is held, and when filled it must be a remarkable sight. From this we went to the Cemetery, which, like all others in this country, is neatly laid out, and kept in very good order. The grave-stones and monuments are invariably of beautiful white marble, with the single exception of a very lofty monument which is being raised to the memory of Mr. Clay. It is not yet finished, but to judge either from what has been accomplished, or from a drawing papa saw of it on a large scale, in a shop window, it is not likely to prove[Pg 252] pretty, and the yellowish stone of which it is being built, contrasts badly with the white marble about it.
We went next to see a very large pen, in which there were about forty negroes for sale; they had within the last few days, sold about 100, who had travelled by railway chained together. Those we saw, were divided into groups, and we went through a variety of rooms in which they were domiciled, and were allowed to converse freely with them all. This is one of the largest slave markets in the United States, and is the great place from which the South is supplied. There are, in this place, five of these pens where slaves are kept on sale, and, judging from this one, they are very clean and comfortable. But these pens give one a much more revolting idea of the institution than seeing the slaves in regular service. There was one family of a man and his wife and four little children, the price of "the lot" being $3500, or 700l. sterling, but neither the man nor the woman seemed to care much whether they were sold together or not. There was one poor girl of eighteen, with a little child of nine weeks old, who was sold, and she was to set off to-night with her baby, for a place in the State. The slave-dealer himself was a civil, well-spoken man, at least to us,[Pg 253] and spoke quite freely of his calling, but we thought he spoke harshly to the poor negroes, especially to the man with the wife and four children. It appears he had bought the man separately from the woman and children, in order to bring them together, but the man had attempted to run away, and told us in excuse he did not like leaving his clothes behind him; whereupon papa asked him if he cared more for his clothes than his wife, and gave him a lecture on his domestic duties. The dealer said they sometimes are much distressed when separated from their wives, or husband and children, but that it was an exception when this was so. One can hardly credit this, but so far as it is true it is one of the worst features of slavery that it can thus deaden all natural feelings of affection. We have spoken a good deal to the slaves here, and they seem anxious to obtain their freedom. The brother of one of the waiters at our hotel had twice been swindled by his master of the money he had saved to purchase his freedom. I spoke to the housemaid at our hotel, also a slave, who shuddered with horror when she described the miseries occasioned by the separation of relations. She had been sold several times, and was separated from her husband by being sold away from him. She said the poor negroes are generally taken out of[Pg 254] their beds in the middle of the night, when sold to the slave-dealers, as there is a sense of shame about transacting this trade in the day-time. From what the slaves told us, they are, no doubt, frequently treated with great severity by the masters, though not always, as they sometimes fall into the hands of kind people; but though they may have been many years in one family, they never know from hour to hour what may be their fate, as the usual cause for parting with slaves is, the master falling into difficulties, when he sells them to raise money, or to pay his debts. The waiter told us, he would rather starve as a freeman than remain a slave, and said this with much feeling and energy.
Cincinnati, Nov. 15th, 9 P.M.—We arrived here again this evening at about seven o'clock. The road, the whole way from Lexington, 100 miles, is very pretty, following the course of the Licking for a long way, with high steep banks on both sides, sometimes rising into high hills, but opening occasionally into wide valleys, with distant views of great beauty. In many places the trees here have still their red, or rather brown leaves, which formed a strange contrast with the thick snow covering their branches and the ground beneath. The snow storm last night, of which we had but the[Pg 255] tail at Lexington, was very heavy further north, and the snow on the ground lighted up by the moon, enabled us to see and enjoy the beauty of the scenery as we approached Covington, at which place we embarked on board the steamboat to cross the Ohio. I omitted, when we were here before, to mention that in our Sunday walk at Covington, when we first crossed over to Kentucky, we witnessed on the banks of the river a baptism by immersion, though the attending crowd was so large that we could not distinctly see what was going on. We are told, that on these occasions, the minister takes the candidate for baptism so far into the river, that they are frequently drowned. I forget if I mentioned before that Covington is built immediately opposite Cincinnati, at the junction of the Ohio and the Licking, which is here a considerable river, about 100 yards wide, and navigable for steamboats sixty miles further up. The streets of Covington are all laid out in a direct line with the corresponding streets in Cincinnati, and as the streets on both sides mount up the hills on which the towns are built, the effect is very pretty, especially at night, when the line of lamps, interrupted only by the river, appears of immense length. When the river is frozen over,[Pg 256] the streets of the two cities may be said to form but one, as carts and carriages can then pass uninterruptedly from the streets of Cincinnati, to those on the opposite side, and vice versâ. This snow storm, which has made us beat a rapid retreat from the cold and draughty hotels in Kentucky, makes us feel very glad to be back in this comfortable hotel.
Pittsburgh, Nov. 17th.—Lord Radstock made his appearance at Cincinnati yesterday, having come from Louisville in a steamer. The day was very bright and beautiful, though intensely cold; and as papa was very anxious to show Lord Radstock the view of Clifton from the heights above, we hired a carriage and went there. We were, however, somewhat disappointed, for the trees were entirely stripped of the beautiful foliage which clothed them when we saw them three weeks ago, and were laden with snow, with which the ground also was deeply covered; and although the effect was still pretty, this gave a harshness to the scene, the details being brought out too much in relief. The same cause detracted, no doubt, from the beauty of the scenery we passed through to day on our way here, and greatly spoilt the appearance of the hills which surround Pittsburgh.
But I must not anticipate a description of our[Pg 257] journey here, but first tell you of our further proceedings at Cincinnati. Lord Radstock is much interested in reformatories and houses of refuge, and we were glad to visit with him the one situated at about three miles from the town, the exterior only of which we had seen in our drive with Mr. Anderson. The building is very large and capacious, having cost 2700l. It is capable of holding 200 boys and 80 girls, and the complement of boys is generally filled up; but there are seldom above 60 girls. The whole establishment seems admirably conducted. The boys and girls are kept apart, and each one has a very nice, clean bed-room, arranged in prison fashion, and opening on to long galleries; but with nothing to give the idea of a cell, so perfectly light and airy is each room. There is an hospital for the boys and one for the girls, large and well ventilated rooms; that of the girls is beautifully cheerful, with six or eight nice clean beds; but it says a good deal for the attention paid to their health, that out of the whole number of boys and girls, there was only one boy on the sick list, and he did not appear to have much amiss with him. This is somewhat surprising, as the rooms in which they work are heated by warm water, to a temperature which we should have thought must be very[Pg 258] prejudicial to their health, but with this exception, they have every advantage. A large playground, a very large chapel, where they meet for prayers and reading the Bible, the boys below, and the girls in a gallery, and large airy schoolrooms. The children are admitted from the age of 7 up to 16, and the boys are usually kept till 21, and the girls till they are 18. The girls are taught needlework and household work, or rather are employed in this way, independently of two hours and a half daily instruction in the school, and the boys are brought up to a variety of trades, either as tailors, shoemakers, workers of various articles in wire, or the like. The proceeds of their work go in part to pay the expenses of the establishment, but the cost is, with this small exception, defrayed by the town, and amounts to about 20l. annually for each boy. These poor children are generally sent there by the magistrates on conviction of some crime or misdemeanour, but are often sent by parents when they have troublesome or refractory children, and the result is, in most cases, very satisfactory. They all seemed very happy, and the whole had much more the appearance of a large school, than of anything partaking of the character of a prison. Having called in the afternoon and taken leave of the Longworths, Ander[Pg 259]sons, and others, who had shown us so much kindness when we were last here, we started at half-past ten at night for this place.
As we were already acquainted with the first part of the road to Columbus, we thought we should not lose much by this plan, and we wished besides to try the sleeping cars, which has not proved altogether a successful experiment as far as papa is concerned, for he had very little sleep, and is very headachy to-day in consequence. Thrower, too, was quite knocked up by it; my powers of sleeping at all times and places prevented my suffering in the same way, and I found these sleeping cars very comfortable. They are ingeniously contrived to be like an ordinary car by day; but by means of cushions spread between the seats and a flat board let down half way from the ceiling, two tiers of very comfortable beds are made on each side of the car, with a passage between. The whole looks so like a cabin of a ship, that it is difficult not to imagine oneself on board a steamboat. Twenty-four beds, each large enough to hold two persons, can be made up in the cars, and the strange jumble of ladies and gentlemen all huddled together was rather ludicrous, and caused peals of laughter from some of the laughter-loving American damsels. The cots are[Pg 260] provided with pillows and warm quilted counter-panes and curtains, which are all neatly packed away under the seats in the daytime. The resemblance to the steamboat in papa's half-waking moments seemed too much for his brain to be quite clear on the subject of where he was. Thrower, who had shared my couch, got up sea sick at about four in the morning, the motion of the carriage not suiting her while in a recumbent position, and retired to a seat at one end of the carriage. As we neared Columbus, papa became very restless, and made a descent from over my head, declaring the heat was intolerable. "Where," said I, "is your cloth cap?" "Oh!" he answered, "I have thrown that away long ago; that's gone to the fishes." He said he had so tossed himself about, that he did not think he had a button left on his coat; things were not, however, quite so bad as this, and on finding my couch too cold for him, I at last succeeded in making your dear restless fidgetty papa mount up again to his own place, where, to my comfort, and no doubt to his own also, he soon fell asleep. I got up at five and sat by poor Thrower, and watched the lights of the rising sun on hills, valleys, and rivers for an hour; when in came the conductor, and thrusting his lamp into the face of the sleepers, and giving them a shake, told them[Pg 261] to get up, a quarter of an hour being allowed them for breakfast. In one second the whole place was alive; down came gentlemen without their boots, and ladies with their night caps, and in a few minutes all were busily employed in the inn, breakfasting. I had said we did not care about missing the first part of the road which we had seen before; but the joint light of a brilliant full moon and the snow on the hills, made us see the dear old Ohio and the bold Kentucky banks as clearly, almost, as if it had been daylight, till we retired to our beds; and, even then, I could not help lying awake to view the glorious scene out of my cabin window.
When we got up this morning we were entering a new country, and for many miles went along a beautiful valley of one of the tributaries of the Ohio. We again fell in with the Ohio at Steubenville, having traced the tributary down to its mouth. Our road then lay along the bank of the Ohio for about seventy miles, and anything more perfect in river scenery it would be difficult to imagine. Many large tributaries fell into it, the mouths of which we crossed over long bridges, and from these bridges had long vistas up their valleys. For about thirty miles we had the bold banks of Virginia opposite to us; but, after that, we quitted the state[Pg 262] of Ohio, and for forty miles the course of the river was through the state of Pennsylvania. A number of steamboats enlivened the scene, with their huge stern wheels making a great commotion in the water. The river too was studded with islands, and the continuous bend, the river taking one prolonged curve from Steubenville to Pittsburg, added greatly to the beauty of the scene. On approaching Pittsburg we crossed the Alleghany, which is a fine broad stream. The Monongahela, which here meets it, is a still finer one, and the two together, after their junction, constitute the noble river which then, for the first time, takes the name of the Ohio, or, as it is most appropriately called by the French, "La belle rivière"—for anything more beautiful than the seventy miles of it which we saw to-day it would be difficult to imagine.
We are lodged here at a very comfortable hotel, facing the Alleghany river. The town forms a triangle, situated between this river and the Monongahela, and after dinner, having arrived here early, we took a walk from the hotel, across the town, until we arrived at the latter river. The opposite bank here is of great height, and we crossed a bridge, 1500 feet long, with the magnanimous intention of going to the top of the hill to see the[Pg 263] magnificent prospect which the summit is said to afford. But our strength, and breath, and courage failed us before we had ascended a third of the height, although there is a good carriage road up and in good condition, from the hard frost which still prevails. The view, however, even at that height, was very fine, although it was greatly marred by the smoky atmosphere which hangs over the city. After recrossing the bridge we went to the point forming the apex of the triangle, to see the confluence of the two rivers, and, as we could from there look up both rivers and down the Ohio, the view is very remarkable. The town itself disappointed us; but, perhaps, we expected more than we ought reasonably to have done from a great and dirty manufacturing town.
Harrisburgh, Nov. 18th.—We started this morning by the six o'clock train in order to see the wonderful Pennsylvania railroad by daylight. It is the great rival of the Baltimore and Ohio railway, on which we travelled with Mr. Tyson, and we were rather anxious to have an opportunity of comparing the two, which, having now seen them both, we feel competent to do. The great change which nature presents now, to what it did when the leaves were in full foliage, may make us[Pg 264] underrate the beauties of the road we passed over to-day, but, notwithstanding this, we think there can be no doubt that the Baltimore and Ohio, taken as a whole, is by far the most picturesque and beautiful. The length of the two roads is very nearly the same; but, while the whole of the Baltimore and Ohio was beautiful, one side of the mountain being as much so as the other, the first part of the road to-day, till we reached the summit level, was very much of the same character as many other mountain regions we have passed. For many miles the road followed the course of the Conemaugh, crossing and recrossing the river, but without any very striking feature. But the moment we had passed through a tunnel, 3612 feet long, and began the descent of 2200 feet, on the eastern side of the Alleghany chain, the scene quite baffled description. The summit level of the Baltimore and Ohio is 500 feet higher; but the descent occupies a distance of seventeen miles, while the descent to-day was effected in eleven, so that, with all our partiality for the Baltimore and Ohio, it must be confessed there is nothing on it so wonderful and sublime as this. One curve was quite appalling, and it was rendered more so by the slow rate at which the train moved—not more, I should think, than at the rate of two miles an hour[Pg 265]—certainly not nearly so fast as we could have walked, so that we had full leisure to contemplate the chasm into which we should have been plunged headlong had the slightest slip of the wheels occurred. How they can ever venture to pass it at night is quite surprising. The curve is like a horse shoe, and goes round the face of a rock which has been cut away to make room for the road. Another superiority in the road we travelled to-day is the much greater height of the surrounding mountains, and the extent of the distant views;—but the greater height of the mountains had the attendant disadvantage of the trees being chiefly pines, instead of the lovely forest trees, of every description, which adorned the hills amongst which we travelled in Maryland and Virginia, by the Baltimore and Ohio railway.
I must, however, do justice here to the eastern side of the mountains. For more than 100 miles we closely followed the course of the Juniata, from its source to where it ends its career by falling, quite a magnificent river, into the Susquehanna, about twenty-two miles above this place. After the junction, the noble Susquehanna was our companion for that distance, this town being situated upon it. The source of the Juniata is seen very soon after[Pg 266] passing Altamont, and perhaps we were more disposed to do justice to the beauty of the river, from the happy frame of body and mind we were in, owing to the excellent dinner we had just partaken of at that place, consisting of roast beef, roast turkey, apple tart, cranberry preserve, and a most superlative Charlotte Russe—pretty good fare for an hotel in a mountain pass! No wine or stimulants of any kind were allowed, or what the consequence might have been on papa's restless state of mind it would be difficult to say; as it was, I counted that he rose from his seat to look at the view from the other side of the car, thirty times in the space of an hour and a half, making a move, therefore, upon an average, of once in every three minutes; and this he afterwards continued to do as often as the road crossed the river. I foolishly, at first, partook of his locomotive propensities, but my exhausted frame soon gave way, so that he declares I only saw one half of its beauties, namely, the half on the side where I was seated; but this half was ample to satisfy any reasonable mortal. I am at a loss to imagine what our fellow-travellers could have thought of him, as they lounged on their seats, and scarcely ever condescended to look out of window.
We arrived here, not the least tired with our long[Pg 267] journey, though it occupied twelve hours, and were so fresh afterwards, that we started after tea, this being the great annual Thanksgiving-day, to the nearest place of worship we could find, which turned out to be a Baptist "Church," as it is called here, where we heard a most admirable sermon, and felt we had reason to offer up our thanks with as much earnestness as any one of the congregation, for having been spared to make this journey to the Far West, and to have returned to civilised life, without encountering a single difficulty or drawback of any kind. I may as well state, that this Thanksgiving-day was established by the Puritans, and is still kept up throughout the whole of the United States, its object being to return thanks for the blessings of the year, and more especially for the harvest. There are services in all the churches, and we much regretted not finding out till late yesterday, that this was the day set apart for it, for had we known this, we should not have travelled to-day; but once on our journey, with the fear of snow accumulating in the mountains, we were afraid of stopping on the road, and we were very glad to be able to attend the service this evening. There is something very beautiful, I think, in thus setting apart one day in the[Pg 268] year for such a purpose, and it is interesting too, as being a relic left by the Puritans.
November 19th.—We are quite charmed with this place, which is a rare exception to all the other capitals we have seen, inasmuch as more has not been undertaken than has been carried out; in fact, it has much more the appearance of a village than of a large city. The beauty of the river surpasses all description. It is a mile wide, and bends gracefully towards the direction of the mountains through the gorge from which it issues forth in its course towards Chesapeake Bay, and here, where the hills recede to a distance, it expands into a great width, and its face is covered with islands. The only drawback to its being a grand river is its shallowness, and want of adaptation, therefore, to the purpose of navigation. There are no splendid steamboats to be seen here as on the Ohio, which make one feel that river, at the distance of more than 2000 miles from the sea, to be a noble highway of commerce, linking together with a common interest distant portions of this vast continent. In the Susquehanna, one feels that there is nothing but its beauty to admire, but this is perfect.
Two bridges connect the town with the opposite shore, each of them being about a mile long. The[Pg 269] weather is so piercingly cold, that we did not venture across, but we took a long walk up the banks, of the river. The town of Harrisburgh is very small, consisting of only three or four streets parallel to the river, intersected by about a dozen others at right angles to it. The centre one of these is a fine broad street, closed in at the further end by the Capitol. This is a handsome, but unpretending building of red brick, adorned by a portico, and, as usual, surmounted by a dome. On entering at the top of a flight of stairs, there is a circular area, covered in by the dome. Out of this, on one side, is a very neat Senate House, and on the opposite side is the House of Representatives. The State library, a very good one, is upstairs. The flight of stairs up to this, which is continued up to the dome, is wide and handsome, and of such easy ascent, that I ventured up to the top, in order to take a bird's-eye view of the scenery we so much enjoyed below. We were very well repaid for the trouble, especially as the gallery was glazed, so that we could see the view without being exposed to the cutting wind which was blowing outside.
The houses here are generally of brick, painted a deep red colour, which, not being in too great masses, and picked out with a good deal of white,[Pg 270] has a very good effect. Some few houses, however, especially towards the outskirts of the town, were of wood, painted white. We yesterday passed many villages and towns of these pretty houses, but with the snow lying around them, scarcely whiter than the houses themselves, they had a very chilly appearance, and looked far less tempting than the houses of this description in New England when we first saw them, each in its pretty clean lawn, and surrounded by a lovely foliage. To return to this town—and, as a climax to its perfection, it has, out and out, the most comfortable hotel we have seen in America. It is quite a bijou, with a very pretty façade, and, being new last year, everything is in the best style. The ground floor, as is generally the case in this country, consists, like the Hôtel du Louvre in Paris, of good shops, which gives a gayer appearance to the whole than if it were one mass of dwelling rooms. We find it so comfortable that, instead of going on this afternoon to Philadelphia, we mean to remain here to-night, and to go on to-morrow to New York.
New York, Nov. 22nd.—We took one more walk at Harrisburgh, before starting on Saturday. The morning was lovely, and from the hill above the town, which we had time to reach, the view was[Pg 271] very beautiful. But, of all the picturesque things that I have lately seen, I think the scene which presented itself this morning, when I opened our bedroom shutters at six o'clock, was the most striking. The night, on which I had looked out before going to bed, was clear and most beautiful; but a few stars now only remained as the day had begun to dawn, and the east was reddened by the approaching sunrise. Below the window was a very large market-place, lighted up and crowded with buyers and sellers. The women all had on the usual bonnet worn by the lower classes in this country,—a sun-bonnet, made of coloured cotton, with a very deep curtain hanging down the back. They wore besides warm cloaks and coloured shawls, and the men large wide-awakes. I have already described the brilliantly red houses, and the day being sufficiently advanced to bring out the colour very conspicuously, I think I never saw a prettier or busier scene, nor one which I could have wished more to have drawn, but there was no time even to attempt it.
