
The Project Gutenberg EBook of Talks about Flowers., by M. D. Wellcome This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license Title: Talks about Flowers. Author: M. D. Wellcome Release Date: August 19, 2012 [EBook #40534] Language: English Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK TALKS ABOUT FLOWERS. *** Produced by Jennifer Linklater, sp1nd and the Online Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was produced from images generously made available by The Internet Archive)

DEXTER SMITH.
PUBLISHED FOR THE AUTHOR,
BY I. C. WELLCOME,
YARMOUTH, ME.
Entered according to Act of Congress, in the year 1881,
By I. C. WELLCOME,
In the Office of the Librarian of Congress at Washington.
PRINTED BY B. THURSTON & CO.,
PORTLAND, MAINE.
To all Flower Lovers who may read these pages, we come with kindly greetings. To you we dedicate our Work.
Encouraged by the many testimonials of favor with which our Flower Sketches have been received, which have appeared in the Boston Journal, Portland Transcript, and the leading Floricultural journals, we were induced to prepare this volume, intending it to be made up chiefly of those articles revised and enlarged for this purpose; but after entering upon this work, we found so little that was adapted for use, nearly every page has been written while the sheets were passing through the press.
Before we were aware, the printed matter had exceeded our proposed limits, and we were obliged to enlarge the work by additional pages, and even then omit our chapter of "Floricultural Notes," for we wished to put the book at a low price, that it might reach the masses. As it is, we are sure that we have given you a great amount of valuable information, and just such as amateurs need, respecting the habits and requirements of those flowers which are best adapted for general cultivation, and in a form specially new and attractive, combining the history and literature of flowers, with description and mode of culture.
It may be deemed strange that we should omit from a work of this character a "Talk" about the Queen of Flowers, but the subject was so full that we thought best to devote the space to other varieties and refer our readers to our recently published "Essay on Roses,"—advertised in another part of this work—in which they will find the subject fully treated.
We would here acknowledge our obligation to Mr. James Vick for the beautiful Bouquet of Flowers which constitutes our Frontispiece.
Mrs. M. D. Wellcome.
Yarmouth, Me., June 9, 1881.
Dexter Smith.
 IHAVE been thinking for some time of writing a few articles
about flowers, not for the entertainment nor instruction
of those who have extensive gardens artistically laid out,
and fine conservatories with skilled gardeners to care for
the rare and costly plants, but for those, who, like myself, have only
a few beds filled with flowers, cared for by one's own self.
IHAVE been thinking for some time of writing a few articles
about flowers, not for the entertainment nor instruction
of those who have extensive gardens artistically laid out,
and fine conservatories with skilled gardeners to care for
the rare and costly plants, but for those, who, like myself, have only
a few beds filled with flowers, cared for by one's own self.
Every year there is a marked advance in the floricultural kingdom. Books and periodicals devoted to flower culture are on the increase; florists are enlarging their domain; catalogues are scattered broadcast, and as free as autumn leaves, some of them beautiful with their colored plates, handsome enough to frame. Very many of the literary, religious, and political journals of the day have their floral department, in which the ladies gossip of their experience and exchange opinions, and we doubt if any column is read with greater interest.
What recreation for the mind and body more pure, refining, healthful, than that of the cultivation of flowers? How they reveal the Father's love, and wisdom, and power! How perfect his work! Very fully have I realized this, as I have examined bud, blossom, and leaf under the microscope. Its magnifying power when applied to man's work, reveals coarseness and imperfection, but in God's work only reveals new beauties, and greater perfectness. The tiny flower, the details of which cannot be perceived by the eye unaided,[10] when magnified, surprises us with its loveliness. We wonder and adore that Being whose hand created its perfect form and arranged its tints with so much harmony. The study of flowers with the microscope is one of never failing delight, and one needs not the costly instrument to enjoy this study. The round open glass, the size of a half dollar, and costing the same, serves every needful purpose.