After leaving Harrisburgh our road lay for some miles along the course of the Susquehanna, and papa, who had bought a copy of Gertrude of Wyoming, made me read it aloud to him, to the[Pg 272] great astonishment of our fellow-travellers and at the expense of my lungs, the noise of a railway carriage in America not being much suited for such an occupation. The river presented a succession of rich scenery, being most picturesquely studded with islands. We were quite sorry to take leave of it; but after these few miles of great beauty, the road made a dash across the country to Philadelphia. Papa, during the whole of the morning, had been most wonderfully obtuse in his geography, and was altogether perplexed when, before reaching Philadelphia, we came to the margin of the river we had to cross to reach that town. He had been quite mystified all the morning at Harrisburg, and at fault as to the direction in which the river was running, and as to whether the streets we were in were at right angles or parallel to it. This state of confusion became still worse when we got into the carriage, as he had miscalculated on which side, after leaving the town, we should first see the river, and had placed me on the left side of the car, when it suddenly appeared, in all its glory, on the right. He almost lost his temper, we all know how irritable he can become, and exclaimed impatiently,—"Well, are we now on this side of the river or the other?" but his puzzle at Philadelphia was from the river which[Pg 273] we then came upon, being the Schuylkill, while he thought we had got, in some mysterious way, to the Delaware, on the west bank of which the town is situated, as well as on the east of the Schuylkill. The discovery of the river it really was of course solved the puzzle; but for a long time he insisted that the steamboat we were to embark upon, later in the day, on the Delaware, must be the one we now saw, and it was all the passengers could do to persuade him to sit still. He exclaimed, "But why not stay on this side, instead of crossing the river to cross back again to take the cars?" It was altogether a ludicrous state of confusion that poor Papa was in; but it ended, not only in our crossing the river, but in our traversing the whole town of Philadelphia, at its very centre, in the railway cars, going through beautiful streets and squares; and, as we went at a slow pace, we had a capital view of the shops and of the town, which was looking very clean and brilliant, the day being fine and frosty.
We made no stay at Philadelphia, but at length taking the cars on the east side of the Delaware, we proceeded in them to South Amboy; where, embarking again, we had a fine run of twenty-four miles between Staten Island and the coast of New Jersey, and reached this place[Pg 274] in time for dinner. We regretted thus turning our backs on Philadelphia, and Baltimore, and Washington, without seeing more of them; but the time we have spent in the west has exceeded what we had counted on this part of our journey occupying, and we are anxious to get home to you all.
On our railway and on the steamer, we had with us a body of the firemen of Philadelphia, who were on their way to pay to their brother-firemen here one of those complimentary visits we have spoken of. There was loud cheering from their cars as we left Philadelphia, and as we passed through the different towns on the road, which was well responded to by the bystanders who had collected to witness the sight. The men were dressed in a most picturesque uniform, and had a good brass band, which played during the whole time that we were on board the steamer. On landing, there were bonfires on the quay, and rockets let off in honour of their arrival; but, though the crowd was great, we had not the slightest difficulty in landing, for all these matters are carried on with the greatest order in this country, which is the more remarkable, as the people have very excitable natures. Late at night, when we were going to bed, a company of firemen[Pg 275] crossed this street with lights and torches, with a band playing, and dragging a fire-engine covered with lamps; forming quite a moving blaze of light.
We yesterday spent our first Sunday in New York, having hitherto been always away on that day; and we heard a wonderfully impressive and admirable sermon from Dr. Tyng. The church in which he preached was of very large dimensions, but his voice penetrated it throughout; he stood on a small platform instead of a pulpit, with a low desk in front, so that his whole figure could be seen. He had a good deal of action, but it was in very good taste, and the matter of his sermon was beyond all praise. The text was from the latter part of Col. i. 17, "And by Him all things consist." In the afternoon we heard a good, but not so striking a sermon, from Dr. Bedell; and it was suggested to us to go in the evening to the Opera-house to hear a great Presbyterian preacher, Mr. Alexander; but this we did not feel disposed to do. The Opera-house is being made use of, as our Exeter Hall is, for Special Services.
I think I may as well fill up the rest of this sheet by describing the arrangements of American hotels. There are frequently two entrances, one for ladies and the other for gentlemen. That for the ladies[Pg 276] leads by a private staircase to the ladies' drawing-room; and the gentlemen's entrance opens upon what is called the office. Whether there are separate entrances or not, the gentleman is at once conducted to the office, which is usually crowded with spitters and smokers; and there he enters his name in the travellers' book. This done, the waiter shows him to the drawing-room, where the lady has been requested, in the meantime, to wait, and they are then taken, often through long and wide passages, to their bedrooms. A private drawing-room may be had by paying extra for it; but the custom is to do without one, and to make use of the ladies' drawing-room, which is always a pretty room, and often a very handsome one. In it are invariably to be found a piano, at which the ladies frequently perpetrate most dreadful music; a marble table, in the centre of which always stand a silver tray and silver tankard and goblets containing iced water, a rocking chair, besides other easy-chairs and sofas, and a Bible. It is a rare thing not to find a Bible, the gift of a Society, in every bedroom and drawing-room in the hotel. The bedrooms never have bed-curtains, and sometimes no window-curtains; but the windows usually have Venetian or solid shutters.
The dining-hall is a spacious apartment, often 80[Pg 277] or sometimes 100 feet long, and in some large hotels there are two of these, one used for railway travellers, and the other for the regular guests. The meals are always at a table-d'hôte, with printed bills of fare; the dishes are not handed round, as in Germany, but the guests are required to look at the bill of fare and name their dishes, which does not seem a good plan, as one's inclination is always to see how the dish looks before ordering it. Everything comes as soon as asked for, and there is a great choice of dishes. There is very little wine drunk at table, but to every hotel there is appended a bar, where, we are told, the gentlemen make amends for their moderation at table by discussing gin sling, sherry cobbler, &c.; but of course I know nothing of this, excepting from hearsay. The utmost extent of Papa's excesses on the rare occasions when he went into these bars, was to get a glass of Saratoga water; but he has failed to give me any description of what he saw. The breakfasts are going on usually from seven till nine. The general dinner-hour is one; but there is sometimes a choice of two hours, one and three. Tea, consisting of tea, coffee, and sweet cakes and preserves, takes place at six; and there is a cold meat supper at nine. Meals are charged extra if taken in private. It is a good[Pg 278] plan in travelling never to reserve oneself at the end of the day's journey for the hotel dinner, as there is a chance of arriving after it is over, when the alternative is to go without; the railway dinners are quite as good, find often better, than those at the hotel. The use of the ladies' drawing-room is restricted to ladies and gentlemen accompanying them; no single gentleman, is allowed to sit in it unless invited by a lady; but there is a separate reading-room for gentlemen, supplied with newspapers, and there is generally another room reserved for smoking, but the accommodation in these rooms is, in general, very inferior to those set apart for the ladies. In the hall of the hotel there is frequently a counter for the sale of newspapers, books, and periodicals, and all hotels have a barber's shop, which is a marvellous part of the establishment. The fixed charge at the hotels is generally from 8s. to 10s. per day for each person.
We have just settled to sail for England on the 1st December, so I shall have only one more journal letter to write to you, and shall be myself the bearer of it.
[13] The account referred to was written as far back as 1839, and is so much more accurate a description of the Falls, and of the canal, than that given in the Railway Guide, that I must here extract it.
"The falls of the Ohio are occasioned by an irregular ledge of rock stretching across the river. They are only perceptible at low water, the whole descent being but twenty-two feet, while the difference of level between the highest and lowest stages of the water is about sixty feet. When the river is full, they present, therefore, no serious obstruction to the navigation. To obviate the inconvenience, however, at low water, a canal, called the Louisville and Portland Canal, has been constructed round the falls, which is deserving of notice, as being, perhaps, the most important work of the kind ever undertaken. The cross section of the canal is 200 feet at the top of the bank, 50 feet at the bottom, and 42 feet deep, making its capacity about fifteen times greater than that contemplated for the Erie Canal after its enlargement is completed: its sides are sloping and paved with stone. The guard lock contains 21,775 perches of masonry, being equal to that of fifteen locks on the New York Canals; and three others contain 12,300 perches. This canal is capable of admitting steamboats of the largest class. It is scarcely two miles in length; but, considering the quantity of mason work, and the difficulty of excavating earth and rock from so great a depth, together with the contingencies attending its construction, from the fluctuations in the depth of the river, it is probably no over-statement when it is said, that the work in it is equal to that of seventy or seventy-five miles of an ordinary canal.
NEW YORK— ASTOR LIBRARY.— COOPER INSTITUTE.— BIBLE HOUSE.— DR. RAE— DR. TYNG.— TARRYTOWN.— ALBANY.— SLEIGHING— FINAL RETURN TO BOSTON.— HALIFAX.— VOYAGE HOME.— CONCLUSION.
Albany, Nov. 27th, 1858.
My last letter was despatched to you on the 23rd inst.;—that evening we dined at Mr. Aspinwall's. He has a handsome house in New York, and a large picture gallery, and as we wished to see this by daylight, we called on him after breakfast on the following morning, and had an opportunity of examining the pictures, many of which are very good, especially some by early Dutch masters.
Mr. Aspinwall afterwards took us to the Astor Library. This library was founded by the munificence of the late Mr. Astor, a very rich merchant, who bequeathed a large sum of money for the purpose. It is remarkably well arranged and pretty, and capable of containing about 300,000 volumes. Mr. Cogswell, the librarian, showed us some of the most valuable[Pg 280] books. He was acquainted with Papa's name, as he had bought his book in London for the library, and appeared familiar with its contents. He said he valued it as filling up a gap in the financial history of America that was not supplied by any work in this country.
Mr. Aspinwall took us afterwards to the Cooper Institute, founded by Mr. Peter Cooper, another very eminent citizen of New York, who has done this good deed in his lifetime. He happened to be there, and as Mr. Aspinwall introduced us to him, he showed us round the building himself. He is a rich ironmonger, and an eccentric man. The building has cost 100,000l.; it is intended for public lectures and for a school of design. At the time we were there, some specimens of drawings, penmanship, &c., by the scholars of the Free Schools in New York were being exhibited, and were, in general, very creditable performances. We went to the top of the building, and, the weather being remarkably clear and fine, we had a good view of the town and of the surrounding country. Anything like country, however, can only be seen on one side across the Hudson, although, on the opposite side of New York Bay, Staten Island can be seen stretching "right away" to the south;[Pg 281] but the wonderful sight is the immense city itself, extending for miles in a northern direction.
We rather crowded into this last day all the sights that we had hitherto omitted to see at New York; for we went also to the Bible House, a very large building near the Cooper Institute. In this Bible House not only are copies of the Bible sold, as in our corresponding institution in London, but the whole process of printing, making up, and binding the Bible is carried on. The number of Bibles and Testaments issued by the establishment is very great, amounting, during the last year, to 712,045. During that period there were 250,000 Bibles printed and 381,000 Testaments, besides 500 books for the blind printed in raised types, making a total of 631,500 volumes; and this, owing to a scarcity of funds, arising out of the late pecuniary pressure, is a decrease from the year before of 110,000 volumes, so that it was from the store in hand that the excess of the volumes issued above the number printed was taken. These Bibles and Testaments are in every language, and in every form and size. The machinery is worked by steam, and the immense building is warmed from the same source. Some idea of its extent may be conceived by the fact[Pg 282] that there are twelve miles of pipes used in this warming process.[14]
After this hard day's work we dined at Mr. Russell's, to meet Dr. Rae, the Arctic traveller, and in the evening we went to the Geographical Society to hear a lecture on his last northern expedition, when he gained all the information known respecting poor Sir John Franklin, in search of whom he had been sent by the British Government. He showed us many relics of that unfortunate party, consisting of spoons, watch-cases, &c.; the lecture was very interesting, especially with regard to the origin and transportation of boulders. He produced an enormous head of a deer, which had a curious horn in front between the two side ones; this is a common appendage to the antlers of the deer of that region. He told us an amusing anecdote of his having been present when Professor Owen was lecturing on this strange appearance, and described the wisdom of this provision, to enable the animal to clear its way in the snow in search of its food below it; but Dr. Rae was able entirely to[Pg 283] overset this theory, by stating that the whole horny appendages of this deer are always shed before any snow makes its appearance on the ground.
At dinner we met Mr. Rutherford, who begged us to go after the lecture to see his observatory, in which, he said, he had the best and largest telescope in America, not excepting the one at Washington; we went therefore to see it, though the lecture was not over till half-past ten, and were repaid by a sight of Jupiter, and his belts and satellites: but though the telescope was larger than the one at Washington, being of the same focal length, and having an object glass nearly two inches wider, it did not strike us as being so clear and good an instrument. It is undoubtedly, however, a very fine one, and entirely of American make. Much as we have had to record this day, there was more jumbled into it; but instead of going to see the last sight I have to record, it obtruded itself upon us at every turn. This was a military procession, flags flying, &c., to commemorate the evacuation of the town of New York by the British, after the first war of Independence. A great dinner is always given on this day by the members of the Order of Cincinnati, and Papa was asked to go to it, but our engagement to Mr. Russell prevented his accepting the invitation.[Pg 284]
I think the only further thing of interest which I have to record about our visit this time to New York, was our calling on Dr. Tyng; he is a most interesting person, and talked much about revivals and slavery. He said there was undoubtedly a greater degree of serious feeling gradually spreading in New York, especially among the artisans and labouring classes; but he could see nothing of that work of the Spirit on the large scale which others speak of, and he thinks the nature and extent of the revivals have been over-estimated.
With regard to slavery, Dr. Tyng is a very good judge, as, for the first six years of his ministry, he had a considerable parish in the slave state of Maryland, extending over a large tract of plantation lands, cultivated entirely by slaves. The slave population in this parish was about 8000, and he says the treatment of the slaves was almost all that could be desired for their temporal comfort, as far as good clothing, good food, and kind treatment went, and he had known but very few cases of slaves being ill-treated or even flogged during his six years' residence there: still no one can condemn more strongly than he does the whole system, as lowering and degrading the moral tone, both of the white and the black population.[Pg 285]
As I shall probably have no occasion to allude again to slavery, as the rest of our short stay on this continent will now be among the free states, I may say I have seen nothing to lessen, and everything to confirm, the strong impression I have always entertained respecting it. Besides what we have seen, we have read as much as we could on the subject, and must record a little book called "Aunt Sally, or the Cross the Way to Freedom," as being the most faithful account of the evils of slavery we have met with. It is the story of a female slave's life, and is said to be strictly true and devoid of all exaggeration, and it is a most touching account of the power of religion in her case, in upholding her through a long life of trials and degradation.[15]
On Friday, the 26th instant, we took our final leave of New York. We left it by the Hudson River Railway, the same by which we went to West Point two days after our arrival in America, and it was curious to contrast our feelings on getting into the cars now with those which we experienced when we first set our foot into them; we thought at first that we never could encounter a long journey[Pg 286] in them, and dreaded all sorts of disasters. Yet now, independently of steamboat travelling, we have travelled altogether in railways over more than 5500 miles, and it is somewhat singular that in the great number of separate journeys we have taken, we have only on one occasion been late on arriving at our destination, which was on reaching Chicago. The train was then two hours late in a journey of 281 miles, and that not owing to any accident, but solely to the slippery state of the rails, after a heavy rain, which rendered caution necessary. The only hitch from accident (if it was one), was for five minutes at Rome, on the New York Central Railway, when we were delayed for that time, on account of what William told us was "something wrong with the engine." We have only 200 miles left to travel between this and Boston, and we have great reason to be thankful for having performed so long a journey not only in perfect safety, but without any anxiety, and scarcely any fatigue.[16]
[Pg 287]One marked improvement in the eastern over the western railways, is in the gentlemen's special accomplishment of spitting being much less active in the east, owing to their chewing tobacco less vigorously. In the west it is dreadful to see and hear how this habit goes on during the whole day, not out of window, but on the floors of the cars and omnibuses, and all over the hall and passages of the hotels.
But to return to our journey from New York on the Hudson. It was a beautiful day, and the scenery quite lovely. We had only twenty-seven miles to go to Mr. Bartlett's, to whom we had brought letters from England, and who asked us to pass the first night of our journey at his country place near Tarrytown. On arriving at the station there, he drove us to his house, which stands on an eminence three miles higher up the river. The river here is rather more than three miles in width, but the atmosphere was so clear that every house on the opposite bank could be distinctly seen, and the opposite shore is so high, that we could hardly imagine the river to be[Pg 288] as wide as it is. The view from the house is perfectly magnificent. The eye takes in a distance of thirty miles up and down the river, there being here a long reach, having almost the appearance of a lake, the river above and below not being more than from a mile to a mile and a half in width. Immediately opposite Tarrytown is the town of Nyach, which is connected with Tarrytown by a steam ferry. In passing from Tarrytown to Mr. Bartlett's house, we drove through the Sleepy Hollow, the scene of one of Washington Irving's tales, and passed the old Dutch church, which is mentioned by him in the legend, as the place of sanctuary where Ichabod took refuge. In fact, the whole scenery is classic ground here; and Mr. Irving himself, who has rendered it so, lives only two miles off, at Sunnyside.
After giving us some luncheon, Mr. Bartlett took Papa a walk up a high hill behind the house, the view from which he describes as perfectly enchanting; but it would be difficult for anything to surpass the one seen from the house, combining every possible feature of wood, hill, dale, and water; but if I cannot describe this, it would be equally impossible to describe the perfect taste and beauty of the house itself. The chief features are the carving of the wooden staircase, the chimney-pieces in the library[Pg 289] and dining-room, and of the book-cases in the library. The carpet of the drawing-room was Aubusson tapestry, and the furniture was entirely from French patterns or imported from Paris, where it was made on purpose for the different rooms; every part of the house, including the bed-rooms, was filled with choice engravings. One bed-room specially struck us, the paper and chintz furniture of which were exactly of the same pattern of roses on a white ground, and the effect was beautiful; but there were many others in equally good taste, all with French papers. Hot and cold water were laid on in the rooms, and hot air likewise, though not so as to be in the least oppressive. Mrs. Bartlett's bed-room and dressing-room were the climax of all. The woodwork throughout the house was varied in every story: there was black oak, red pine, and white pine, all of very fine grain; the hall was covered with encaustic tiles from Minton's; the offices were in keeping, dairy, laundry, &c. Papa went over the farm and gardens, which were in the same exquisite order; and there were greenhouses and hothouses, which looked at a distance like a little Crystal Palace. Mrs. Bartlett is a very amiable person, but a great invalid, and seldom leaves her room.[Pg 290]
This morning we proceeded on our way to this place; before getting into the train at twelve o'clock, we drove over to Sunnyside; but, alas! Mr. Irving was out, and we could only walk about his grounds, and peep in at his study window. As this brought us to Tarrytown sooner than we counted upon, I had time to climb up one of the hills, and much enjoyed the view, although it was not so extensive as the one Papa saw yesterday. As we got northward, on our way to Albany, the snow, which had almost disappeared at Tarrytown, became very deep, the land was covered with a white garment, and the river partially with a coating of ice. At Hudson, opposite the Catskill mountains, we, for the first time, saw sledging, sledges having there taken the place of the usual carriages which come to meet the train. There were many carts, also, and an omnibus, all on sledges, and the whole had a singularly wintry appearance.
We are housed again at the Delavan House, and find the twenty-four damsels have donned long sleeves to their gowns, which are now of dark cotton instead of pink; but their hoops are as large, and their faces as impudent as ever, forcing Papa to restrain his grin, particularly when they stand in double file on each side of the table, all in the[Pg 291] same pose, with their arms crossed before them, when we enter the dining-room.
We are glad to find ourselves again here, for this hotel bears away the palm from all others we have seen in America, with the exception of that at Harrisburgh, which can alone compare with it in the general beauty of the rooms. To describe, for instance, the bedroom in which we are now sitting. The room is about twenty-four feet square, having two large windows looking to the street, and a mirror and handsome marble consol-table between them. The windows have very handsome gilt cornices, with tamboured muslin curtains, and others of a blue and gold coloured damask; there are two large sofas, and four small chairs of dark walnut wood, carved and covered with the same material as the curtains, and a smaller chair with a tapestry seat—also a large rocking-chair covered with Utrecht velvet. The bed is of prettily carved black walnut, the wash-hand-stand the same, with marble slab; there is a very handsome Brussels carpet, a large round table, at which I am now writing, a very handsome bronze and ormolu lustre, with six gaslights, and two ormolu candelabra on the chimney-piece. The chimney-piece is of white marble, and over it is a most gorgeously carved mirror. The room is about[Pg 292] fourteen feet high; the ceiling slightly alcoved and painted in medallions of flowers on a blue ground, with a great deal of very well painted and gilt moulding, which Papa at first thought was really in relief. The paper is a white ground, with a gold pattern, and a coloured border above, and below, and at the angles of the room; the door leads into a very fine wide passage, and there are two others, each leading into an adjoining room, all painted pure white; so is the skirting-board; and the door handles are white porcelain. Thrower's room, next ours, is much the same, but of about half the size. There are Venetian blinds to the windows, not made to draw up, but folding like shutters, and divided into several small panels. Our two windows look into a broad cheerful street, in which the snow is lying deep, and the whole scene is enlivened, every now and then, by the sleighs and their merry bells as they pass along.
Nov. 29th.—Yesterday the morning was very brilliant. Being desirous of seeing a Shaker village, and the nature of their service, we had ordered a vehicle over night to be ready at nine o'clock, when a sleigh made its appearance at the door, with skins of fur and every appliance to keep us warm. These sleighs are most elegant machines, and this one[Pg 293] had a hood, though this is not a common appendage. It was drawn by a pair of horses, the driver standing in front. The road was, at first, up a steep hill, but the horses seemed as if they had no weight behind them. On reaching the high land the view, looking back upon the river, was very pretty. The whole country was deeply covered with snow, and in many places, where it had drifted, it had the appearance of large waves, of which the crests curled gracefully over, and looked as if they had been frozen in the act of curling: some of these crests or waves were four or five feet above the level of the road. We were about an hour reaching the village, and were much disappointed to find the gate at the entrance closed, and a painted board hung on it, to announce there would be no meeting that day. Nothing could exceed the apparent order and decorum of the place; but we could not effect a closer approach, though our driver tried hard to gain admittance for us. We therefore returned to Albany, but took a different road home, and enjoyed our sleighing much; and the cheerful sound of the bells round our horses' necks was quite enlivening; still, in spite of our wraps, we must confess that we were not sorry when it was over. On our return to the town we entered[Pg 294] a church and heard the end of a sermon. It was a large Baptist church; but we were rather late, for we were told, by a boy at the door, that "the text had been on about forty minutes;" but, to judge from the sample we had of the discourse, we were probably no great losers. The church was a handsome building, but we were chiefly attracted by the following notice, in large letters, at the entrance.
"Come in, if only for a few moments; all are welcome."
After leaving the church we walked towards the Capitol, which is situated at the end of a very wide street, State Street, and, as this street rises by a tolerably steep ascent from the river, there is an extensive view over the river and the adjacent country from the plateau on which the Capitol stands. There are two very handsome buildings adjoining, of fine white stone, with Greek porticoes; but the Capitol itself, which is a considerably older building than the others, is of red brick. We had not time to explore further, for a heavy snow storm came on, which lasted for the rest of the day.
Boston, Nov. 30th.—Yesterday morning we[Pg 295] started early for this place, and the journey occupied the whole day. We had travelled this road before when the country was rich in its summer clothing, and the contrast was very strange as we saw it to-day. The heavy fall of snow the night before had covered not only the ground but the trees of the forests and the ponds and lakes, which were all frozen over. The Connecticut, however, glided calmly along, though it too was frozen over above the places where falls in the river obstructed the current. We passed several of these, which had a curious appearance, long and massive icicles hanging along the whole crest of the fall, and curiously intermingling with the water which was pouring over the rocks. The beautiful New England villages were as white as ever, the white snow scarcely detracting from the purity of the whiteness of the buildings. It was a splendid day, without a cloud in the sky, and the sun shining on the snow gave it a most brilliant and sparkling appearance.
To-day we have been chiefly engaged in shopping; but we contrived, besides, to see the public Library and Athenæum, as well as the Hospital and Prison, which Papa went over with Lord Radstock when we were first here, both of which fully bear out the account he gave me of them.[Pg 296] We feel quite sad to think that this is our last day in America, for we have enjoyed ourselves much; Papa has, indeed, up till late this evening, been engaged in business; but you are not to suppose from this that he has never had any relaxation; I am most thankful to say, on the contrary, that much of our time has been a holiday, and I trust his health has much benefited by our travels. But, whatever our regrets may be at leaving this interesting country, I need scarcely say with what delight we look forward to a return home to our dear children, where, I trust, a fortnight hence, to find you all well and prospering. We embark, at nine to-morrow morning, in the "Canada" for Liverpool, where I shall hope to add a few lines to this on landing.
December 11th, off Cape Clear.—As it may be late to-morrow before we land, and we may not have time to write from Liverpool, I shall close this now, or at all events only add a line from that place. Barring a severe gale of wind, our voyage has been tolerably prosperous since we left Halifax; but I must not anticipate, as I wish to say a little more about Boston, for I omitted in my last day's Journal to mention the admirable arrangement on the Western Railway, by which we came from[Pg 297] Albany, as regards checking the luggage. This practice, as I have already told you, is universal, but, generally speaking, one of the employés of the Packet Express Company takes charge of the checks before the passengers leave the cars, and for a trifling charge the luggage is delivered at any hotel the passenger may direct; where this is not done, the checks are usually given to the conductor of the omnibus, of which almost every hotel sends its own to the station. But this latter practice leads to much noise, each conductor shouting out the name of his hotel, as is done at Boulogne and elsewhere on the arrival of the packets. On gliding into the spacious station at Boston we were prepared to encounter this struggle, our checks not having been given up in the car; but, to our surprise, there was a total absence of this noisy scene, and on looking out we saw along the platform a range of beautiful gothic recesses, over each of which was written the name of an hotel, and we had only to walk along till we came to "Tremont House," when, without a word passing, we slipped into the hand of a man stationed within, the checks for our baggage, he simply indicating "No. 2" as the omnibus we were to get into. Walking to the end of the platform, we found a complete row of omnibuses, all consecu[Pg 298]tively numbered, and marched in silence to No. 2, which in a minute or two drove off with us and the other passengers destined for the Tremont House; we found this, as before, a very comfortable hotel, and our luggage was there within a few minutes after our arrival.
Before quitting the subject of the American hotels, we ought to state that, from what we hear, unhappy single gentlemen meet with a very different fate to that of persons travelling in company with ladies. One poor friend greatly bewailed his lot after he had left his wife at Toronto; on presenting himself at the "office" of the hotel he used to be eyed most suspiciously, especially when they saw his rough drab coloured travelling dress, for the criterion of a genteel American is a black coat and velvet collar. He was accordingly sent in general to a garret, and other travellers have told us the same; one on board the steamers quite confirmed this account, and told us he considered it a piece of great luxury when he had a gaslight in his room. He made this remark on our reading to him the account I have given of our room in Albany and its splendid six-light candelabra.
But to go on with our adventures: we embarked on board the steamer at 9 A.M. on Wednesday,[Pg 299] the 1st December. The view of the harbour of Boston, formed by a variety of islands, was most beautiful, in spite of the deep snow which covered them. The day was brilliantly sunny, but intensely cold, and it continued bitterly cold till we reached Halifax on Thursday night. The Boston steamers always touch at that place, and the liability to detention by fogs in making the harbour, renders this passage often a disagreeable one in the foggy season; but when the weather is as cold as now, it is invariably clear, and we steered up the beautiful harbour of Halifax with no interruption but that caused by the closing in of the day, rendering it necessary to slacken our speed as we neared the town. It was dark when we arrived, but having two hours to spare, we took a walk, and after passing through the town-gate, saw what we could of the place, respecting which I felt great interest, from my father having been Chief-justice there many years; his picture by West, of which we have a copy in D. P. H. by West himself, is at the Court House; but of course we could not see it so late at night; and, in fact, could only go to one or two shops to make some purchases as memorials of the place. It began to snow hard before we returned on board, and the cold was so intense, though less so[Pg 300] since the snow began, that the upper part of the harbour above where we stopped was frozen over.
We took Sir Fenwick Williams, of Kars, and a great many other officers, on board at Halifax, and sailed again at midnight. Next day the intense cold returned, and a severe north-wester made it almost impossible to keep on deck. Every wave that dashed over us, left its traces behind in a sheet of ice spread over the deck, and in the icicles which were hanging along the bulwarks, and formed a fringe to the boats which were hanging inside the ship; one poor passenger, with a splendid beard, told us he found it quite hard and stiff, and we could have told him how much we admired the icicles which were hanging to it. The thermometer, however, was only at 15°, it being the wind that made it so intensely cold. I did not get on deck, for, owing to the coating of ice, walking on it became a service of some danger; and I did my best to keep Papa from going up, though he often insisted on doing so, to enjoy the beauty of the scene. The captain says that it is sometimes most trying to be on this coast in winter, as the thermometer, instead of being 15° above zero as it was then, is often 15° below, when the ropes and everything become frozen. This cold lasted till Monday, when we were clear of "the[Pg 301] banks," and fairly launched into the wide Atlantic. The wind continued to blow strongly from the north-west, with a considerable amount of sea, which put an end to my even thinking of going on deck, but Papa persevered, and every day passed many hours there, walking up and down and enjoying it much, especially as it was daily getting warmer. I wished much I could have accompanied him, but by this time I was completely prostrated by sea-sickness.
The weather, though blowy, continued very fine till Tuesday at four o'clock, when Papa came down and told me to prepare for a gale; an ominous black cloud had shown itself in the north-west horizon; this would not of itself have created much sensation, had it not been accompanied by an extraordinary fall in the barometer; it had, in fact, been falling for twenty-four hours, for at noon on Monday it stood rather above 30, and at midnight was as low as 29·55, which, in these latitudes, is a great fall. But on Tuesday, at nine A.M., it had fallen to 28·80, when it began rapidly to sink, till at half-past three it stood at 28·40, showing a fall of more than an inch and a half since the preceding day at noon. It seems that this is almost unprecedented, so that when the little black cloud appeared, every sail was taken[Pg 302] in, and the main topmast and fore top-gallantmast lowered down on deck, and this was not done a bit too soon, for by half-past four, it blew a hurricane. The captain told a naval officer on board, that he had thought of putting the ship's head towards the gale, to let it blow past, but on further consideration, he put her right before it, though at the expense of losing a good deal of ground, as it made us go four points out of our course. Papa, who was on deck, said it was most magnificent to hear the fierce wind tearing past the vessel, and to see the ship not swaying in the least one way or another, but driving forwards with the masts perpendicular, as if irresistibly impelled through the water, without appearing to feel the waves. But alas, alas, this absence of motion, which was a paradise to me, lasted but some twenty minutes, while the fury of the blast continued. We ran before the gale for the next four hours, when it sufficiently moderated to enable us to resume our proper course.
The gale continued, however, till four next morning, and such a night I never passed. The doctor said, neither he nor any officer in the ship could sleep, and next morning the poor stewardess and our peculiar cabin boy mournfully deplored their fate, the former being forced to confess that, though[Pg 303] for years accustomed to the sea, she had been desperately sick. In fact no one had ever known the vessel to roll before as she did this night, and the sounds were horrible. The effect of one sea, in particular, striking the ship was appalling, from the perfect stillness which followed it. The vessel seemed quite to stagger under the blow and to be paralysed by it, so that several seconds must have elapsed before the heavy rolling recommenced. This, and the creaking and groaning of the vessel, had something solemn about it; but some minor sounds were neither so grand nor so philosophically borne by either Papa or myself. One of the most persevering of these arose from my carelessness in having forgotten to bolt the door of a cupboard which I made use of, in our cabin, the consequence of which was that, with every lurch of the vessel, the door gave a violent slam, and our lamp having been put out at midnight, as it invariably was, we were in total darkness, and without the means of ascertaining whether the irritating noise proceeded, as we suspected, from the cupboard door, or from one of the doors having been left open in the passage adjoining our cabin. It would have been dangerous to have got up in the dark, and with a violent lurching of the vessel, to discover the real[Pg 304] cause of this wearisome noise. I had a strong feeling of self-reproach in my own mind at having brought such a calamity on poor Papa, when it could have been avoided if I had been a little more careful before going to bed. On, therefore, the noise went, for the rest of that night, with great regularity—slam—slam—slam—defying every attempt to obtain even five minutes of sleep. With the first gleam of dawn I plainly saw that our own peccant door was the cause, and I was able by that time, with some caution, to rise and secure the bolt, and thus relieve ourselves, and probably our neighbours, from the weary sound.
Sleep, however, on my part was, under any circumstances, out of the question, for I was under great anxiety lest Papa should be pitched out of his berth, as he slept in the one above mine. Before retiring for the night I had consulted the surgeon on the subject, having heard that a steward had been once thrown out of his berth in this vessel under similar circumstances. The surgeon assured me that he had never heard of such an accident, and Papa reminded me that his height would save him from such a calamity, for the berths being only six feet long he could, by stretching himself out to his full length, wedge himself in and hold on by his head and heels, and[Pg 305] so, in fact, he did; but many passed the night on the floors in their cabin, particularly the children, who had not the advantage of being six feet three. Next morning the surgeon said he would not himself have slept where Papa did, and I suspect few of the upper berths were occupied. So much for the value of a medical opinion!
I was very sorry I could not go on deck on either of the following days, for though the gale had abated, the wind continued sufficiently strong to keep up a splendid sea. Papa, however, says that it was more the force of the wind when the gale first began, than the height of the sea that was remarkable, as the gale did not last long enough to get up a proper sea, though what that would have been I cannot imagine, as the effects, such as they were, were sufficiently serious for me. Since then, things have gone on prosperously, but we have only to-night come in sight of the lights on Cape Clear. The sea mercifully is somewhat smoother, and has allowed me to write this long story; and I am going to bed with a fairer prospect of sleep than I have had for the last few nights.
Sunday night, Sept. 12th.—The wind got up again in the night, and has delayed us much, so that we are still outside the bar of the Mersey: for[Pg 306] some hours it has been doubtful whether we should land to-night in Old England, or pass another night on board. The uncertainty of our fate has caused an evening of singular excitement, owing to several of the passengers going perpetually on deck and bringing down news, either that we were in the act of crossing the bar, or that we had crossed it, or that all this was wrong and that we were still outside. As often as it was announced, and that with the most positive assertion, that we should land to-night, there was great joy and glee among all the passengers, excepting ourselves and a few others who had visions of a late Custom House examination in a dark and dismal night with pouring rain, and a conviction that landing before morning would not bring us to London any sooner than doing so early to-morrow, and so we secretly hoped all the time that we were neither on nor over the bar. Betting, as usual, began on the subject, and the excitement was still at its height when official information was brought to us that we neither had attempted nor meant to attempt to cross the bar till five o'clock to-morrow morning. We have therefore easily made up our minds to what I fear is a disappointment to many. We trust now to have a quiet night, for we are lying-to, and are as still as at anchor, and hope on awaking[Pg 307] to-morrow morning, to find ourselves in the dock at Liverpool; in which case we shall rush up by an early train to London.
Here, therefore, ends our Journal; but before closing it, I must add a few lines to say what cause we have had to feel deeply thankful for all the mercies that have followed us by land and by sea. We have travelled a distance of nearly 6000 miles, in a country where accidents frequently occur, both on the railways and in steam-boats, and have never for one moment been exposed to peril, or experienced one feeling of anxiety. We have met everywhere with great attention, kindness, and hospitality, and have been preserved in perfect health. Besides our land and river journeys, we have made two long voyages across the wide Atlantic, and in the midst of a tempest, which was a very severe one, the Hand of God protected us and preserved us from danger, and, better still, kept our minds in peace and confidence, and in remembrance that He who ruleth the waves, could guide and succour us in every time of need, so that even I felt no fear; Papa has had more experience of storms at sea, and was less likely to feel any, but his confidence, too, was in knowing that we were under Divine protection, and that our part was to TRUST; and in this we had our reward.[Pg 308]
In thus enumerating the many subjects of thankfulness during our absence from home, I must reckon as one of the chief of our blessings, the comfort we have experienced in so constantly receiving the very best accounts of you all; and when we think of the many thousands of miles that have separated us, we may indeed feel full of gratitude that, neither on one side of the ocean nor the other, have we had any reason for anxiety concerning each other. In a few hours more, we shall, I trust, have the joy and gladness of seeing all your dear faces again, and be rejoicing together over our safe return from our interesting and delightful expedition to the New World.
[14] The issues of the British and Foreign Bible Society during the same period were 1,517,858; but the circulation of the American Bible Society is almost entirely limited to the American continent, and for their foreign Missions, while a large portion of ours goes to supply the Colonies.
[15] Aunt Sally is a real person still living at Detroit on Lake Michigan, with her son, the Rev. Isaac Williams, who is the minister there of the Methodist church.
[16] We must admit that our experience differs greatly from that of many; and, looking at the statistics of railway travelling, accidents do occur with frightful frequency. In a report recently published by the Philadelphia and Reading Railway, the accidents which occurred on that line alone in 1855, amounted to no less than 179 in a year, and this on a line where there is no great press of traffic. In these accidents, 619 cars were broken, 29 people killed, and 7 wounded. Things are since a little improved; as, last year, 1858, there were only 26 cases of killed and wounded, and, the Report adds, as if consolatory to the feelings of the natives, "of these 18 were strangers."