Not only have I enjoyed the examination of flowers, but also of insect life, specially of those terrible pests to our rosebushes and some other plants—the aphides. I have closely watched their development, from the tiny egg to the portly insect, so filled with the juice of the leaf, that like it, he is green all over. First I observe a little speck of red in the egg—then it has slight motion—next it runs about, and the spot is a little larger, sometimes it is black. Sometimes the baby aphis is all red. Now and then I find a different sort mixed up with them; the body is much larger and transparent white. Some have wings. Skeletons, or more properly, cast-off skins, are often seen, but with the closest observation I have never been able to trace these to their source. Once, I was sure that a fellow was divesting himself of his overcoat, and I watched him till my eyes ached too badly for further investigation.
These insects are the cows of a certain species of ant, and I am sure they are quite welcome to all I have, provided they will have their yard on other premises, though I would like to detain them long enough to see the milking process. Some have seen it and written about it, so, strange as it seems, it is no fiction.
In this series of articles which I have entitled "Talks About Flowers," I shall, in a very informal manner, talk to you about just those matters pertaining to the flower garden, in which beginners and amateurs are interested; to this class I belong; I am not a skilled florist, my experience is limited; I am only a student in the lower classes of floriculture, but I dearly love my lessons. I am[11] acquiring knowledge both from books and personal observation, and I shall enjoy imparting to those not so favored with time and resources the results of this study, believing it will be duly appreciated by my readers, and their interest in the cultivation of flowers be thereby increased. I shall talk to you about the sowing of seeds, the arrangement of your garden, the plants with which to stock it, treating of them historically and descriptively, with mode of culture. I shall talk to you about the most desirable bulbs, about climbing plants, hanging pots, and the window garden, and shall seek to meet in all these the wishes of many inquirers.
 ONCE more I take my pen in hand," as the old time
epistle was wont to begin. While a "Young Farmer"
discourseth of matters pertaining to the farm, I propose
to talk to farmers' wives and daughters of matters
relating to the flower garden. This article is specially dedicated
to them, and not to them as a whole, but to that class among them
who take no periodical devoted to flower culture, and find no time
even to study the various catalogues scattered broadcast, as sure
precursors of spring as are the falling leaves of autumn. Therefore
you who have your floral papers, your bay windows filled with plants,
or your fine conservatories, whether a farmer's wife or not, this is
not written for you, and you need not read any further.
ONCE more I take my pen in hand," as the old time
epistle was wont to begin. While a "Young Farmer"
discourseth of matters pertaining to the farm, I propose
to talk to farmers' wives and daughters of matters
relating to the flower garden. This article is specially dedicated
to them, and not to them as a whole, but to that class among them
who take no periodical devoted to flower culture, and find no time
even to study the various catalogues scattered broadcast, as sure
precursors of spring as are the falling leaves of autumn. Therefore
you who have your floral papers, your bay windows filled with plants,
or your fine conservatories, whether a farmer's wife or not, this is
not written for you, and you need not read any further.
There are many farmers' wives who give little attention to the cultivation of flowers. Busy lives the most of them lead, and their indoor work shuts them off largely from the enjoyment of those beauties nature has so lavishly spread around them. It is a pity that any of them should say, "I have no time to waste over flowers; they bring neither food nor clothing."