| Agriculture and Rural Affairs. | |
|---|---|
| Bayldon on Valuing Rents, &c. | 5 |
| Cecil's Stud Farm | 8 |
| Hoskyns's Talpa | 11 |
| Loudon's Agriculture | 14 |
| Low's Elements of Agriculture | 14 |
| Morton on Landed Estates | 17 |
| Arts, Manufactures, and Architecture. | |
| Bourne on the Screw Propeller | 6 |
| Brande's Dictionary of Science, &c. | 6 |
| " Organic Chemistry | 6 |
| Chevreul on Colour | 8 |
| Cresy's Civil Engineering | 8 |
| Fairbairn's Information for Engineers | 9 |
| Gwilt's Encyclopædia of Architecture | 10 |
| Harford's Plates from M. Angelo | 10 |
| Humphreys's Parables Illuminated | 12 |
| Jameson's Sacred and Legendary Art | 12, 13 |
| " Commonplace-Book | 13 |
| Konig's Pictorial Life of Luther | 10 |
| Loudon's Rural Architecture | 14 |
| Mac Dougall's Campaigns of Hannibal | 15 |
| " Theory of War | 15 |
| Moseley's Engineering | 17 |
| Piesse's Art of Perfumery | 18 |
| Richardson's Art of Horsemanship | 19 |
| Scoffern on Projectiles, &c. | 20 |
| Scrivenor on the Iron Trade | 20 |
| Steam Engine, by the Artisan Club | 6 |
| Ure's Dictionary of Arts, &c. | 23 |
| Biography. | |
| Arago's Lives of Scientific Men | 5 |
| Brialmont's Wellington | 6 |
| Bunsen's Hippolytus | 7 |
| Crosse's (Andrew) Memorials | 9 |
| Gleig's Essays | 10 |
| Green's Princesses of England | 10 |
| Harford's Life of Michael Angelo | 10 |
| Lardner's Cabinet Cyclopædia | 13 |
| Maunder's Biographical Treasury | 15 |
| Mountain's (Col.) Memoirs | 17 |
| Parry's (Admiral) Memoirs | 18 |
| Russell's Memoirs of Moore | 16 |
| " (Dr.) Life of Mezzofanti | 20 |
| SchimmelPenninck's (Mrs.) Life | 20 |
| Southey's Life of Wesley | 21 |
| " Life and Correspondence | 21 |
| Stephen's Ecclesiastical Biography | 22 |
| Strickland's Queens of England | 22 |
| Sydney Smith's Memoirs | 21 |
| Symonds's (Admiral) Memoirs | 22 |
| Taylor's Loyola | 22 |
| " Wesley | 22 |
| Uwins's Memoirs and Letters | 23 |
| Waterton's Autobiography and Essays | 34 |
| Books of General Utility. | |
| Acton's Bread-Book | 5 |
| " Cookery-Book | 5 |
| Black's Treatise on Brewing | 6 |
| Cabinet Gazetteer | 7 |
| " Lawyer | 7 |
| Cust's Invalid's Own Book | 9 |
| Gilbart's Logic for the Million | 10 |
| Hints on Etiquette | 11 |
| How to Nurse Sick Children | 12 |
| Hudson's Executor's Guide | 12 |
| " on Making Wills | 12 |
| Kesteven's Domestic Medicine | 13 |
| Lardner's Cabinet Cyclopædia | 13 |
| Loudon's Lady's Country Companion | 14 |
| Maunder's Treasury of Knowledge | 15 |
| " Biographical Treasury | 15 |
| " Geographical Treasury | 16 |
| " Scientific Treasury | 15 |
| " Treasury of History | 16 |
| " Natural History | 16 |
| Piesse's Art of Perfumery | 18 |
| Pocket and the Stud | 10 |
| Pycroft's English Reading | 19 |
| Reece's Medical Guide | 19 |
| Rich's Companion to Latin Dictionary | 19 |
| Richardson's Art of Horsemanship | 19 |
| Riddle's Latin Dictionaries | 19 |
| Roget's English Thesaurus | 20 |
| Rowton's Debater | 20 |
| Short Whist | 21 |
| Thomson's Interest Tables | 22 |
| Webster's Domestic Economy | 24 |
| West on Children's Diseases | 24 |
| Willich's Popular Tables | 24 |
| Wilmot's Blackstone | 24 |
| Botany and Gardening. | |
| Hassall's British Freshwater Algæ | 11 |
| Hooker's British Flora | 11 |
| " Guide to Kew Gardens | 11 |
| " " Kew Museum | 11 |
| Lindley's Introduction to Botany | 14 |
| " Theory of Horticulture | 14 |
| Loudon's Hortus Britannicus | 14 |
| " Amateur Gardener | 14 |
| " Trees and Shrubs | 14 |
| " Gardening | 14 |
| " Plants | 14 |
| Pereira's Materia Medica | 18 |
| Rivers's Rose Amateur's Guide | 19 |
| Wilson's British Mosses | 24 |
| Chronology. | |
| Blair's Chronological Tables | 6 |
| Brewer's Historical Atlas | 6 |
| Bunsen's Ancient Egypt | 7 |
| Calendars of English State Papers | 7 |
| Haydn's Beatson's Index | 11 |
| Jaquemet's Chronology | 13 |
| " Abridged Chronology | 13 |
| Commerce and Mercantile Affairs. | |
| Gilbart's Treatise on Banking | 10 |
| Lorimer's Young Master Mariner | 14 |
| Macleod's Banking | 15 |
| M'Culloch's Commerce and Navigation | 15 |
| Murray on French Finance | 18 |
| Scrivenor on the Iron Trade | 20 |
| Thomson's Interest Tables | 22 |
| Tooke's History of Prices | 22 |
| Criticism, History, and Memoirs. | |
| Blair's Chron. and Historical Tables | 6 |
| Brewer's Historical Atlas | 6 |
| Bunsen's Ancient Egypt | 7 |
| " Hippolytus | 7 |
| Calendars of English State Papers | 7 |
| Capgrave's Illustrious Henries | 8 |
| Chapman's Gustavus Adolphus | 8 |
| Chronicles and Memorials of England | 8 |
| Connolly's Sappers and Miners | 8 |
| Conybeare and Howson's St. Paul | 8 |
| Crowe's History of France | 9 |
| Fischer's Francis Bacon | 9 |
| Gleig's Essays | 10 |
| Gurney's Historical Sketches | 10 |
| Hayward's Essays | 11 |
| Herschel's Essays and Addresses | 11 |
| Jeffrey's (Lord) Contributions | 13 |
| Kemble's Anglo-Saxons | 13 |
| Lardner's Cabinet Cyclopædia | 13 |
| Macaulay's Critical and Hist. Essays | 14 |
| " History of England | 14 |
| " Speeches | 14 |
| Mackintosh's Miscellaneous Works | 15 |
| " History of England | 15 |
| M'Culloch's Geographical Dictionary | 15 |
| Maunder's Treasury of History | 16 |
| Merivale's History of Rome | 16 |
| " Roman Republic | 16 |
| Milner's Church History | 16 |
| Moore's (Thomas) Memoirs, &c. | 16 |
| Mure's Greek Literature | 17 |
| Normanby's Year of Revolution | 18 |
| Perry's Franks | 18 |
| Raikes's Journal | 19 |
| Riddle's Latin Dictionaries | 19 |
| Rogers's Essays from Edinb. Review | 20 |
| Roget's English Thesaurus | 20 |
| Schmitz's History of Greece | 20 |
| Southey's Doctor | 21 |
| Stephen's Ecclesiastical Biography | 22 |
| " Lectures on French History | 22 |
| Sydney Smith's Works | 21 |
| " Lectures | 21 |
| " Memoirs | 21 |
| Taylor's Loyola | 22 |
| " Wesley | 22 |
| Thirlwall's History of Greece | 22 |
| Thomas's Historical Notes | 27 |
| Townsend's State Trials | 22 |
| Turner's Anglo-Saxons | 23 |
| " Middle Ages | 23 |
| " Sacred History of the World | 23 |
| Uwins's Memoirs and Letters | 23 |
| Vehse's Austrian Court | 23 |
| Wade's England's Greatness | 24 |
| Young's Christ of History | 24 |
| Geography and Atlases. | |
| Brewer's Historical Atlas | 6 |
| Butler's Geography and Atlases | 7 |
| Cabinet Gazetteer | 7 |
| Johnston's General Gazetteer | 13 |
| M'Culloch's Geographical Dictionary | 16 |
| Maunder's Treasury of Geography | 16 |
| Murray's Encyclopædia of Geography | 17 |
| Sharp's British Gazetteer | 21 |
| Juvenile Books. | |
| Amy Herbert | 20 |
| Cleve Hall | 20 |
| Earl's Daughter (The) | 20 |
| Experience of Life | 20 |
| Gertrude | 20 |
| Howitt's Boy's Country Book | 12 |
| " (Mary) Children's Year | 12 |
| Ivors | 20 |
| Katharine Ashton | 20 |
| Laneton Parsonage | 20 |
| Margaret Percival | 20 |
| Pycroft's Collegian's Guide | 19 |
| Medicine, Surgery, &c. | |
| Brodie's Psychological Inquiries | 7 |
| Bull's Hints to Mothers | 6 |
| " Management of Children | 6 |
| Copland's Dictionary of Medicine | 8 |
| Cust's Invalid's Own Book | 9 |
| Holland's Mental Physiology | 11 |
| " Medical Notes and Reflections | 11 |
| How to Nurse Sick Children | 12 |
| Kesteven's Domestic Medicine | 13 |
| Pereira's Materia Medica | 18 |
| Reece's Medical Guide | 19 |
| Richardson's Cold-water Cure | 19 |
| Spencer's Principles of Psychology | 21 |
| West on Diseases of Infancy | 24 |
| Miscellaneous Literature. | |
| Bacon's (Lord) Works | 5 |
| Defence of Eclipse of Faith | 9 |
| Eclipse of Faith | 9 |
| Greathed's Letters from Delhi | 10 |
| Greyson's Select Correspondence | 10 |
| Gurney's Evening Recreations | 10 |
| Hassall's Adulterations Detected, &c. | 11 |
| Haydn's Book of Dignities | 11 |
| Holland's Mental Physiology | 11 |
| Hooker's Kew Guides | 11 |
| Howitt's Rural Life of England | 12 |
| " Visits to Remarkable Places | 12 |
| Jameson's Commonplace-Book | 13 |
| Jeffrey's (Lord) Contributions | 13 |
| Last of the Old Squires | 18 |
| Letters of a Betrothed | 13 |
| Macaulay's Critical and Hist. Essays | 14 |
| " Speeches | 14 |
| Mackintosh's Miscellaneous Works | 15 |
| Martineau's Miscellanies | 15 |
| Pycroft's English Reading | 19 |
| Raikes on the Indian Revolt | 19 |
| Rees's Siege of Lucknow | 19 |
| Rich's Companion to Latin Dictionary | 19 |
| Riddle's Latin Dictionaries | 19 |
| Rowton's Debater | 20 |
| Seaward's Narrative of his Shipwreck | 20 |
| Sir Roger De Coverley | 21 |
| Smith's (Rev. Sydney) Works | 21 |
| Southey's Doctor, &c. | 21 |
| Spencer's Essays | 21 |
| Stephen's Essays | 22 |
| Stow's Training System | 22 |
| Thomson's Laws of Thought | 22 |
| Tighe and Davis's Windsor | 22 |
| Townsend's State Trials | 22 |
| Yonge's English-Greek Lexicon | 24 |
| " Latin Gradus | 24 |
| Zumpt's Latin Grammar | 24 |
| Natural History in general. | |
| Catlow's Popular Conchology | 8 |
| Ephemera's Book of the Salmon | 9 |
| Garratt's Marvels of Instinct | 10 |
| Gosse's Natural History of Jamaica | 10 |
| Kirby and Spence's Entomology | 13 |
| Lee's Elements of Natural History | 13 |
| Maunder's Natural History | 16 |
| Quatrefages' Rambles of a Naturalist | 19 |
| Turton's Shells of the British Islands | 23 |
| Van der Hoeven's Handbook of Zoology | 23 |
| Waterton's Essays on Natural History | 24 |
| Youatt's The Dog | 24 |
| " The Horse | 24 |
| One-Volume Encyclopædias and Dictionaries. | |
| Blaine's Rural Sports | 6 |
| Brande's Science, Literature, and Art | 6 |
| Copland's Dictionary of Medicine | 8 |
| Cresy's Civil Engineering | 8 |
| Gwilt's Architecture | 10 |
| Johnston's Geographical Dictionary | 13 |
| Loudon's Agriculture | 14 |
| " Rural Architecture | 14 |
| " Gardening | 14 |
| " Plants | 14 |
| " Trees and Shrubs | 14 |
| M'Culloch's Geographical Dictionary | 15 |
| " Dictionary of Commerce | 15 |
| Murray's Encyclopædia of Geography | 17 |
| Sharp's British Gazetteer | 21 |
| Ure's Dictionary of Arts, &c. | 23 |
| Webster's Domestic Economy | 24 |
| Religious and Moral Works. | |
| Amy Herbert | 20 |
| Bloomfield's Greek Testament | 6 |
| Calvert's Wife's Manual | 8 |
| Cleve Hall | 20 |
| Conybeare and Howson's St. Paul | 8 |
| Cotton's Instructions in Christianity | 8 |
| Dale's Domestic Liturgy | 9 |
| Defence of Eclipse of Faith | 9 |
| Earl's Daughter (The) | 20 |
| Eclipse of Faith | 9 |
| Englishman's Greek Concordance | 9 |
| " Heb. & Chald. Concord. | 9 |
| Experience (The) of Life | 20 |
| Gertrude | 20 |
| Harrison's Light of the Forge | 10 |
| Horne's Introduction to Scriptures | 11 |
| " Abridgment of ditto | 11 |
| Huc's Christianity in China | 12 |
| Humphrey's Parables Illuminated | 12 |
| Ivors, by the Author of Amy Herbert | 20 |
| Jameson's Saints and Martyrs | 12 |
| " Monastic Legends | 13 |
| " Legends of the Madonna | 13 |
| " on Female Employment | 13 |
| Jeremy Taylor's Works | 13 |
| Katharine Ashton | 21 |
| Konig's Pictorial Life of Luther | 10 |
| Laneton Parsonage | 20 |
| Letters to my Unknown Friends | 13 |
| " on Happiness | 13 |
| Lyra Germanica | 7 |
| Maguire's Rome | 15 |
| Margaret Percival | 20 |
| Martineau's Christian Life | 15 |
| " Hymns | 15 |
| " Studies of Christianity | 15 |
| Merivale's Christian Records | 16 |
| Milner's Church of Christ | 26 |
| Moore on the Use of the Body | 26 |
| " " Soul and Body | 26 |
| " 's Man and his Motives | 26 |
| Morning Clouds | 17 |
| Neale's Closing Scene | 18 |
| Pattison's Earth and Word | 18 |
| Powell's Christianity without Judaism | 19 |
| Readings for Lent | 20 |
| " Confirmation | 20 |
| Riddle's Household Prayers | 19 |
| Robinson's Lexicon to the Greek Testament | 20 |
| Saints our Example | 20 |
| Sermon in the Mount | 20 |
| Sinclair's Journey of Life | 21 |
| Smith's (Sydney) Moral Philosophy | 21 |
| " (G.V.) Assyrian Prophecies | 21 |
| " (G.) Wesleyan Methodism | 21 |
| " (J.) Shipwreck of St. Paul | 21 |
| Southey's Life of Wesley | 21 |
| Stephen's Ecclesiastical Biography | 22 |
| Taylor's Loyola | 22 |
| " Wesley | 22 |
| Theologia Germanica | 7 |
| Thumb Bible (The) | 22 |
| Turner's Sacred History | 23 |
| Young's Christ of History | 24 |
| " Mystery | 24 |
| Poetry and the Drama. | |
| Aikin's (Dr.) British Poets | 5 |
| Arnold's Merope | 5 |
| " Poems | 5 |
| Baillie's (Joanna) Poetical Works | 5 |
| Calvert's Wife's Manual | 8 |
| Goldsmith's Poems, illustrated | 10 |
| Horace, edited by Yonge | 24 |
| L. E. L.'s Poetical Works | 13 |
| Linwood's Anthologia Oxoniensis | 14 |
| Lyra Germanica | 7 |
| Macaulay's Laws of Ancient Rome | 14 |
| MacDonald's Within and Without | 15 |
| " Poems | 14 |
| Montgomery's Poetical Works | 26 |
| Moore's Poetical Works | 26 |
| " Selections (illustrated) | 26 |
| " Lalla Rookh | 17 |
| " Irish Melodies | 17 |
| " National Melodies | 17 |
| " Sacred Songs (with Music) | 17 |
| " Songs and Ballads | 16 |
| Reade's Poetical Works | 19 |
| Shakspeare, by Bowdler | 20 |
| Southey's Poetical Works | 21 |
| Thomson's Seasons, illustrated | 22 |
| Political Economy & Statistics. | |
| Macleod's Political Economy | 15 |
| M'Culloch's Geog. Statist. &c. Dict. | 15 |
| " Dictionary of Commerce | 15 |
| Willich's Popular Tables | 21 |
| The Sciences in general and Mathematics. | |
| Arago's Meteorological Essays | 5 |
| " Popular Astronomy | 5 |
| Bourne on the Screw Propeller | 6 |
| " 's Catechism of Steam-Engine | 6 |
| Boyd's Naval Cadet's Manual | 6 |
| Brande's Dictionary of Science, &c. | 6 |
| " Lectures on Organic Chemistry | 6 |
| Cresy's Civil Engineering | 8 |
| Delabeche's Geology of Cornwall, &c. | 9 |
| De la Rive's Electricity | 9 |
| Grove's Correlation of Physical Forces | 10 |
| Herschel's Outlines of Astronomy | 11 |
| Holland's Mental Physiology | 11 |
| Humboldt's Aspects of Nature | 12 |
| " Cosmos | 12 |
| Hunt on Light | 12 |
| Lardner's Cabinet Cyclopædia | 13 |
| Marcet's (Mrs.) Conversations | 15 |
| Morell's Elements of Psychology | 17 |
| Moseley's Engineering and Architecture | 17 |
| Ogilvie's Master-Builder's Plan | 18 |
| Owen's Lectures on Comp. Anatomy | 18 |
| Pereira on Polarised Light | 18 |
| Peschel's Elements of Physics | 18 |
| Phillips Fossils of Cornwall | 18 |
| " Mineralogy | 18 |
| " Guide to Geology | 18 |
| Portlock's Geology of Londonderry | 18 |
| Powell's Unity of Worlds | 19 |
| " Christianity without Judaism | 19 |
| Smee's Electro-Metallurgy | 21 |
| Steam-Engine (The) | 6 |
| Rural Sports. | |
| Baker's Rifle and Hound in Ceylon | 5 |
| Blaine's Dictionary of Sports | 6 |
| Cecil's Stable Practice | 8 |
| " Stud Farm | 8 |
| Davy's Fishing Excursions, 2 Series | 9 |
| Ephemera on Angling | 9 |
| " Book of the Salmon | 9 |
| Hawker's Young Sportsman | 11 |
| The Hunting-Field | 10 |
| Idle's Hints on Shooting | 12 |
| Pocket and the Stud | 10 |
| Practical Horsemanship | 10 |
| Pycroft's Cricket-Field | 9 |
| Rarey's Horse-Taming | 19 |
| Richardson's Horsemanship | 19 |
| Ronalds's Fly-Fisher's Entomology | 20 |
| Stable Talk and Table Talk | 10 |
| Stonehenge on the Dog | 22 |
| " " Greyhound | 22 |
| Thacker's Courser's Guide | 22 |
| The Stud, for Practical Purposes | 10 |
| Veterinary Medicine, &c. | |
| Cecil's Stable Practice | 8 |
| " Stud Farm | 8 |
| Hunting-Field (The) | 10 |
| Miles's Horse-Shoeing | 26 |
| " on the Horse's Foot | 26 |
| Pocket and the Stud | 10 |
| Practical Horsemanship | 10 |
| Rarey's Horse-Taming | 19 |
| Richardson's Horsemanship | 19 |
| Stable Talk and Table Talk | 10 |
| Stonehenge on the Dog | 22 |
| Stud (The) | 10 |
| Youatt's The Dog | 24 |
| " The Horse | 24 |
| Voyages and Travels. | |
| Baker's Wanderings in Ceylon | 5 |
| Barth's African Travels | 5 |
| Burton's East Africa | 7 |
| " Medina and Mecca | 7 |
| Davies's Visit to Algiers | 9 |
| Domenech's Texas and Mexico | 9 |
| Forester's Sardinia and Corsica | 10 |
| Hinchliff's Travels in the Alps | 11 |
| Howitt's Art-Student in Munich | 12 |
| " (W.) Victoria | 12 |
| Huc's Chinese Empire | 12 |
| Hudson and Kennedy's Mont Blanc | 12 |
| Humboldt's Aspects of Nature | 12 |
| Hutchinson's Western Africa | 12 |
| M'Clure's North-West Passage | 18 |
| Mac Dougall's Voyage of the Resolute | 15 |
| Osborn's Quedah | 18 |
| Scherzer's Central America | 20 |
| Seaward's Narrative | 20 |
| Snow's Tierra del Fuego | 21 |
| Von Tempsky's Mexico and Guatemala | 23 |
| Wanderings in the Land of Ham | 24 |
| Weld's Vacations in Ireland | 24 |
| " United States and Canada | 24 |
| Works of Fiction. | |
| Cruikshank's Falstaff | 9 |
| Heirs of Cheveleigh | 11 |
| Howitt's Tallangetta | 12 |
| Moore's Epicurean | 17 |
| Sir Roger De Coverley | 21 |
| Sketches (The), Three Tales | 21 |
| Southey's Doctor, &c. | 21 |
| Trollope's Barchester Towers | 22 |
| " Warden | 22 |
| Ursula | 20 |
Miss Acton's Modern Cookery for Private Families, reduced to a System of Easy Practice in a Series of carefully-tested Receipts, in which the Principles of Baron Liebig and other eminent writers have been as much as possible applied and explained. Newly-revised and enlarged Edition; with 8 Plates, comprising 27 Figures, and 150 Woodcuts. Fcp. 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Acton's English Bread-Book for Domestic Use, adapted to Families of every grade. Fcp. 8vo. price 4s. 6d.
Aikin's Select Works of the British Poets from Ben Jonson to Beattie. New Edition; with Biographical and Critical Prefaces, and Selections from recent Poets. 8vo. 18s.
Arago (F.)—Biographies of Distinguished Scientific Men. Translated by Admiral W. H. Smyth, D.C.L., F.R.S., &c.; the Rev. Baden Powell, M.A.; and Robert Grant, M.A., F.R.A.S. 8vo. 18s.
Arago's Meteorological Essays. With an Introduction by Baron Humboldt. Translated under the superintendence of Lieut.-Col. E. Sabine, R.A., Treasurer and V.P.R.S. 8vo. 18s.
Arago's Popular Astronomy. Translated and edited by Admiral W. H. Smyth, D.C.L., F.R.S.; and Robert Grant, M.A., F.R.A.S. In Two Volumes. Vol. I. 8vo. with Plates and Woodcuts, 21s.—Vol. II. is in the press.
Arnold.—Merope, a Tragedy. By Matthew Arnold. With a Preface and an Historical Introduction. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Arnold.—Poems. By Matthew Arnold. First Series, Third Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 5s. 6d. Second Series, price 5s.
Lord Bacon's Works. A New Edition, collected and edited by R. L. Ellis, M.A., Fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge; J. Spedding, M.A. of Trinity College, Cambridge; and D. D. Heath, Esq., Barrister-at-Law, and late Fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge. Vols. I. to III. 8vo. 18s. each; Vol. IV. 14s.; and Vol. V. 18s. comprising the Division of Philosophical Works; with a copious Index.
Vols. VI. and VII. comprise Bacon's Literary and Professional Works. Vol. VI. price 18s. now ready.
Joanna Baillie's Dramatic and Poetical Works: Comprising Plays of the Passions, Miscellaneous Dramas, Metrical Legends, Fugitive Pieces, and Ahalya Baee; with the Life of Joanna Baille, Portrait and Vignette. Square crown 8vo. 21s. cloth; or 42s. morocco.
Baker.—The Rifle and the Hound in Ceylon. By S. W. Baker, Esq. New Edition, with 13 Illustrations engraved on Wood. Fcp. 8vo. 4s. 6d.
Baker.—Eight Years' Wanderings in Ceylon. By S. W. Baker, Esq. With 6 coloured Plates. 8vo. 15s.