Call that wasted time when tired, nervous, fretful perhaps, you leave the heated rooms and run out to see if the seeds you sowed last week have come up, or how the seedlings you set out are thriving? To look at that opening rosebud, pick off the withered leaves from the geranium, stir the earth a bit around that heliotrope, and linger over the dear little pansies as their bright faces are up-turned[13] to greet you and cheer you with their diversified beauty? Gather a few; they will bloom all the more because of it. There, now, don't you feel nicely rested? The feeling of fretfulness is all gone. Refreshed in body and mind, you resume your housework, and accomplish it much more effectively than if you had kept right on, so tired and all out of sorts. Better far these moments of out-door recreation than blue pill or bitters. All this is anticipatory of the "good time coming" to you this summer. That kind husband of yours when he goes to the store to buy his garden seeds, or order them from abroad, is going to include an equal number of flower seeds. He would have done it long ago but he did not think anything about it. But you are going to give him a hint this spring. You can tell him that in the general seed box there is one corner where are certain dainty little packages labeled Candytuft—purple, carmine, white or mixed; Mignonnette, Aster, Balsam, Pink, Petunia, Sweet Peas, etc., etc., and you tell him that those Sweet Peas bloom the most fragrant blossoms for five months, while his "Extra Early," whether "Blue Peter" or "Blue Tom Thumb," last only a little while. So as he goes on his way he will think to himself, "Wife works hard; she makes capital butter and keeps the house real tidy, and I guess I must indulge her." When he returns home he gives you those little packages, in each tiny brown seed of which there lies hidden a beautiful life—a life that shall, by loving care, develop "the red, white and blue" in settings of emerald, the influence of which shall be felt by the entire household, and bring forth a fruitage of brightness, gladness and love.
It may be that you live remote from the village store, or perhaps there may not be kept there a good, reliable assortment of flower seeds, so I will tell you what to do in that case, for I wish to be helpful every step of the way. You must send to some good florist for what you want, enclosing stamps, if for an amount less than one dollar. You have your seeds now, and some of them need to be[14] started in the house in order to secure early flowers, Asters, Petunias, Pinks, Pansies, Snapdragon and Sweet Peas. Sift your earth through a coarse sieve. A little sharp sand is good to mix with it. Shallow boxes are best, except for the peas. I use cigar boxes. Dampen the earth, then sow thickly in rows, cover lightly with more soil, dampen again, label, cover with paper so that the moisture may not evaporate rapidly, and place in a sunny window. Daily sprinkle through a fine rose pot, or with your fingers lightly if you have none. However good your seeds may be, they will not grow if kept dry, and will rot if kept too wet. The seedlings must be nursed with care, not too much sun while tender. I do not thin out mine till I transplant to the border, but many do, potting them singly. Peas can be set out earliest of any. Sunny days in May often tempt one to bed out their tender plants, and sow seed in open ground; then come cold nights, when the fragile seedlings need a hot soapstone to their feet. It is best to wait till warm weather is fully established, and then choose a cloudy day for the work. Protect from the sun's rays till the plants are established in their new quarters. Now, all this looks like much work and care, I know, but it is only a little work, a little care each day, and it is a work that will be a restful change, and bring you better health and better feelings, and when you gather the lovely flowers from the seeds you have sown and cultured, you will not say: "My time was all misspent."
 WHEN the annual house cleaning treads heavily on the toes
of spring gardening, and one feels tempted to crowd the
work of two days into one, though sufficient for the present
is the work thereof. The bright warm days draw
one forth to spend "an hour or two" they say, and they mean it
too—with shovel or spade in hand to prepare the flower beds, but
the air is so refreshing, and there is so much to be done, that they
keep on "a little while longer," "just a few minutes more," till Sol
pours his burning rays down upon them with the unmistakable assurance
that it is near the hour of noon.
WHEN the annual house cleaning treads heavily on the toes
of spring gardening, and one feels tempted to crowd the
work of two days into one, though sufficient for the present
is the work thereof. The bright warm days draw
one forth to spend "an hour or two" they say, and they mean it
too—with shovel or spade in hand to prepare the flower beds, but
the air is so refreshing, and there is so much to be done, that they
keep on "a little while longer," "just a few minutes more," till Sol
pours his burning rays down upon them with the unmistakable assurance
that it is near the hour of noon.
These are the days that try men's souls, and women's, too; days when one wishes with Dudley Warner for a "cast iron back," but would fain add the improvement of rubber hinges; days when the inquiry is often provoked, "Will it pay?"
As we change the numerous boxes of seedlings from one position to another, that they may catch the sunbeams, "Will it pay?" As we take them out of doors these warm days, and bring them all back again at night, lest the air prove too harsh for the tender things, "Will it pay?"
Yes, we know from past experience that it will pay even a hundred fold for all our care when the restful days shall come, and we watch with hopeful hearts each bud of promise as it grows, and gather our hands full of lovely flowers, the fruitage of our seed sowing and unceasing care.
Have been bedding out to-day my old stocky geraniums, after[16] cutting off all the dead and unsightly branches. These were just packed into large boxes in the autumn—as closely as possible—dirt then thrown in to fill up the spaces, and they were put into the cellar and severely let alone till the weather admitted of their being taken out of doors.
Many throw away their geraniums, if the stalks decay by being frost-bitten or for some other cause, when often the roots are alive, and with proper care will sprout again. I had a few in my window box that were touched by frost one intense cold night in December, and died down to the roots. To my surprise, they sprouted in March, for I did not suppose they would be seemingly lifeless so long in a sunny window.
Some of my neighbors hang up their large geraniums by the roots in the cellar, and thus keep them throughout the winter nicely, but I have never been successful with this method.
My house plants are nearly all re-potted, ready to be plunged into the ground the first of June. I put in a bit of potsherd to keep the roots from going astray, then small pieces of coal for drainage, then fill with mellow sifted soil, enriched with well-rotted manure. I found it so much better last year to bed out in pots that I shall practice it more fully this summer. When the time comes in the autumn for taking them in doors, the work can be done in half the time.
My seedlings will be six weeks or more in advance than those sown in the open border. My sweet peas must go out very soon or I shall have to give them a support, they are so tall.
Now I am going to tell you about another sort of a garden—"a spick-span new" sort—and I know you will be pleased to hear about it, and I think you will want to have one of your own.
Mr. B. K. Bliss, of New York, in a note, said: "We have put[17] into your box a packet of flower seeds for the wild garden, which we think will interest you. We also send you the initial number of our new paper, "The American Garden." In this journal I find a very interesting article on "The Wild Garden," how to make it, and a description of one at the country residence of Mr. M. S. Beach, near Peekskill, from his own pen. We will quote a part of it. He says: "We plowed a strip about six feet wide all around a five-acre field, close to the fence. On this plowed ground, the seed, previously well mixed, was thrown just as it happened to come. The surface having afterwards been well smoothed over, we waited the result. This proved satisfactory. We had a wild garden indeed. The plants came up as thickly as they could grow, and flourished and blossomed as freely as though they had enjoyed all the care usually given to hot-house exotics.
"Sweet Alyssum, Mignonnette, the pretty blue Nemophila and bright colored Phlox Drummondii seemed to cover the ground. Morning Glories of every shade and delicate Cypress vines tried to cover the fences and run up every tree. Quaint little yellow and green Gourds appeared in the most unexpected places, and the whole bed seemed to be ablaze with the orange and yellow of the Eschscholtzia, Marigolds, Calendula Officinalis and Zinnias. One of the chief charms of this wild flower bed was the variety and change—not from season to season, but from day to day. Every morning would find some new, unexpected, and previously forgotten flower in bloom."
The packet of Flower Seeds for the "Wild Garden" consists of more than a hundred varieties, sufficient for a square rod of ground. There must needs be a peculiar charm in the "Wild Garden." When one wearies of the monotonous ribbon beds and geometrical designs so long in fashion, they can turn to the spot where flowers run riot at their own sweet will, and give daily surprises because sown broadcast without any regard to their names and location.[18] Multitudes there are, who, with abundance of land at their command, can have one on a large scale, others can have, but a small spot. There are many who have ground specially adapted by its wildness for the blending of the cultivated flowers with those which grow in their native dells or woods. Wild shrubs, wild flowers, wild climbers, can be transplanted to situations quite like their own. There can be ferneries and rockeries, beds of violets and wild evergreens, and combined with careless grace, such tropical plants and brilliant annuals as would give the most pleasing effect and afford a beauty wholly unique.