Barth.—Travels and Discoveries in North and Central Africa: Being the Journal of an Expedition undertaken under the auspices of Her Britannic Majesty's Government in the Years 1849-1855. By Henry Barth, Ph.D., D.C.L., &c. With numerous Maps and Illustrations. 5 vols. 8vo. £5. 5s. cloth.
Bayldon's Art of Valuing Rents and Tillages, and Claims of Tenants upon Quitting Farms, at both Michaelmas and Lady-day; as revised by Mr. Donaldson. Seventh Edition, enlarged and adapted to the Present Time. By Robert Baker, Land Agent and Valuer. 8vo. price 10s. 6d.
Black's Practical Treatise on Brewing, based on Chemical and Economical Principles. With Formulæ for Public Brewers, and Instructions for Private Families. 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Blaine's Encyclopædia of Rural Sports; or, a complete Account, Historical, Practical, and Descriptive, of Hunting, Shooting, Fishing, Racing, &c. New Edition, revised and corrected to the Present Time; with above 600 Woodcut Illustrations, including 20 Subjects now added from Designs by John Leech.
Blair's Chronological and Historical Tables, from the Creation to the Present Time: With Additions and Corrections from the most authentic Writers; including the Computation of St. Paul, as connecting the Period from the Exode to the Temple. Under the revision of Sir Henry Ellis, K.H. Imperial 8vo. 31s. 6d. half-morocco.
Boyd.—A Manual for Naval Cadets. Published with the sanction and approval of the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty. By John M'Neill Boyd, Captain, R.N. With Compass-Signals in Colours, and 236 Woodcuts. Fcp. 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Bloomfield.—The Greek Testament: with copious English Notes, Critical, Philological, and Explanatory. Especially adapted to the use of Theological Students and Ministers. By the Rev. S. T. Bloomfield, D.D., F.S.A. Ninth Edition, revised. 2 vols. 8vo. with Map, £2. 8s.
Dr. Bloomfield's College & School Edition of the Greek Testament: With brief English Notes, chiefly Philological and Explanatory. Seventh Edition; with Map and Index. Fcp. 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Dr. Bloomfield's College & School Lexicon to the Greek Testament. New Edition, revised. Fcp. 8vo. price 10s. 6d.
Bourne's Catechism of the Steam Engine in its various Applications to Mines, Mills, Steam Navigation, Railways, and Agriculture: With Practical Instructions for the Manufacture and Management of Engines of every class. Fourth Edition, enlarged; with 89 Woodcuts. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
Bourne.—A Treatise on the Steam Engine, in its Application to Mines, Mills, Steam Navigation, and Railways. By the Artisan Club. Edited by John Bourne, C.E. New Edition; with 33 Steel Plates, and 349 Wood Engraving. 4to. 27s.
Bourne.—A Treatise on the Screw Propeller: With various Suggestions of Improvement. By John Bourne, C.E. New Edition, with 20 large Plates and numerous Wood Engravings. 4to. 38s.
Brande's Dictionary of Science, Literature, and Art; comprising the History, Description, and Scientific Principles of every Branch of Human Knowledge; with the Derivation and Definition of all the Terms in general use. Third Edition, revised and corrected; with numerous Woodcuts. 8vo. 60s.
Professor Brande's Lectures on Organic Chemistry, as applied to Manufactures, including Dyeing, Bleaching, Calico Printing, Sugar Manufacture, the Preservation of Wood, Tanning, &c. Edited by J. Scoffern, M.B. Fcp. Woodcuts, 7s. 6d.
Brewer.—An Atlas of History and Geography, from the Commencement of the Christian Era to the Present Time: Comprising a Series of Sixteen Coloured Maps, arranged in Chronological Order, with Illustrative Memoirs. By the Rev. J. S. Brewer, M.A. Second Edition, revised and corrected. Royal 8vo. 12s. 6d. half-bound.
Brialmont.—The Life of the Duke of Wellington. From the French of Alexis Brialmont, Captain on the Staff of the Belgian Army: With Emendations and Additions. By the Rev. G. R. Gleig, M.A., Chaplain-General to the Forces and Prebendary of St. Paul's. With Maps, Plans, and Portraits. Vols. I. and II. 8vo. price 30s.
Vol. III. (completion) is in preparation.
Dr. T. Bull's Hints to Mothers on the Management of their Health during the Period of Pregnancy and in the Lying-in Room: With an Exposure of Popular Errors in connexion with those subjects, &c.; and Hints upon Nursing. New Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Bull.—The Maternal Management of Children in Health and Disease. By T. Bull, M.D., formerly Physician-Accoucheur to the Finsbury Midwifery Institution. New Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Brodie.—Psychological Inquiries, in a Series of Essays intended to illustrate the Influence of the Physical Organisation on the Mental Faculties. By Sir Benjamin C. Brodie, Bart. Third Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Bunsen.—Christianity and Mankind, their Beginnings and Prospects. By Baron C. C. J. Bunsen, D.D., D.C.L., D.Ph. Being a New Edition, corrected, re-modelled, and extended, of Hippolytus and his Age. 7 vols. 8vo. £5. 5s.
*** This Edition is composed of three distinct works, as follows:—
1. Hippolytus and his Age, or, the Beginnings and Prospects of Christianity. 2 vols. 8vo £1. 10s.
2. Outline of the Philosophy of Universal History applied to Language and Religion; containing an Account of the Alphabetical Conferences. 2 vols. 33s.
3. Analecta Ante-Nicæna. 3 vols. 8vo. £2. 2s.
Bunsen.—Lyra Germanica. Translated from the German by Catherine Winkworth. Fifth Edition of the First Series, Hymns for the Sundays and Festivals of the Christian Year. Second Series, the Christian Life. Fcp. 8vo. 5s. each Series.
*** These selections of German Hymns have been made from collections published in Germany by Baron Bunsen, and form companion volumes to
Theologia Germanica: Which setteth forth many fair lineaments of Divine Truth, and saith very lofty and lovely things touching a Perfect Life. Translated by Susanna Winkworth. With a Preface by the Rev. Charles Kingsley; and a Letter by Baron Bunsen. Third Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
BUNSEN.—Egypt's Place in Universal History: An Historical Investigation, in Five Books. By Baron C. C. J. Bunsen, D.C.L., D.Ph. Translated from the German by C. H. Cottrell, Esq., M.A. With many Illustrations. Vol. I. 8vo. 28s.; Vol. II. 8vo. 30s. Vols. III. IV. and V. completing the work, are in the press.
Bishop Butler's Sketch of Modern and Ancient Geography. New Edition, thoroughly revised, with such Alterations introduced as continually progressive Discoveries and the latest information have rendered necessary. Post 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Bishop Butler's General Atlas of Modern and Ancient Geography, comprising Fifty-two full-coloured Maps; with complete Indices. New Edition, enlarged, and greatly improved. Edited by the Author's Son. Royal 4to. 24s.
Burton.—First Footsteps in East Africa; or, an Exploration of Harar. By Richard F. Burton, Captain, Bombay Army. With Maps and coloured Plate. 8vo. 18s.
Burton.—Personal Narrative of a Pilgrimage to El Medinah and Meccah. By Richard F. Burton, Captain, Bombay Army. Second Edition, revised; with coloured Plates and Woodcuts. 2 vols. crown 8vo. 24s.
The Cabinet Lawyer: A Popular Digest of the Laws of England, Civil and Criminal, with a Dictionary of Law Terms, Maxims, Statutes, and Judicial Antiquities; Correct Tables of Assessed Taxes, Stamp Duties, Excise Licenses, and Post-Horse Duties; Post-Office Regulations; and Prison Discipline. 17th Edition, comprising the Public Acts of the Session 1858. Fcp. 8vo. 10s. 6d.
The Cabinet Gazetteer: A Popular Exposition of All the Countries of the World. By the Author of The Cabinet Lawyer. Fcp. 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Calendars of State Papers, Domestic Series, published under the Direction of the Master of the Rolls, and with the Sanction of H.M. Secretary of State for the Home Department:
The Reign of JAMES I. 1603-23, edited by Mrs. Green. Vols. I. to III. imperial 8vo. 15s. each.
The Reign of CHARLES I. 1625-26, edited by John Bruce, V.P.S.A. Imperial 8vo. 15s.
The Reigns of EDWARD VI., MARY, ELIZABETH, 1547-80, edited by R. Lemon, Esq. Imperial 8vo. 15s.
Historical Notes relative to the History of England, from the Accession of HENRY VIII. to the Death of ANNE (1509-1714), compiled by F. S. Thomas, Esq. 3 vols. imperial 8vo. 40s.
State Papers relating to SCOTLAND, from the Reign of HENRY VIII. to the Accession of JAMES I. (1509-16??), and of the Correspondence relating to MARY QUEEN of SCOTS, during her Captivity in England, edited by M. J. Thorpe, Esq. 2 vols. imperial 8vo. 30s.
Calvert.—The Wife's Manual; or, Prayers, Thoughts, and Songs on Several Occasions of a Matron's Life. By the Rev. W. Calvert, M.A. Ornamented from Designs by the Author in the style of Queen Elizabeth's Prayer-Book. Crown 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Catlow's Popular Conchology; or, the Shell Cabinet arranged according to the Modern System: With a detailed Account of the Animals, and a complete Descriptive List of the Families and Genera of Recent and Fossil Shells. Second Edition, improved; with 405 Woodcuts. Post 8vo. 14s.
Cecil.—The Stud Farm; or, Hints on Breeding Horses for the Turf, the Chase, and the Road. Addressed to Breeders of Race-Horses and Hunters, Landed Proprietors, and Tenant Farmers. By Cecil. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Cecil's Stable Practice; or, Hints on Training for the Turf, the Chase, and the Road; with Observations on Racing and Hunting, Wasting, Race-Riding, and Handicapping: Addressed to all who are concerned in Racing, Steeple-Chasing, and Fox-Hunting. Fcp. 8vo. with Plate, 5s.
Chronicles and Memorials of Great Britain and Ireland during the Middle Ages, published by the authority of H. M. Treasury under the Direction of the Master of the Rolls:—
Capgrave's Chronicle of England, edited by the Rev. F. C. Hingeston, M.A. Royal 8vo. 8s. 6d.
Chronicon Monasterli de Abingdon, edited by the Rev. J. Stevenson, M.A. Vol. I. royal 8vo. 8s. 6d.
Lives of Edward the Confessor, edited by the Rev. H. R. Luard, M.A. 8s. 6d.
Monumenta Franciscana, edited by the Rev. J. S. Brewer, M. A. 8s. 6d.
Fasciculi Zizaniorum Magistri Johannis Wyclif cum Tritico, edited by the Rev. W. W. Shirley, M.A. 8s. 6d.
Stewart's Buik of the Croniclis of Scotland, edited by W. B. Turnbull, Barrister. Vol. I. royal 8vo. 8s. 6d.
Johannis Capgrave Liber de Illustribus Henricis, edited by the Rev. F. C. Hingeston, M.A. Royal 8vo. 8s. 6d.
English Translation of Capgrave's Book of the Illustrious Henries, by the Rev. F. C. Hingeston, M.A. 10s. 6d.
Elmham's Historia de Monasterii S. Augustini Cantuarensis, edited by the Rev. C. Hardwicke, M.A. 8s. 6d.
Chapman.—History of Gustavus Adolphus, and of the Thirty Years' War up to the King's Death: With some Account of its Conclusion by the Peace of Westphalia, in 1648. By B. Chapman, M.A. 8vo. Plans, 12s. 6d.
Chevreul On the Harmony and Contrast of Colours and their Applications to the Arts: Including Painting, Interior Decoration, Tapestries, Carpets, Mosaics, Coloured Glazing, Paper-Staining, Calico-Printing, Letterpress-Printing, Map-Colouring, Dress, Landscape and Flower-Gardening, &c. &c. Translated by Charles Martel. With 4 Plates. Crown 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Connolly.—History of the Royal Sappers and Miners: Including the Services of the Corps in the Crimea and at the Siege of Sebastopol. By T. W. J. Connolly, Quartermaster of the Royal Engineers. Second Edition; with 17 coloured Plates. 2 vols. 8vo. 30s.
Conybeare and Howson's Life and Epistles of Saint Paul; Comprising a complete Biography of the Apostle, and a Translation of his Epistles inserted in Chronological Order. Third Edition, revised and corrected; with several Maps and Woodcuts, and 4 Plates. 2 vols. square crown 8vo. 31s. 6d.
*** The Original Edition, with more numerous Illustrations, in 2 vols. 4to. price 48s.—may also be had.
Dr. Copland's Dictionary of Practical Medicine: Comprising General Pathology, the Nature and Treatment of Diseases, Morbid Structures, and the Disorders especially incidental to Climates, to Sex, and to the different Epochs of Life; with numerous approved Formulæ of the Medicines recommended. Now complete in 3 vols. 8vo. price £5. 11s. cloth.
Bishop Cotton's Instructions in the Doctrine and Practice of Christianity. Intended as an Introduction to Confirmation, 4th Edition. 18mo. 2s. 6d.
Cresy's Encyclopædia of Civil Engineering, Historical, Theoretical, and Practical. Illustrated by upwards of 3,000 Woodcuts. Second Edition, revised; and extended in a Supplement, comprising Metropolitan Water-Supply, Drainage of Towns, Railways, Cubical Proportion, Brick and Iron Construction, Iron Screw Piles, Tubular Bridges, &c. 8vo. 68s.
Crosse.—Memorials, Scientific and Literary, of Andrew Crosse, the Electrician. Edited by Mrs. Crosse. Post 8vo. 9s. 6d.
Crowe.—The History of France. By Eyre Evans Crowe. In Five Volumes. Vol. I. 8vo. 14s.
Cruikshank.—The Life of Sir John Falstaff, illustrated in a Series of Twenty-four original Etchings by George Cruikshank. Accompanied by an imaginary Biography of the Knight, by Robert B. Brough. Royal 8vo. price 12s. 6d. cloth.
Lady Cust's Invalid's Own Book: A Collection of Recipes from various Books and various Countries. Second Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 2s. 6d.
The Rev. Canon Dale's Domestic Liturgy and Family Chaplain, in Two Parts: Part I. Church Services adapted for Domestic Use, with Prayers for Every Day of the Week, selected from the Book of Common Prayer; Part II. an appropriate Sermon for Every Sunday in the Year. Second Edition. Post 4to. 21s. cloth; 31s. 6d. calf; or £2. 10s. morocco. {The Family Chaplain, 12s. Separately: {The Domestic Liturgy, 10s.6d.
Davies.—Algiers in 1857: Its Accessibility, Climate, and Resources described with especial reference to English Invalids; with details of Recreation obtainable in its Neighbourhood added for the use of Travellers in general. By the Rev. E. W. L. Davies, M.A. Oxon. Post 8vo. 6s.
Delabeche.—Report on the Geology of Cornwall, Devon, and West Somerset. By Sir H. T. Delabeche, F.R.S. With Maps, Plates, and Woodcuts. 8vo. 14s.
Davy (Dr. J.)—The Angler and his Friend; or, Piscatory Colloquies and Fishing Excursions. By John Davy, M.D., F.R.S., &c. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
By the same Author,
The Angler in the Lake District; or, Piscatory Colloquies and Fishing Excursions in Westmoreland and Cumberland. Fcp. 8vo. 6s. 6d.
De la Rive's Treatise on Electricity in Theory and Practice. Translated for the Author by C. V. Walker, F.R.S. 3 vols. 8vo. Woodcuts, £3. 13s.
Abbé Domenech's Missionary Adventures in Texas and Mexico: A Personal Narrative of Six Years' Sojourn in those Regions. Translated from the French under the Author's superintendence. 8vo. 10s. 6d.
The Eclipse of Faith; or, a Visit to a Religious Sceptic. 9th Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Defence of The Eclipse of Faith, by its Author: Being a Rejoinder to Professor Newman's Reply: Including a full Examination of that Writer's Criticism on the Character of Christ; and a Chapter on the Aspects and Pretensions of Modern Deism. Second Edition, revised. Post 8vo. 5s. 6d.
The Englishman's Greek Concordance of the New Testament: Being an Attempt at a Verbal Connexion between the Greek and the English Texts; including a Concordance to the Proper Names, with Indexes, Greek-English and English-Greek. New Edition, with a new Index. Royal 8vo. 42s.
The Englishman's Hebrew and Chaldee Concordance of the Old Testament: Being an Attempt at a Verbal Connexion between the Original and the English Translations; with Indexes, a List of the Proper Names and their Occurrences, &c. 2 vols. royal 8vo. £3. 13s. 6d.; large paper, £4. 14s. 6d.
Ephemera's Handbook of Angling; teaching Fly-fishing, Trolling, Bottom-Fishing, Salmon-Fishing: With the Natural History of River-Fish, and the best Modes of Catching them. Third Edition, corrected and improved; with Woodcuts. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Ephemera's Book of the Salmon: The Theory, Principles, and Practice of Fly-Fishing for Salmon; Lists of good Salmon Flies for every good River in the Empire; the Natural History of the Salmon, its Habits described, and the best way of artificially Breeding it. Fcp. 8vo. with coloured Plates, 14s.
Fairbairn.—Useful Information for Engineers: Being a Series of Lectures delivered to the Working Engineers of Yorkshire and Lancashire. By William Fairbairn, F.R.S., F.G.S. Second Edition; with Plates and Woodcuts. Crown 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Fischer.—Francis Bacon of Verulam: Realistic Philosophy and its Age. By Dr. K. Fischer. Translated by John Oxenford. Post 8vo. 9s. 6d.
Forester.—Rambles in the Islands of Corsica and Sardinia: With Notices of their History, Antiquities, and present Condition. By Thomas Forester. With coloured Map; and numerous Lithographic and Woodcut Illustrations from Drawings made during the Tour by Lieut.-Col. M. A. Biddulph, R.A. Imperial 8vo. 28s.
Garratt.—Marvels and Mysteries of Instinct; or, Curiosities of Animal Life. By George Garratt. Second Edition, improved. Fcp. 8vo. 4s. 6d.
Gilbart.—A Practical Treatise on Banking. By James William Gilbart, F.R.S., General Manager of the London and Westminster Bank. Sixth Edition. 2 vols. 12mo. 16s.
Gilbart.—Logic for the Million: a Familiar Exposition of the Art of Reasoning, By J. W. Gilbart, F.R.S. 5th Edition; with Portrait. 12mo. 3s. 6d.
Gleig.—Essays, Biographical, Historical, and Miscellaneous, contributed chiefly to the Edinburgh and Quarterly Reviews. By the Rev. G. R. Gleig, M.A., Chaplain-General to the Forces, and Prebendary of St. Paul's. 2 vols. 8vo. price 21s.
The Poetical Works of Oliver Goldsmith. Edited by Bolton Corney, Esq. Illustrated by Wood Engravings, from Designs by Members of the Etching Club. Square crown 8vo. cloth, 21s.; morocco, £1. 16s.
Gosse.—A Naturalist's Sojourn in Jamaica. By P. H. Gosse, Esq. With Plates. Post 8vo. 14s.
Greathed.—Letters from Delhi during the Siege. By H. H. Greathed, Esq., Political Agent. Post 8vo.
Green.—Lives of the Princesses of England. By Mrs. Mary Anne Everett Green, Editor of the Letters Of Royal and Illustrious Ladies. With numerous Portraits. Complete in 6 vols. post 8vo. 10s. 6d. each.
Greyson.—Selections from the Correspondence of R. E. Greyson, Esq. Edited by the Author of The Eclipse of Faith. New Edition. Crown 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Grove.—The Correlation of Physical Forces. By W. R. Grove, Q.C., M.A. Third Edition. 8vo. 7s.
Gurney.—St. Louis and Henri IV.: Being a Second Series of Historical Sketches. By the Rev. John H. Gurney, M.A. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
Evening Recreations; or, Samples from the Lecture-Room. Edited by Rev. J. H. Gurney. Crown 8vo. 5s.
Gwilt's Encyclopædia of Architecture, Historical, Theoretical, and Practical. By Joseph Gwilt. With more than 1,000 Wood Engravings, from Designs by J. S. Gwilt. 8vo. 42s.
Hare (Archdeacon).—The Life of Luther, in Forty-eight Historical Engravings. By Gustav König. With Explanations by Archdeacon Hare and Susannah Winkworth. Fcp. 4to. 28s.
Harford.—Life of Michael Angelo Buonarroti: With Translations of many of his Poems and Letters; also Memoirs of Savonarola, Raphael, and Vittoria Colonna. By John S. Harford, Esq., D.C.L., F.R.S. Second Edition, revised; with 20 Plates. 2 vols. 8vo. 25s.