 "HOW shall I stock my garden?" is a question often asked
by amateurs. That depends very much on the size,
location and soil of the ground to be furnished. If the
site is elaborate, and the beds to be geometrically laid
out, much skill, artistic taste and generous expenditure is needful to
produce a fine effect. If the flower beds are cut in the lawn a
different classification and arrangement of plants will be needful.
If they consist of long beds bordering a walk, or one bed only, beneath
the front window, there needs to be a grouping of flowers
adapted to the situation. None but the "wild garden" ought to
be stocked hap-hazard style. Arrange always so that there shall be
a succession of flowers during the entire season, for if you devote
a space for those of brief duration, you will by and by have a barren
spot by no means pleasing. The most exposed situations ought,
of course, to be arranged with special reference to the best possible
effects or continuity of bloom and harmony of colors. Don't mix
in all sorts of colors and sizes of plants in any bed. Masses of
distinctive colors always have a fine effect. Where there are varieties
that have more show of flowers than of leaves, it is well to
intersperse plants whose beauty lies more in their foliage than in
blossoms.
"HOW shall I stock my garden?" is a question often asked
by amateurs. That depends very much on the size,
location and soil of the ground to be furnished. If the
site is elaborate, and the beds to be geometrically laid
out, much skill, artistic taste and generous expenditure is needful to
produce a fine effect. If the flower beds are cut in the lawn a
different classification and arrangement of plants will be needful.
If they consist of long beds bordering a walk, or one bed only, beneath
the front window, there needs to be a grouping of flowers
adapted to the situation. None but the "wild garden" ought to
be stocked hap-hazard style. Arrange always so that there shall be
a succession of flowers during the entire season, for if you devote
a space for those of brief duration, you will by and by have a barren
spot by no means pleasing. The most exposed situations ought,
of course, to be arranged with special reference to the best possible
effects or continuity of bloom and harmony of colors. Don't mix
in all sorts of colors and sizes of plants in any bed. Masses of
distinctive colors always have a fine effect. Where there are varieties
that have more show of flowers than of leaves, it is well to
intersperse plants whose beauty lies more in their foliage than in
blossoms.
The beautiful Coleuses, Achyranthes and Alternanthera, with their richly colored leaves, and Pyrethrums with their vivid green[20] lancelated foliage, are very effective for this purpose. Cannas are very fine among tall, free blooming plants, particularly for centers. Care ought always to be had in selections, so that a tall and coarse plant shall never have for its surroundings the low and delicate growers. Imagine the effect of a gorgeous California Sunflower or a towering Hollyhock in the midst of a bed of Pansies, or Tea Roses, or a Dahlia in a bed of Verbenas! Have your large stocky plants in a bed by themselves, unless it be as a background border for the more delicate flowers. A long bed running beside a fence, or one beneath the windows of a dwelling-house, can have, with good effect, a dense background of shrubs or Pompone Dahlias, or even the taller Dahlias, if relieved by a fence. Where there is a large bed directly beneath the front windows, a good arrangement is to have, first, trailing vines that shall cover far up the sides of the dwelling. For this, the Ipomœas are very appropriate; of these there are numerous varieties. I. Bona Nox, with its large fragrant blossoms, which however, expand in the evening; Mexicana Grandiflora Alba, immense flowers of white, long tube, a native of Mexico; grows to the height of ten feet. I. Hederacea Superba is bright blue, with white margin, Ivy-like foliage, and I. Fol Mormoratis, a new Japanese variety, with foliage beautifully mottled and marbled with white; Coccinea, or "Star" Ipomea bears a great profusion of small flowers, scarlet striped with white. With any of these, vines of the Canary Bird Flower intermingled, would have a superb effect; the light green, deeply lacinated leaves and bright, yellow fringed flowers, proving a marked contrast to the foliage and blossoms of the Ipomea. It is a very rapid grower, and will climb and branch out ten feet or more. In front of these climbers, or whatever others may be preferred, a row of Sweet Peas, quite thickly set, can be trained so as to fully cover the vines below the flowering branches, and to conceal the unsightliness of these low down, a row of Pyrethrums or some dwarf compact plants would be attractive.[21] Then a walk, if the bed is sufficiently wide. The plants on the opposite side can be arranged so as to have those of medium height next to the path, and low bedding ones for the foreground. Verbenas are very fine for this, and so is the Double Portulaca. For an edging, many things are appropriate; whether one desires merely a low green, or a border of dwarf blooming plants. For the latter, we know of nothing prettier than the new dwarf Candytuft, Tom Thumb. Its habit is low and bushy, and its clusters of white blossoms continue a very long time.