Illustrations, Architectural and Pictorical, of the Genius of Michael Angelo Buonarroti. With Descriptions of the Plates, by the Commendatore Canina; C. R. Cockerell, Esq., R.A.; and J. S. Harford, Esq., D.C.L., F.R.S. Folio, 73s. 6d. half-bound.
Harrison.—The Light of the Forge; or, Counsels from the Sick-Bed of E. M. By the Rev. W. Harrison, M.A., Domestic Chaplain to the Duchess of Cambridge. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Harry Hieover's Stable Talk and Table Talk; or, Spectacles for Young Sportsmen. New Edition. 2 vols. 8vo. Portrait, 24s.
Harry Hieover.—The Hunting-Field. By Harry Hieover. With Two Plates. Fcp. 8vo. 5s. half-bound.
Harry Hieover.—Practical Horsemanship. Second Edition; with 2 Plates. Fcp. 8vo. 5s. half-bound.
Harry Hieover.—The Pocket and the Stud; or, Practical Hints on the Management of the Stable. By Harry Hieover. Fcp. 8vo. Portrait, 6s.
Harry Hieover.—The Stud, for Practical Purposes and Practical Men: Being a Guide to the Choice of a Horse for use more than for show. Fcp. 5s.
Hassall.—A History of the British Freshwater Algæ: Including Descriptions of the Desmideæ and Diatomaceæ. By Arthur Hill Hassall, M.D. 2 vols. 8vo. With 103 Plates, £1. 15s.
Hassall.—Adulterations Detected; or, Plain Instructions for the Discovery of Frauds in Food and Medicine. By Arthur Hill Hassall, M.D. Lond., Analyst of The Lancet Sanitary Commission, and Author of the Reports of that Commission published under the title of Food and its Adulterations (which may also be had, in 8vo. price 28s.) With 225 Illustrations, engraved on Wood. Crown 8vo. 17s. 6d.
Col. Hawker's Instructions to Young Sportsmen in all that relates to Guns and Shooting. 10th Edition, revised by the Author's Son, Major P. W. L. Hawker. With Portrait, Plates, and Woodcuts. 8vo. 21s.
Haydn's Book of Dignities: Containing Rolls of the Official Personages of the British Empire, Civil, Ecclesiastical, Judicial, Military, Naval, and Municipal, from the Earliest Periods to the Present Time. Together with the Sovereigns of Europe, from the Foundation of their respective States; the Peerage and Nobility of Great Britain, &c. 8vo. 25s.
Hayward.—Biographical and Critical Essays, reprinted from Reviews, with Additions and Corrections. By A. Hayward, Esq., Q.C. 2 vols. 8vo. 24s.
The Heirs of Cheveleigh: A Novel. By Gervaise Abbott. 3 vols. post 8vo. 31s. 6d.
Sir John Herschel's Outlines of Astronomy. Fifth Edition, revised and corrected to the existing state of astronomical knowledge; with Plates and Woodcuts. 8vo. 18s.
Sir John Herschel's Essays from the Edinburgh and Quarterly Reviews, with Addresses and other Pieces. 8vo. 18s.
Hinchliff.—Summer Months among the Alps: With the Ascent of Monte Rosa. By Thos. W. Hinchliff, Barrister-at-Law. Post 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Hints on Etiquette and the Usages of Society: With a Glance at Bad Habits. New Edition, revised (with Additions) by a Lady of Rank. Fcp. 8vo. 2s. 6d.
Holland.—Medical Notes and Reflections. By Sir Henry Holland, M.D., F.R.S., &c., Physician in Ordinary to the Queen and Prince-Consort. Third Edition. 8vo. 18s.
Holland.—Chapters on Mental Physiology. By Sir Henry Holland, Bart., F.R.S., &c. Founded chiefly on Chapters contained in Medical Notes and Reflections by the same Author. Second Edition. Post 8vo. 8s. 6d.
Hooker.—Kew Gardens; or, a Popular Guide to the Royal Botanic Gardens of Kew. By Sir William Jackson Hooker, K.H., &c., Director. With many Woodcuts. 16mo. 6d.
Hooker's Museum of Economic Botany; or, Popular Guide to the Useful and Remarkable Vegetable Products of the Museum in the Royal Gardens of Kew. 16mo. 1s.
Hooker and Arnott's British Flora; comprising the Phænogamous or Flowering Plants, and the Ferns. Seventh Edition, with Additions and Corrections; and numerous Figures illustrative of the Umbelliferous Plants, the Composite Plants, the Grasses, and the Ferns. 12mo. with 12 Plates, 14s.; with the Plates coloured, 21s.
Horne's Introduction to the Critical Study and Knowledge of the Holy Scriptures. Tenth Edition, revised, corrected, and brought down to the present time. Edited by the Rev. T. Hartwell Horne, B.D. (the Author); the Rev. Samuel Davidson, D.D. of the University of Halle, and LL.D.; and S. Prideaux Tregelles, LL.D. With 4 Maps and 22 Vignettes and Facsimiles. 4 vols. 8vo. £3. 13s. 6d.
Horne.—A Compendious Introduction to the Study of the Bible. By the Rev. T. Hartwell Horne, B.D. New Edition, with Maps, &c. 12mo. 9s.
Hoskyns.—Talpa; or, the Chronicles of a Clay Farm: An Agricultural Fragment. By Chandos Wren Hoskyns, Esq. Fourth Edition. With 24 Woodcuts from Designs by George Cruikshank. 16mo. 5s. 6d.
How to Nurse Sick Children: Intended especially as a Help to the Nurses in the Hospital for Sick Children; but containing Directions of service to all who have the charge of the Young. Fcp. 8vo. 1s. 6d.
Howitt (A. M.)—An Art-Student in Munich. By Anna Mary Howitt. 2 vols. post 8vo. 14s.
Howitt.—The Children's Year. By Mary Howitt. With Four Illustrations. Square 16mo. 5s.
Howitt.—Tallangetta, the Squatter's Home: A Story of Australian Life. By William Howitt. 2 vols. post 8vo. 18s.
Howitt.—Land, Labour, and Gold; or, Two Years in Victoria: With Visit to Sydney and Van Diemen's Land. By William Howitt. Second Edition. 2 vols. crown 8vo. 10s.
W. Howitt's Visits to Remarkable Places: Old Halls, Battle-Fields, and Scenes illustrative of Striking Passages in English History and Poetry. With about 80 Wood Engravings. New Edition. 2 vols. square crown 8vo. 25s.
William Howitt's Boy's Country Book: Being the Real Life of a Country Boy, written by himself; exhibiting all the Amusements, Pleasures, and Pursuits of Children in the Country. With 40 Woodcuts. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
William Howitt's Rural Life of England. With Woodcuts by Bewick and Williams. Medium 8vo. 21s.
Huc.—Christianity in China, Tartary, and Thibet. By M. l'Abbé Huc, formerly Missionary Apostolic in China. Vols. I. and II. 8vo. 21s.; and Vol. III. 10s. 6d.
Huc.—The Chinese Empire: A Sequel to Huc and Gabet's Journey through Tartary and Thibet. By the Abbé Huc, formerly Missionary Apostolic in China. Second Edition; with Map. 2 vols. 8vo. 24s.
Hudson and Kennedy's Ascent of Mont Blanc by a New Route and Without Guides. Second Edition, with Plate and Map. Post 8vo. 5s. 6d.
Hudson's Plain Directions for Making Wills in conformity with the Law: With a clear Exposition of the Law relating to the distribution of Personal Estate in the case of Intestacy, two Forms of Wills, and much useful information. Fcp. 8vo. 2s. 6d.
Hudson's Executor's Guide. New and improved Edition; with the Statutes enacted, and the Judicial Decisions pronounced since the last Edition incorporated. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
Humboldt's Cosmos. Translated, with the Author's authority, by Mrs. Sabine. Vols. I. and II. 16mo. Half-a-Crown each, sewed; 3s. 6d. each, cloth; or in post 8vo. 12s. each, cloth. Vol. III. Post 8vo. 12s. 6d. cloth: or in 16mo. Part I. 2s. 6d. sewed, 3s. 6d. cloth; and Part II. 3s. sewed, 4s. cloth. Vol. IV. Part I. post 8vo. 15s. cloth; 16mo. 7s. 6d. cloth.
Humboldt's Aspects of Nature. Translated, with the Author's authority, by Mrs. Sabine. 16mo. price 6s.: or in 2 vols. 3s. 6d. each, cloth; 2s. 6d. each, sewed.
Humphreys.—Parables of Our Lord, illuminated and ornamented in the style of the Missals of the Renaissance by H. N. Humphreys. Square fcp. 8vo. 21s. in massive carved covers; or 30s. bound in morocco, by Hayday.
Hunt.—Researches on Light in its Chemical Relations; embracing a Consideration of all the Photographic Processes. By Robert Hunt, F.R.S. Second Edition, with Plate and Woodcuts 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Hutchinson.—Impressions of Western Africa: With a Report on the Peculiarities of Trade up the Rivers in the Bight of Biafra. By J. T. Hutchinson, Esq., British Consul for the Bight of Biafra and the Island of Fernando Po. Post 8vo. 8s. 6d.
Idle.—Hints on Shooting, Fishing, &c., both on Sea and Land, and in the Fresh-Water Lochs of Scotland: Being the Experiences of C. Idle, Esq. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Mrs. Jameson's Legends of the Saints and Martyrs, as represented in Christian Art: Forming the First Series of Sacred and Legendary Art. Third Edition; with 17 Etchings and upwards of 180 Woodcuts. 2 vols. square crown 8vo. 81s. 6d.
Mrs. Jameson's Legends of the Monastic Orders, as represented in Christian Art. Forming the Second Series of Sacred and Legendary Art. Second Edition, enlarged; with 11 Etchings by the Author and 88 Woodcuts. Square crown 8vo. 28s.
Mrs. Jameson's Legends of the Madonna, as represented in Christian Art: Forming the Third Series of Sacred and Legendary Art. Second Edition, corrected and enlarged; with 27 Etchings and 165 Wood Engravings. Square crown 8vo. 28s.
Mrs. Jameson's Commonplace-Book of Thoughts, Memories, and Fancies, Original and Selected. Second Edition, revised and corrected; with Etchings and Woodcuts. Crown 8vo. price 18s.
Mrs. Jameson's Two Lectures on the Employment of Women:—
1. Sisters of Charity, Catholic and Protestant, Abroad and at Home. Second Edition, with new Preface. Fcp. 8vo. 4s.
2. The Communion of Labour: A Second Lecture on the Social Employments of Women. Fcp. 8vo. 3s.
Jaquemet's Compendium of Chronology: Containing the most important Dates of General History, Political, Ecclesiastical, and Literary, from the Creation of the World to the end of the Year 1854. Post 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Jaquemet's Chronology for Schools: Containing the most important Dates of General History, Political, Ecclesiastical, and Literary, from the Creation of the World to the end of the Year 1857. Fcp. 8vo. 3s. 6d.
Lord Jeffrey's Contributions to The Edinburgh Review. A New Edition, complete in One Volume, with Portrait and Vignette. Square crown 8vo. 21s. cloth; or 30s. calf.—Or in 3 vols. 8vo. price 42s.
Bishop Jeremy Taylor's Entire Works: With Life by Bishop Heber. Revised and corrected by the Rev. Charles Page Eden, Fellow of Oriel College, Oxford. Now complete in 10 vols. 8vo. 10s. 6d. each.
Kemble.—The Saxons in England: A History of the English Commonwealth till the Conquest. By J. M. Kemble, M.A. 2 vols. 8vo. 28s.
Keith Johnston's Dictionary of Geography. Descriptive, Physical, Statistical, and Historical: Forming a complete General Gazetteer of the World. Second Edition, thoroughly revised. In 1 vol. of 1,360 pages, comprising about 50,000 Names of Places, 8vo. 36s. cloth; or half-bound in russia, 41s.
Kesteven.—A Manual of the Domestic Practice of Medicine. By W. B. Kesteven, F.R.C.S.E., &c. Square post 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Kirby and Spence's Introduction to Entomology; or, Elements of the Natural History of Insects; Comprising an Account of Noxious and Useful Insects, of their Metamorphoses, Food, Stratagems, Habitations, Societies, Motions, Noises, Hybernation, Instinct, &c. Seventh Edition, with an Appendix relative to the Origin and Progress of the work. Crown 8vo. 5s.
Lardner's Cabinet Cyclopædia of History, Biography, Literature, the Arts and Sciences, Natural History, and Manufactures. A Series of Original Works by Eminent Writers. Complete in 132 vols. fcp. 8vo. with Vignette Titles, price £19. 19s. cloth lettered.
The Works separately, in single Volumes or Sets, price 3s. 6d. each Volume, cloth lettered.
Mrs. R. Lee's Elements of Natural History; or, First Principles of Zoology: Comprising the Principles of Classification, interspersed with amusing and instructive Accounts of the most remarkable Animals. New Edition; Woodcuts. Fcp. 8vo. 7s. 6d.
The Letters of a Betrothed. Fcp. 8vo. price 5s. cloth.
Letters to my Unknown Friends. By a Lady, Author of Letters on Happiness. Fourth Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Letters on Happiness, addressed to a Friend. By the Author of Letters to my Unknown Friends. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
L. E. L.—The Poetical Works of Letitia Elizabeth Landon; comprising the Improvisatrice, the Venetian Bracelet, the Golden Violet, the Troubadour, and Poetical Remains. 2 vols. 16mo. 10s. cloth; morocco, 21s.
Dr. John Lindley's Theory and Practice of Horticulture; or, an Attempt to explain the principal Operations of Gardening upon Physiological Grounds: Being the Second Edition of the Theory of Horticulture, much enlarged; with 93 Woodcuts. 8vo. 21s.
Dr. John Lindley's Introduction to Botany. New Edition, with corrections and copious Additions. 2 vols. 8vo. with Plates and Woodcuts, 24s.
Linwood.—Anthologia Oxoniensis, sive Florilegium e Lusibus poeticis diversorum Oxoniensium Græcis et Latinis decerptum. Curante Gulielmo Linwood, M.A. 8vo. 14s.
Lorimer's Letters to a Young Master Mariner on some Subjects connected with his Calling. Fcp. 8vo. price 5s. 6d.
Loudon's Encyclopædia of Gardening: Comprising the Theory and Practice of Horticulture, Floriculture, Aboriculture, and Landscape-Gardening. With 1,000 Woodcuts. 8vo. 50s.
Loudon's Encyclopædia of Trees and Shrubs, or Aboretum et Fructicetum Britannicum abridged: Containing the Hardy Trees and Shrubs of Great Britain, Native and Foreign, Scientifically and Popularly Described. With about 2,000 Woodcuts. 8vo. 50s.
Loudon's Encyclopædia of Agriculture: Comprising the Theory and Practice of the Valuation, Transfer, Laying-out, Improvement, and Management of Landed Property, and of the Cultivation and Economy of the Animal and Vegetable Productions of Agriculture. With 1,100 Woodcuts. 8vo. 31s. 6d.
Loudon's Encyclopædia of Plants: Comprising the Specific Character, Description, Culture, History, Application in the Arts, and every other desirable Particular respecting all the Plants found in Great Britain. With upwards of 12,000 Woodcuts. 8vo. price £3. 13s. 6d.
Loudon's Encyclopædia of Cottage, Farm, and Villa Architecture and Furniture. New Edition, edited by Mrs. Loudon; with more than 2,000 Woodcuts. 8vo. 63s.
Loudon's Hortus Britannicus; or, Catalogue of all the Plants found in Great Britain. New Edition, corrected by Mrs. Loudon. 8vo. 31s. 6d.
Mrs. Loudon's Lady's Country Companion; or, How to Enjoy a Country Life Rationally. Fourth Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Mrs. Loudon's Amateur Gardener's Calendar, or Monthly Guide to what should be avoided and done in a Garden. Second Edition, revised. Crown 8vo. with Woodcuts, 7s. 6d.
Low's Elements of Practical Agriculture; comprehending the Cultivation of Plants, the Husbandry of the Domestic Animals, and the Economy of the Farm. New Edition; with 200 Woodcuts. 8vo. 21s.
Macaulay.—Speeches of the Right Hon. Lord Macaulay. Corrected by Himself. 8vo. 12s.
Macaulay.—The History of England from the Accession of James II. By the Right Hon. Lord Macaulay. New Edition. Vols. I. and II. 8vo. 32s.; Vols. III. and IV. 36s.
Lord Macaulay's History of England from the Accession of James II. New Edition of the first Four Volumes of the Octavo Edition, revised and corrected. 7 vols. post 8vo. 6s. each.
Lord Macaulay's Critical and Historical Essays contributed to The Edinburgh Review. Four Editions:—
1. A Library Edition (the Eighth), in 3 vols. 8vo. price 36s.
2. Complete in One Volume, with Portrait and Vignette. Square crown 8vo price 21s. cloth; or 30s. calf.
3. Another New Edition, in 3 vols. fcp. 8vo. price 21s. cloth.
4. The People's Edition, in 2 vols. crown 8vo. price 8s. cloth.
Macaulay.—Lays of Ancient Rome, with Ivry and the Armada. By the Right Hon. Lord Macaulay. New Edition. 16mo. price 4s. 6d. cloth; or 10s. 6d. bound in morocco.
Lord Macaulay's Lays of Ancient Rome. With numerous Illustrations, Original and from the Antique, drawn On Wood by George Scharf, jun. Fcp. 4to. 21s. boards; or 42s. bound in morocco.
Mac Donald.—Poems. By George Mac Donald, Author of Within and Without. Fcp. 8vo. 7s.
Mac Donald.—Within and Without: A Dramatic Poem. By George Mac Donald. Fcp. 8vo. 4s. 6d.
Mac Dougall.—The Theory of War illustrated by numerous Examples from History. By Lieutenant-Colonel Mac Dougall, Commandant of the Staff College. Second Edition, revised. Post 8vo. with Plans, 10s. 6d.
Mac Dougall.—The Campaigns of Hannibal, arranged and critically considered, expressly for the use of Students of Military History. By Lieut.-Col. P. L. Mac Dougall, Commandant of the Staff College. Post 8vo. 7s. 6d.
M'Dougall.—The Eventful Voyage of H.M. Discovery Ship Resolute to the Arctic Regions in search of Sir John Franklin and the Missing Crews of H.M. Discovery Ships Erebus and Terror, 1852, 1853, 1854. By George F. M'Dougall, Master. With a coloured Chart, Illustrations in Lithography, and Woodcuts. 8vo. 21s.
Sir James Mackintosh's Miscellaneous Works: Including his Contributions to The Edinburgh Review. Complete in One Volume; with Portrait and Vignette. Square crown 8vo. 21s. cloth; or 30s. bound in calf; or in 3 vols. fcp. 8vo. 21s.
Sir James Mackintosh's History of England from the Earliest Times to the final Establishment of the Reformation. 2 vols. 8vo. 21s.
Macleod.—The Elements of Political Economy. By Henry Dunning Macleod, Barrister-at-Law. 8vo. 16s.
Macleod.—The Theory and Practice of Banking: With the Elementary Principles of Currency, Prices, Credit, and Exchanges. By Henry Dunning Macleod, Barrister-at-Law. 2 vols. royal 8vo. 30s.
M'Culloch's Dictionary, Practical, Theoretical, and Historical, of Commerce, and Commercial Navigation. Illustrated with Maps and Plans. New Edition, corrected; with Supplement. 8vo. 50s. cloth; half-russia, 55s.
M'Culloch's Dictionary, Geographical, Statistical, and Historical, of the various Countries, Places, and principal Natural Objects in the World. Illustrated with Six large Maps. New Edition, revised. 2 vols. 8vo. 63s.
Maguire.—Rome; its Ruler and its Institutions. By John Francis Maguire, M.P. With a Portrait of Pope Pius IX. Post 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Mrs. Marcet's Conversations on Natural Philosophy, in which the Elements of that Science are familiarly explained. Thirteenth Edition, enlarged and corrected; with 34 Plates. Fcp. 8vo. price 10s, 6d.
Mrs. Marcet's Conversations on Chemistry, in which the Elements of that Science are familiarly explained and illustrated by Experiments. New Edition, improved. 2 vols. fcp. 8vo. 14s.
Martineau.—Studies of Christianity: A Series of Original Papers, now first collected, or New. By James Martineau. Crown 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Martineau.—Endeavours after the Christian Life: Discourses. By James Martineau. 2 vols. post 8vo. price 7s. 6d. each.
Martineau.—Hymns for the Christian Church and Home. Collected and edited by James Martineau. Eleventh Edition, 12mo. 3s. 6d. cloth, or 5s. calf; Fifth Edition, 32mo. 1s. 4d. cloth, or 1s. 8d. roan.
Martineau.—Miscellanies: Comprising Essays chiefly religious and controversial. By James Martineau. Crown 8vo. 9s.
Maunder's Scientific and Literary Treasury: A new and popular Encyclopædia of Science and the Belles-Lettres; including all Branches of Science, and every subject connected with Literature and Art. Fcp. 8vo. 10s.
Maunder's Biographical Treasury; consisting of Memoirs, Sketches, and brief Notices of above 12,000 Eminent Persons of All Ages and Nations, from the Earliest Period of History: Forming a complete Dictionary of Universal Biography. Fcp. 8vo. 10s.
Maunder's Treasury of Knowledge, and Library of Reference; comprising an English Dictionary and Grammar, a Universal Gazetteer, a Classical Dictionary, a Chronology, a Law Dictionary, a Synopsis of the Peerage, numerous useful Tables, &c. Fcp. 8vo. 10s.
Maunder's Treasury of Natural History; or, a Popular Dictionary of Animated Nature: In which the Zoological Characteristics that distinguish the different Classes, Genera, and Species, are combined with a variety of interesting Information illustrative of the Habits, Instincts, and General Economy of the Animal Kingdom. With 900 Woodcuts. Fcp. 10s.
Maunder's Historical Treasury; comprising a General Introductory Outline of Universal History, Ancient and Modern, and a Series of Separate Histories of every principal Nation that exists; their Rise, Progress, and Present Condition, the Moral and Social Character of their respective Inhabitants, their Religion, Manners, and Customs, &c. Fcp. 8vo. 10s.
Maunder's Treasury of Geography, Physical, Historical, Descriptive, and Political; containing a succinct Account of Every Country in the World: Preceded by an Introductory Outline of the History of Geography; a Familiar Inquiry into the Varieties of Race and Language exhibited by different Nations; and a View of the Relations of Geography to Astronomy and the Physical Sciences. Completed by William Hughes, F.R.G.S. With 7 Maps and 16 Steel Plates. Fcp. 8vo. 10s.
Merivale.—A History of the Romans under the Empire. By the Rev. Charles Merivale, B.D., late Fellow of St. John's College, Cambridge. 8vo. with Maps.
Vols. I and II. comprising the History to the Fall of Julius Cæsar. Second Edition. 28s.
Vol. III. to the Establishment of the Monarchy by Augustus. Second Edition. 14s.
Vols. IV. and V. from Augustus to Claudius, B.C. 27 to A.D. 54. 32s.
Vol. VI. from the Reign of Nero, A.D. 54, to the Fall of Jerusalem, A.D. 70. 16s.
Merivale.—The Fall of the Roman Republic: A Short History of Last Century of the Commonwealth. By the Rev. C. Merivale, B.D., late Fellow of St. John's College, Cambridge. New Edition. 12mo. 7s. 6d.
Merivale (Miss).—Christian Records: A Short History of Apostolic Age. By L. A. Merivale. Fcp. 8vo. price 7s. 6d.
Miles.—The Horse's Foot and How to Keep it Sound. Eighth Edition; with an Appendix on Shoeing in general, and Hunters in particular. 12 Plates and 12 Woodcuts. By W. Miles, Esq. Imperial 8vo. 12s. 6d.
Miles's Plain Treatise on Horse-Shoeing. With Plates and Woodcuts. Second Edition. Post 8vo. 2s.
Milner's History of the Church of Christ. With Additions by the late Rev. Isaac Milner, D.D., F.R.S. A New Edition, revised, with additional Notes by the Rev. T. Grantham, B.D. 4 vols. 8vo. 52s.
James Montgomery's Poetical Works: Collective Edition; with the Author's Autobiographical Prefaces, complete in One Volume; with Portrait and Vignette. Square crown 8vo. 10s. 6d. cloth; morocco, 21s.—Or, in 4 vols. fcp. 8vo. with Plates, 14s.
Moore.—The Power of the Soul over the Body, considered in relation to Health and Morals. By George Moore, M.D. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
Moore.—Man and his Motives. By George Moore, M.D. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
Moore.—The Use of the Body in relation to the Mind. By G. Moore, M.D. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
Moore.—Memoirs, Journal, and Correspondence of Thomas Moore. Edited by the Right Hon. Lord John Russell, M.P. With Portraits and Vignettes. 8 vols. post 8vo. £4. 4s.
Thomas Moore's Poetical Works: Comprising the Author's Recent Introductions and Notes. The Traveller's Edition, crown 8vo. with Portrait, 12s. 6d. cloth; morocco by Hayday, 21s.—Also the Library Edition, with Portrait and Vignette, medium 8vo. 21s. cloth; morocco by Hayday, 42s.—And the First collected Edition, in 10 vols. fcp. 8vo. with Portrait and 19 Plates, 35s.
Moore.—Poetry and Pictures from Thomas Moore: Being Selections of the most popular and admired of Moore's Poems, copiously illustrated with highly-finished Wood Engravings from original Designs by eminent Artists. Fcp. 4to. price 21s. cloth; or 42s. bound in morocco by Hayday.
Moore's Songs, Ballads, and Sacred Songs. New Edition, printed in Ruby Type; with the Notes, and a Vignette from a Design by T. Creswick, R.A. 32mo. 2s. 6d.—An Edition in 16mo. with Vignette by R. Doyle, 5s.; or 12s. 6d. morocco by Hayday.
Moore's Sacred Songs, the Symphonies and Accompaniments, arranged for One or more Voices, printed with the Words, Imperial 8vo.
[Nearly ready.
Moore's Lalla Rookh: An Oriental Romance. With 13 highly-finished Steel Plates from Original Designs by Corbould, Meadows, and Stephanoff, engraved under the superintendence of the late Charles Heath. New Edition. Square crown 8vo. 15s. cloth; morocco, 28s.
Moore's Lalla Rookh. New Edition, printed in Ruby Type; with the Preface and Notes from the collective edition of Moore's Poetical Works, and a Frontispiece from a Design by Kenny Meadows. 32mo. 2s. 6d.—An Edition in 16mo. with Vignette, 5s.; or 12s. 6d. morocco by Hayday.
Moore's Lalla Rookh. A New Edition, with numerous Illustrations from original Designs by John Tenniel, engraved on Wood by the Brothers Dalziel. Fcp. 4to.
[In preparation.
Moore's Irish Melodies. A New Edition, with 13 highly-finished Steel Plates, from Original Designs by eminent Artists. Square crown 8vo. 21s. cloth; or 31s. 6d. bound in morocco.
Moore's Irish Melodies, printed in Ruby Type; with the Preface and Notes from the collective edition of Moore's Poetical Works, the Advertisements originally prefixed, and a Portrait of the Author. 32mo. 2s. 6d. An Edition in 16mo. with Vignette, 5s.; or 12s. 6d. morocco by Hayday.
Moore's Irish Melodies. Illustrated by D. Maclise, R.A. New Edition; with 161 Designs, and the whole of the Letterpress engraved on Steel, by F. P. Becker. Super-royal 8vo. 31s. 6d. boards; or £2. 12s. 6d. morocco.
Moore's Irish Melodies, the Music, namely, the Symphonies and Accompaniments by Sir John Stevenson and Sir Henry Bishop, printed with the Words. Imperial 8vo. 31s. 6d. cloth; or 42s. half-bound in morocco.
The Harmonised Airs from Moore's Irish Melodies, as originally arranged for Two, Three, or Four Voices, printed with the Words. Imp. 8vo. 15s. cloth; or 25s. half-bound in morocco.
Moore's National Melodies, with Music. National Airs and other Songs, now first collected. By Thomas Moore. The Music, for Voice and Pianoforte, printed with the Words. Imp. 8vo. 31s. 6d. cloth; or 42s. half-bound in morocco.
Moore's Epicurean. New Edition, with the Notes from the Collective Edition of Moore's Poetical Works; and a Vignette engraved on Wood from an original Design by D. Maclise, R.A. 16mo. 5s. cloth; or 12s. 6d. morocco by Hayday.
Morell.—Elements of Psychology; Part I., containing the Analysis of the Intellectual Powers. By J. D. Morell, M.A., One of Her Majesty's Inspectors of Schools. Post 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Morning Clouds. Second and cheaper Edition, revised throughout, and printed in a more convenient form. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Morton.—The Resources of Estates: A Treaties on the Agricultural Improvement and General Management of Landed Property. By John Lockhart Morton, Civil and Agricultural Engineer; Author of Thirteen Highland and Agricultural Prize Essays. With 25 Lithographic Illustrations. Royal 8vo. 31s. 6d.
Moseley's Mechanical Principles of Engineering and Architecture. Second Edition, enlarged; with numerous Woodcuts. 8vo. 24s.
Memoirs and Letters of the late Colonel Armine Mountain, Aide-de-Camp to the Queen, and Adjutant-General of Her Majesty's Forces in India. Edited by Mrs. Mountain. Second Edition, Portrait. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
Mure.—A Critical History of the Language and Literature of Ancient Greece. By William Mure, of Caldwell. Vols. I. to III. 8vo. price 36s.; Vol. IV. 15s.; and Vol. V. 18s.
Murray's Encyclopædia of Geography, comprising a complete Description of the Earth: Exhibiting its Relation to the Heavenly Bodies, its Physical Structure, the Natural History of each Country, and the Industry, Commerce, Political Institutions, and Civil, and Social State of All Nations. Second Edition; with 82 Maps, and upwards of 1,000 other Woodcuts. 8vo. 60s.
Murray.—French Finance and Financiers under Louis the Fifteenth. By James Murray. 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Neale.—The Closing Scene; or, Christianity and Infidelity contrasted in the Last Hours of Remarkable Persons. By the Rev. Erskine Neale, M.A. 2 vols. fcp. 8vo. 6s. each.
Normanby (Marquis of).—A Year of Revolution. From a Journal kept in Paris in the Year 1848. By the Marquis of Normanby, K.G. 2 vols. 8vo. 24s.
Ogilvie.—The Master-Builder's Plan; or, the Principles of Organic Architecture as indicated in the Typical Forms of Animals. By George Ogilvie, M.D. Post 8vo. with 72 Woodcuts, price 6s. 6d.
Oldacre—The last of the Old Squires. A Sketch. By Cedric Oldacre, Esq., of Sax-Normanbury. Crown 8vo. 9s. 6d.
Osborn.—Quedah; or, Stray Leaves from a Journal in Malayan Waters. By Captain Sherard Osborn, R.N., C.B. With a coloured Chart and tinted Illustrations. Post 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Osborn.—The Discovery of the North-West Passage by H.M.S. Investigator, Captain R. M'Clure, 1850-1854. Edited by Captain Sherard Osborn, C.B. Second Edition, revised; with Portrait, Chart, and Illustrations. 8vo. price 15s.
Professor Owen's Lectures on the Comparative Anatomy and Physiology of the Invertebrate Animals, delivered at the Royal College of Surgeons. Second Edition, with 235 Woodcuts. 8vo. 21s.
Professor Owen's Lectures on the Comparative Anatomy and Physiology of the Vertebrate Animals, delivered at the Royal College of Surgeons in 1844 and 1846. Vol. I. 8vo. 14s.
Memoirs of Admiral Parry, the Arctic Navigator. By his Son, the Rev. E. Parry, M.A., Domestic Chaplain to the Bishop of London. Fourth Edition; with a Portrait and coloured Chart of the North-West Passage. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Pattison.—The Earth and the Word; or, Geology for Bible Students. By S. R. Pattison, F.G.S. Fcp. 8vo. with coloured Map, 3s. 6d.
Dr. Pereira's Elements of Materia Medica and Therapeutics. Third Edition, enlarged and improved from the Author's Materials by A. S. Taylor, M.D., and G. O. Rees, M.D. Vol. I. 8vo. 28s.; Vol. II. Part I. 21s.; Vol. II. Part II. 26s.
Dr. Pereira's Lectures on Polarised Light, together with a Lecture on the Microscope. 2d Edition, enlarged from the Author's Materials by Rev. B. Powell, M.A. Fcp. 8vo. Woodcuts, price 7s.
Perry.—The Franks, from their First Appearance in History to the Death of King Pepin. By Walter C. Perry, Barrister-at-Law. 8vo. 12s. 6d.
Peschel's Elements of Physics. Translated from the German, with Notes, by E. West. With Diagrams and Woodcuts. 3 vols. fcp. 8vo. 21s.
Phillips's Elementary Introduction to Mineralogy. A New Edition, with extensive Alterations and Additions, by H. J. Brooke, F.R.S., F.G.S.; and W. H. Miller, M.A., F.G.S. With numerous Woodcuts. Post 8vo. 18s.
Phillips.—A Guide to Geology. By John Phillips, M.A., F.R.S., F.G.S., &c. Fourth Edition, corrected; with 4 Plates. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Phillips.—Figures and Descriptions of the Palæozoic Fossils of Cornwall, Devon, and West Somerset: observed in the course of the Ordnance Geological Survey of that District. By John Phillips, F.R.S., F.G.S., &c. 8vo. with 60 Plates, 9s.
Piesse's Art of Perfumery, and Methods of Obtaining the Odours of Plants; with Instructions for the Manufacture of Perfumes for the Handkerchief, Scented Powders, Odorous Vinegars, Dentifrices, Pomatums, Cosmétiques, Perfumed Soap, &c.; and an Appendix on the Colours of Flowers, Artificial Fruit Essences, &c. Second Edition; Woodcuts. Crown 8vo. 8s. 6d.
Captain Portlock's Report on the Geology of the County of Londonderry, and of Parts of Tyrone and Fermanagh, examined and described under the Authority of the Master-General and Board of Ordnance. 8vo. with 48 Plates, 24s.
Powell.—Essays on the Spirit of the Inductive Philosophy, the Unity of Worlds, and the Philosophy of Creation. By the Rev. Baden Powell, M.A., &c. Crown 8vo. Woodcuts, 12s. 6d.
Powell.—Christianity without Judaism. A Second Series of Essays on the Unity of Worlds and of Nature. By the Rev. Baden Powell, M.A., &c. Crown 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Pycroft.—The Collegian's Guide; or, Recollections of College Days: Setting forth the Advantages and Temptations of a University Education. By the Rev. J. Pycroft, B.A. Second Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
Pycroft's Course of English Reading; or, How and What to Read: Adapted to every taste and capacity. With Literary Anecdotes. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Pycroft's Cricket-Field; or, the Science and History of the Game of Cricket. Second Edition; Plates and Woodcuts. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Quatrefages (A. De).—Rambles of a Naturalist on the Coasts of France, Spain, and Sicily. By A. De Quatrefages, Memb. Inst. Translated by E. C. Otté. 2 vols. post 8vo. 15s.
Raikes (C.)—Notes on the Revolt in the North-Western Provinces of India. By Charles Raikes, Judge of the Sudder Court, and late Civil Commissioner with Sir Colin Campbell. 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Raikes (T.)—Portion of the Journal kept by Thomas Raikes, Esq., from 1831 to 1847: Comprising Reminiscences of Social and Political Life in London and Paris during that period. 2 vols. crown 8vo. price 12s.
Rarey.—A Complete Treatise on the Science of Handling, Educating, and Taming all Horses; with a full and detailed Narrative of his Experience and Practice. By John S. Rarey, of Ohio, U.S. In 1 vol. with numerous Illustrations. [Just ready.
Dr. Reece's Medical Guide: Comprising a complete Modern Dispensatory, and a Practical Treatise on the distinguishing Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, Cure, and Palliation of the Diseases incident to the Human Frame. Seventeenth Edition, corrected and enlarged by Dr. H. Reece. 8vo. 12s.
Reade.—The Poetical Works of John Edmund Reade. New Edition, revised and corrected, with Additional Poems. 4 vols. fcp. 8vo. 20s.
Rees.—Personal Narrative of the Siege of Lucknow, from its commencement to its Relief by Sir Colin Campbell. By L. E. Rees, one of the surviving Defenders. Third Edition. Post 8vo. price 9s. 6d.
Rich's Illustrated Companion to the Latin Dictionary and Greek Lexicon; Forming a Glossary of all the Words representing Visible Objects connected with the Arts, Manufactures, and Every-Day Life of the Ancients. With about 2,000 Woodcuts from the Antique. Post 8vo. 21s.
Richardson.—Fourteen Years' Experience of Cold Water: Its Uses and Abuses. By Captain M. Richardson. Post 8vo. Woodcuts, 6s.
Horsemanship; or, the Art of Riding and Managing a Horse, adapted to the Guidance of Ladies and Gentlemen on the Road and in the Field: With Instructions for Breaking-in Colts and Young Horses. By Captain Richardson, late of the 4th Light Dragoons. With 5 Plates. Square crown 8vo. 14s.
Household Prayers for Four Weeks: With additional Prayers for Special Occasions. To which is added a Course of Scripture Reading for Every Day in the Year. By the Rev. J. E. Riddle, M.A. Crown 8vo. 3s. 6d.
Riddle's Complete Latin-English and English-Latin Dictionary, for the use of Colleges and Schools. New Edition, revised and corrected. 8vo. 21s.
Riddle's Diamond Latin-English Dictionary. A Guide to the Meaning, Quality, and right Accentuation of Latin Classical Words. Royal 32mo. 4s.
Riddle's Copious and Critical Latin-English Lexicon, founded on the German-Latin Dictionaries of Dr. William Freund. Post 4to. 31s. 6d.
Rivers's Rose-Amateur's Guide; containing ample Descriptions of all the fine leading variety of Roses, regularly classed in their respective Families; their History and Mode of Culture. Sixth Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 3s. 6d.
Dr. E. Robinson's Greek and English Lexicon to the Greek Testament. A New Edition, revised and in great part re-written. 8vo. 18s.
Mr. Henry Rogers's Essays selected from Contributions to the Edinburgh Review. Second Edition, with Additions. 3 vols. fcp. 8vo. 21s.
Dr. Roget's Thesaurus of English Words and Phrases classified and arranged so as to facilitate the Expression of Ideas and assist in Literary Composition. Fifth Edition, revised and improved. Crown 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Ronalds's Fly-Fisher's Entomology: With coloured Representation of the Natural and Artificial Insects, and a few Observations and Instructions on Trout and Grayling Fishing. Fifth Edition; with 20 new-coloured Plates. 8vo. 14s.
Rowton's Debater: A Series of complete Debates, Outlines of Debates, and Questions for Discussion; with ample References to the best Sources of Information. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
Dr. C. W. Russell's Life of Cardinal Mezzofanti: With an Introductory Memoir of eminent Linguists, Ancient and Modern. With Portrait and Facsimiles. 8vo. 12s.
The Saints our Example. By the Author of Letters to my Unknown Friends, &c. Fcp. 8vo. 7s.
Scherzer.—Travels in the Free States of Central America: Nicaragua, Honduras, and San Salvador. By Dr. Carl Scherzer. 2 vols. post 8vo. 16s.
SchimmelPenninck (Mrs.)—Life of Mary Anne SchimmelPenninck, Author of Select Memoirs of Port Royal, and other Works. Edited by her relation, Christiana C. Hankin. 2 vols. post 8vo. with Portrait, 15s.
Dr. L. Schmitz's History of Greece, from the Earliest Times to the Taking of Corinth by the Romans, b.c. 146, mainly based upon Bishop Thirlwall's History. Fifth Edition, with Nine new Supplementary Chapters on the Civilisation, Religion, Literature, and Arts of the Ancient Greeks, contributed by C. H. Watson, M.A. Trin. Coll. Camb.; also a Map of Athens and 137 Woodcuts designed by G. Scharf, jun., F.S.A. 12mo. 7s. 6d.
Scoffern (Dr.)—Projectile Weapons of War and Explosive Compounds. By J. Scoffern, M.B. Lond., late Professor of Chemistry in the Aldersgate College of Medicine. Third Edition. Post 8vo. Woodcuts, 8s. 6d.
Scrivenor's History of the Iron Trade, from the Earliest Records to the Present Period. 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Sir Edward Seaward's Narrative of his Shipwreck, and consequent Discovery of certain Islands in the Caribbean Sea. 2 vols. post 8vo. 21s.
The Sermon in the Mount. Printed by C. Whittingham, uniformly with the Thumb Bible. 61mo. 1s. 6d.
Sewell (Miss).—New Edition of the Tales and Stories of the Author of Amy Herbert, in 9 vols. crown 8vo. price £1. 10s. cloth; or each work complete in one volume, separately as follows:—
| AMY HERBERT | 2s. 6d. |
| GERTRUDE | 2s. 6d. |
| The EARL'S DAUGHTER | 2s. 6d. |
| The EXPERIENCE of LIFE | 2s. 6d. |
| CLEVE HALL | 3s. 6d. |
| IVORS, or the Two Cousins | 3s. 6d. |
| KATHARINE ASHTON | 3s. 6d. |
| MARGARET PERCIVAL | 5s. 0d. |
| LANETON PARSONAGE | 4s. 6d. |
By the same Author, New Editions,
Ursula: A Tale of English Country Life. 2 vols. fcp. 8vo. 12s.
Readings for every Day in Lent: Compiled from the Writings of Bishop Jeremy Taylor. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Readings for a Month preparatory to Confirmation: Compiled from the Works of Writers of the Early and of the English Church. Fcp. 8vo. 4s.
Bowdler's Family Shakspeare: In which nothing is added to the Original Text; but those words and expressions are omitted which cannot with propriety be read aloud. Illustrated with 36 Woodcut Vignettes. The Library Edition, in One volume, medium 8vo. price 21s.; a Pocket Edition, in 6 vols. fcp. 8vo. price 5s. each.
Sharp's New British Gazetteer, or Topographical Dictionary of the British Islands and narrow Seas: Comprising concise Descriptions of about 60,000 Places, Seats, Natural Features, and Objects of Note, founded on the best authorities. 2 vols. 8vo, £2. 16s.
Short Whist; its Rise, Progress, and Laws: With Observations to make any one a Whist-Player. Containing also the Laws of Piquet, Cassino, Ecarté, Cribbage, Backgammon. By Major A. New Edition; with Precepts for Tyros, by Mrs. B. Fcp. 8vo. 3s.
Sinclair.—The Journey of Life. By Catherine Sinclair, Author of The Business of Life. Fcp. 8vo. 5s.
Sir Roger De Coverley. From the Spectator. With Notes and Illustrations, by W. Henry Wills; and 12 Wood Engravings from Designs by F. Tayler. Crown 8vo. 10s. 6d.; or 21s. in morocco by Hayday.
The Sketches: Three Tales. By the Authors of Amy Herbert, The Old Man's Home, and Hawkstone. Fcp. 8vo. price 4s. 6d.
Smee's Elements of Electro-Metallurgy. Third Edition, revised; with Electrotypes and numerous Woodcuts. Post 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Smith (G.)—History of Wesleyan Methodism. By George Smith, F.A.S., Author of Sacred Annals, &c. Vol. I. Wesley and his Times; Vol. II. The Middle Age of Methodism, from 1791 to 1816. Crown 8vo. 10s. 6d. each.
Smith (G. V.)—The Prophecies relating to Nineveh and the Assyrians. Translated from the Hebrew, with Historical Introductions and Notes, exhibiting the principal Results of the recent Discoveries. By George Vance Smith, B.A. Post 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Smith (J.)—The Voyage and Shipwreck of St. Paul: With Dissertations on the Life and Writings of St. Luke, and the Ships and Navigation of the Ancients. By James Smith, F.R.S. With Charts, Views, and Woodcuts. Crown 8vo. 8s. 6d.
A Memoir of the Rev. Sydney Smith. By his Daughter, Lady Holland. With a Selection from his Letters, edited by Mrs. Austin. New Edition. 2 vols. 8vo. 28s.
The Rev. Sydney Smith's Miscellaneous Works. Including his Contributions to The Edinburgh Review. Three Editions:—
1. A Library Edition (the Fourth), in 3 vols. 8vo. with Portrait, 36s.
2. Complete in One Volume, with Portrait and Vignette. Square crown, 8vo. 21s. cloth, or 30s. bound in calf.
3. Another New Edition, in 3 vols. fcp. 8vo. 21s.
The Rev. Sydney Smith's Elementary Sketches of Moral Philosophy, delivered at the Royal Institution in the Years 1804 to 1806, Fcp. 8vo. 7s.
Snow.—Two Tears' Cruise off Tierra del Fuego, the Falkland Islands, Patagonia, and in the River Plate: A Narrative of Life in the Southern Seas. By W. Parker Snow, late Commander or the Mission Yacht Allen Gardiner. With Charts and Illustrations, 2 vols. post 8vo. 24s.
Robert Southey's Complete Poetical Works; containing all the Author's last Introductions and Notes. The Library Edition, complete in One Volume, with Portraits and Vignette. Medium 8vo. 21s. cloth; 42s. bound in morocco.—Also, the First collected Edition, in 10 vols. fcp. 8vo. with Portrait and 19 Vignettes, price 35s.
The Life and Correspondence of the late Robert Southey. Edited by his Son, the Rev. C. C. Southey, M.A. With Portraits, &c. 6 vols. post 8vo. price 63s.
Southey's Doctor, complete in One Volume. Edited by the Rev. J. W. Warter, B.D. With Portrait, Vignette, Bust, and coloured Plate. Square crown 8vo. 21s.
Southey's Life of Wesley; and Rise and Progress of Methodism. Fourth Edition, edited by Rev. C. C. Southey, M.A. 2 vols. crown 8vo. 12s.
Spencer.—Essays, Scientific, Political, and Speculative. By Herbert Spencer, Author of Social Statics. Reprinted chiefly from Quarterly Reviews. 8vo. 12s. cloth.
Spencer.—The Principles of Psychology. By Herbert Spencer, Author of Social Statics. 8vo. 16s.
Stephen.—Lectures on the History of France. By the Right Hon. Sir James Stephen, K.C.B., LL.D. Third Edition. 2 vols. 8vo. 24s.
Stephen.—Essays in Ecclesiastical Biography; from The Edinburgh Review. By the Right Hon. Sir James Stephen, K.C.B., LL.D. Third Edition. 2 vols. 8vo. 24s.
Stonehenge.—The Dog in Health and Disease: Comprising the various Modes of Breaking and using him for Hunting, Coursing, Shooting, &c.; and including the Points or Characteristics of Toy Dogs. By Stonehenge. 8vo. with numerous Illustrations.
[In the press.
Stonehenge.—The Greyhound: Being a Treatise on the Art of Breeding, Rearing, and Training Greyhounds for Public Running; their Diseases and Treatment: Containing also Rules for the Management of Coursing Meetings, and for the Decision of Courses. By Stonehenge. With Frontispiece and Woodcuts. Square crown 8vo. 21s.
Stow's Training System, Moral Training School, and Normal Seminary for preparing Schoolmasters and Governesses. Tenth Edition; Plates and Woodcuts. Post 8vo. 6s
Strickland.—Lives of the Queens of England. By Agnes Strickland. Dedicated, by express permission, to Her Majesty. Embellished with Portraits of every Queen, engraved from the most authentic sources. Complete in 8 vols. post 8vo. 7s. 6d. each.
Memoirs of the Life and Services of Rear-Admiral Sir William Symonds, late Surveyor of the Navy. Edited by J. A. Sharp. 8vo. with Illustrations, price 21s.
Taylor.—Loyola: and Jesuitism in its Rudiments. By Isaac Taylor. Post 8vo. Medallion, 10s. 6d.
Taylor.—- Wesley and Methodism. By Isaac Taylor. Post 8vo. Portrait, 10s. 6d.
Thacker's Courser's Annual Remembrancer and Stud-Book: Being an Alphabetical Return of the Running at all Public Coursing Clubs in England, Ireland, and Scotland, for the Season 1857-8; with the Pedigrees (as far as received) of the Dogs. By Robert Abram Welsh, Liverpool. 8vo. 21s.
*** Published annually in October.
Bishop Thirlwall's History of Greece. Library Edition; with Maps. 8 vols. 8vo. £3.—An Edition in 8 vols. fcp. 8vo. with Vignette Titles, 28s.
Thomson's Seasons. Edited by Bolton Corney, Esq. Illustrated with 77 fine Wood Engravings from Designs by Members of the Etching Club. Square crown 8vo. 21s. cloth; or 36s. bound in morocco.
Thomson (the Rev. Dr.)—An Outline of the necessary Laws of Thought: A Treatise on Pure and Applied Logic. By William Thomson, D.D. New Edition. Fcp. 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Thomson's Tables of Interest, at Three, Four, Four-and-a-Half, and Five per Cent., from One Pound to Ten Thousand, and from 1 to 365 Days, in a regular progression of single Days; with Interest at all the above Rates, from One to Twelve Months, and from One to Ten Years. Also, numerous other Tables of Exchange, Time, and Discounts. New Edition. 12mo. 8s.
The Thumb Bible; or, Verbum Sempiternum. By J. Taylor. Being an Epitome of the Old and New Testaments in English Verse. Reprinted from the Edition of 1693. 64mo. 1s. 6d.
Tighe and Davis.—Annals of Windsor; Being a History of the Castle and Town. With some account of Eton and Places adjacent. By R. R. Tighe, Esq.; and J. E. Davis, Esq., Barrister-at-Law. With numerous Illustrations. 2 vols. royal 8vo. £4. 4s.
Tooke.—History of Prices, and of the State of the Circulation, during the Nine Years from 1848 to 1856 inclusive. Forming Vols. V. and VI. of Tooke's History of Prices; and comprising a copious Index to the whole work. By Thomas Tooke, F.R.S. and William Newmarch. 2 vols. 8vo. 52s. 6d.
Townsend.—Modern State Trials, revised and illustrated with Essays and Notes. By W. C. Townsend, Esq., M.A., Q.C. 2 vols. 8vo. 30s.
Trollope.—Barchester Towers: a Novel. By Anthony Trollope. New and cheaper Edition, complete in One Volume. Crown 8vo. 5s.
Trollope.—The Warden. By Anthony Trollope. Post 8vo. 10s. 6d.
The Traveller's Library: A Collection of original Works well adapted for Travellers and Emigrants, for School-room Libraries, the Libraries of Mechanics' Institutions, Young Men's Libraries, the Libraries of Ships, and similar purposes. The separate volumes are suited for School Prizes, Presents to Young People, and for general instruction and entertainment. The Series comprises fourteen of the most popular of Lord Macaulay's Essays, and his Speeches on Parliamentary Reform. The department of Travels contains some account of eight of the principal countries of Europe, as well as Travels in four districts of Africa, in four of America, and in three of Asia. Madame Pfeiffer's First Journey round the World is included, and a general account of the Australian Colonies. In Biography and History will be found Lord Macaulay's Biographical Sketches of Warren Hastings, Clive, Pitt, Walpole, Bacon, and others, besides Memoirs of Wellington, Turenne, F. Arago, &c., an Essay on the Life and Genius of Thomas Fuller, with Selections from his Writings, by Mr. Henry Rogers; and a history of the Leipsic Campaign, by Mr. Gleig,—which is the only separate account of this remarkable campaign. Works of Fiction did not come within the plan of the Traveller's Library, but the Confessions of a Working Man, by Souvestre, which is indeed a fiction founded on fact, has been included, and has been read with unusual interest by many of the working classes, for whose use it is especially recommended. Dumas's story of the Maitre d'Armes, though in form a work of fiction, gives a striking picture of an episode in the history of Russia. Amongst the works on Science and Natural Philosophy, a general view of Creation is embodied in Dr. Kemp's Natural History of Creation, and in his Indications of Instinct remarkable facts in natural history are collected. Dr. Wilson has contributed a popular account of the Electric Telegraph. In the volumes on the Coal-Fields, and on the Tin and other Mining Districts of Cornwall, is given an account of the mineral wealth of England, the habits and manners of the miners, and the scenery of the surrounding country. It only remains to add, that among the Miscellaneous Works are a Selection of the best Writings of the Rev. Sydney Smith, Lord Carlisle's Lectures and Addresses, an account of Mormonism, by the Rev. W. J. Conybeare, an exposition of Railway management and mismanagement by Mr. Herbert Spencer, an account of the Origin and Practice of Printing, by Mr. Stark; and an account of London, by Mr. M'Culloch—To be had, in complete Sets only, at £5. 5s. per Set, bound in cloth and lettered.
![]() The Traveller's Library may also be
had as originally issued in 102 parts, 1s. each, forming 50 vols. 2s.
6d. each; or any separate parts or volumes.
The Traveller's Library may also be
had as originally issued in 102 parts, 1s. each, forming 50 vols. 2s.
6d. each; or any separate parts or volumes.
Sharon Turner's Sacred History of the World, Philosophically considered, in a Series of Letters to a Son. 3 vols. post 8vo. 31s. 6d.
Sharon Turner's History of England during the Middle Ages; Comprising the Reigns from the Norman Conquest to the Accession of Henry VIII. 4 vols. 8vo. 50s.
Sharon Turner's History of the Anglo-Saxons, from the Earliest Period to the Norman Conquest. 3 vols. 36s.
Dr. Turton's Manual of the Land and Fresh-Water Shells of Great Britain. With Figures of each of the kinds. New Edition, with Additions by Dr. J. E. Grey, F.R.S., &c., Keeper of the Zoological Collection in the British Museum. Crown 8vo. with 12 coloured Plates, price 15s. cloth.
Dr. Ure's Dictionary of Arts, Manufactures, and Mines: Containing a clear Exposition of their Principles and Practice. Fourth Edition, much enlarged. With nearly 1,600 Woodcuts. 2 vols. 8vo. 60s.
Uwins.—Memoir of Thomas Uwins. R.A. By Mrs. Uwins. With Letters to his Brothers during Seven Years spent in Italy; and Correspondence with the late Sir Thomas Lawrence, Sir C. L. Eastlake, A. E. Chalon, R.A., and other distinguished persons. 2 vols. post 8vo.
Van der Hoeven's Handbook of Zoology. Translated from the Second Dutch Edition by the Rev. William Clark, M.D., F.R.S., Professor of Anatomy in the University of Cambridge; with additional References by the Author. 2 vols. 8vo. with 24 Plates of Figures, price 60s. cloth; or separately, Vol. I. Invertebrata, 30s., and Vol. II. Vertebrata, 30s.
Vehse.—Memoirs of the Court, Aristocracy, and Diplomacy of Austria. By Dr. E. Vehse. Translated from the German by Franz Demmler. 2 vols. post 8vo. 21s.
Von Tempsky.—Mitla; or, Incidents and Personal Adventures on a Journey in Mexico, Guatemala, and Salvador in the Years 1853 to 1855: With Observations on the Modes of Life in those Countries. By G. F. Von Tempsky. With numerous Illustrations. 8vo. 18s.
Wade.—England's Greatness: Its Rise and Progress In Government, Laws, Religion, and Social Life; Agriculture, Commerce, and Manufactures; Science, Literature and Arts, from the Earliest Period to the Peace of Paris. By John Wade, Author of the Cabinet Lawyer, &c. Post 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Wanderings in the Land of Ham. By a Daughter of Japhet. Post 8vo. 8s. 6d.
Waterton.—Essays on Natural History, chiefly Ornithology. By C. Waterton, Esq. With an Autobiography of the Author, and Views of Walton Hall. 2 vols. fcp. 8vo. 5s. each.
Waterton's Essays on Natural History. Third Series; with a Continuation of the Autobiography, and a Portrait of the Author. Fcp. 8vo. 6s.
Webster and Parkes's Encyclopædia of Domestic Economy; comprising such subjects as are most immediately connected with House-keeping: viz. The Construction of Domestic Edifices, with the Modes of Warming, Ventilating, and Lighting them—A description of the various Articles of Furniture, with the Nature of their Materials—Duties of Servants—&c. With nearly 1,000 Woodcuts. 8vo. 50s.
Weld.—Vacations in Ireland. By Charles Richard Weld, Barrister-at-Law. Post 8vo. 10s. 6d.
Weld.—A Vacation Tour in the United States and Canada. By C. R. Weld, Barrister. Post 8vo. 10s. 6d.
West.—Lectures on the Diseases of Infancy and Childhood. By Charles West, M.D., Physician to the Hospital for Sick Children; Physician-Accoucheur to, and Lecturer on Midwifery at, St. Bartholomew's Hospital. 8vo. 14s.
Willich's Popular Tables for ascertaining the Value of Lifehold, Leasehold, and Church Property, Renewal Fines, &c. With numerous additional Tables—Chemical, Astronomical, Trigonometrical, Common and Hyperbolic Logarithms; Constants, Squares, Cubes, Roots, Reciprocals, &c. Fourth Edition. Post 8vo. 10s.
Wilmot's Abridgment of Blackstone's Commentaries on the Laws of England, in a series of Letters from a Father to his Daughter. 12mo. 6s. 6d.
Wilson's Bryologia Britannica: Containing the Mosses of Great Britain and Ireland systematically arranged and described according to the Method of Bruch and Schimper; with 61 illustrative Plates. Being a New Edition, enlarged and altered, of the Muscologia Britannica of Messrs. Hooker and Taylor. 8vo. 42s.; or, with the Plates coloured, price £4. 4s.
Yonge.—- A New English-Greek Lexicon: Containing all the Greek Words used by Writers of good authority. By C. D. Yonge, B.A. Second Edition, revised. Post 4to. 21s.
Yonge's New Latin Gradus: Containing Every Word used by the Poets of good authority. For the use of Eton, Westminster, Winchester, Harrow, and Rugby Schools; King's College, London; and Marlborough College. Fifth Edition. Post 8vo. 9s.; or, with Appendix of Epithets, 12s.
Yonge's School Edition of Horace.—Horace, with, concise English Notes for Schools and Students. By the Rev. J. E. Yonge, King's College, Cambridge; Assistant Master at Eton. Part I. Odes and Epodes, 12mo. 3s.; Part II. Satires and Epistles, 3s. 6d.
Youatt—The Horse. By William Youatt. With a Treatise of Draught. New Edition, with numerous Wood Engravings, from Designs by William Harvey. (Messrs. Longman and Co.'s Edition should be ordered.) 8vo. 10s.
Youatt.—The Dog. By William Youatt. A New Edition; with numerous Engravings, from Designs by W. Harvey. 8vo. 6s.
Young.—The Christ of History: An Argument grounded in the Facts of His Life on Earth. By John Young, LL.D. Second Edition. Post 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Young.—The Mystery; or, Evil and God. By John Young, LL.D. Post 8vo. 7s. 6d.
Zumpt's Grammar of the Latin Language. Translated and adapted for the use of English Students by Dr. L. Schmitz, F.R.S.E.: With numerous Additions and Corrections by the Author and Translator. 8vo. 14s.
"The chequered and perilous existence of a Catholic missionary consecrating himself to the cure of souls in the wilds of Texas and Western America, his physical and moral struggles, are here portrayed with a vivid truthfulness well calculated to arrest the sympathy of our readers.... This book requires no further recommendation from as than the analysis here given. Since the perusal of Livingstone's Africa, we have read no traveller's journal with more instruction and pleasure. It is eminently suggestive, too."
Leader.
"Domenech's tone throughout is one of profound conviction; and the hardships which he encountered, and which he relates with so much simplicity and modesty as to enforce belief, are proof that he took his mission to heart. In the two journeys he performed to America—journeys that would have supplied a diffuse book-maker with matter for many volumes, the Abbé was almost every day exposed to dangers of his life—sometimes from the climate, sometimes from the privations to which he was subjected, now from the rough character of the country he constantly compelled to traverse in his spiritual journeys, anon from the violence of colonists or Indians.... It will be seen that readers who expect an infinity of enjoyment from these missionary adventures will not be disappointed."
Daily Telegraph.
"The good and brave young Abbé Domenech, whose personal narrative we may at once say we have found more readable and more informing than a dozen volumes of ordinary adventure, is not unworthy to be named with Huc in the annals of missionary enterprise; and we know not how to give him higher praise. We speak of personal characteristics, and in these—in the qualifications for a life of self-denying severity, not exercised under the protecting shadow of a cloister, but in hourly conflict with danger and necessity—the one looks to us like a younger brother in likeness to the other. His account of Texas, its physical geography, its earlier and later history, its populations, settled and nomad, and of the history and customs of the Indian tribes and their forms of religious worship, is concisely full and clear; and now that the new destiny of these regions is beginning to unfold itself, we recommend to particular attention the few pages in which all that is worth knowing about their past and present condition is summed up.... To us, the pages in which the Abbé Domenech confesses the trials and sorrows of his own heart are the most interesting of his book. They bear the stamp of a perfect and most touching sincerity; and, as we read them, we are more and more impressed with the truth which they convey to all churches and all sects. It has been well said, that Heaven is a character before it is a place. The lesson which this personal narrative of a poor missionary teaches, stems to us to be that religion is a life before it is a dogma."
Saturday Review.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of First Impressions of the New World, by
Isabella Strange Trotter
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK FIRST IMPRESSIONS OF THE NEW WORLD ***
***** This file should be named 18634-h.htm or 18634-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/1/8/6/3/18634/
Produced by Robert Cicconetti, Martin Pettit and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This
file was produced from images generously made available
by the Canadian Institute for Historical Microreproductions
(www.canadiana.org))
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, is critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card
donations. To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.
*** END: FULL LICENSE ***