Mr. Vick has for several years recommended Thrift as the best edging plant for northern climates. It is easily propagated from cuttings; every piece will make a plant, if taken in the fall or spring, and is perfectly hardy. It bears tiny clusters of pink flowers, and the foliage is fine for floral work.
In arranging your garden stock study the adaptions of your plants to certain positions. Some require for their best development, a great deal of sunshine, others require somewhat sheltered positions. Portulacas revel in dry and sunny spots, laughing at drought, while Pansies love a cool and moist situation, therefore to bed them in a sandy soil, and a position where they would be exposed to the intense sunshine of mid-day, and the Portulaca in the sheltered, moist situation would be a great mistake.
Coleuses ought not to be set in a very open sunny place, but with plants that will serve as a protection somewhat, or they will lose their vivid markings. We observed this first with C. Shah; when exposed to a strong light, the rich, velvety maroon changed to a dull color hue, but when partially shaded it was of a very deep, rich color. The next summer we had the beautiful Pictus, and its leaves looked as though they were indeed painted with yellow, brown and green, but exposed for a time to the direct sunshine nearly all day, it changed to a dark green, with brown markings, and, robbed of its gold, it possessed no special beauty. We speak only[22] of our own experience, which has not been limited by any means to these two varieties. We have had a few that would retain their distinctive markings well, even in quite an exposed situation.
In the arrangement of your garden, have it adapted to its surroundings. The broad leaved Palms, the Tropical Caladiums, the stately Cannas, the Cape Jessamine and Crape Myrtle are in perfect harmony with the well kept lawn and stately mansion, but quite out of place in the simple border of a vegetable garden, or rough grass-plot belonging to a low, plain cottage.
I will tell you of a bit of a garden furnished in harmony with its surroundings. It was rudely dug and roughly finished by two very small hands. It was a very wee bed, indeed. It was fenced on the west side by a rough board shed; on the north by an old stump; the other side and end had no protection. Without any method of arrangement, or reference to artistic effects, here was massed the following assortment: Monks Hood, Bachelors Buttons, Butter and Eggs, Star of Bethlehem, Poppies and Marigolds; these last more odorous than fragrant. Old fashioned flowers truly. But they harmonized with their surroundings, and the little pale faced child thought them very beautiful.
It is not essential to harmony however, that the flower bed be rudely prepared, though the cot be lowly and its surroundings rough; the garden, however small, can be neatly prepared, provided there are stronger and older hands than those of the little maid referred to, and there may be a display of taste in the arrangement of the most common flowers, in our day at least, where beautiful varieties are within reach of all. But it was not so fifty years ago; boxes of flower seeds were not to be found in the shops; catalogues were not scattered broadcast like autumn leaves and as free; "a greenhouse at your door," was not then, as now, a verity. School girls exchanged their limited floral treasures, and now and then a slip could be begged from the fortunate possessor of a few house[23] plants. But if greenhouse flowers were rare, there were thousands in the meadows, on the hills, in the woods; the sweet May flowers, unknown then to the little maiden as the Trailing Arbutus, the Anemone, Hepatica, Columbine, Violets of different hues, Wild Roses, Gay Lilies, and late in autumn, the lovely fringed Gentian:
What could be more lovely among the garnered treasures of the greenhouse? But our talk is a long one, and we will defer to another what we have further to say on this subject.
 THIS is one of the most desirable of our annuals, coming into
bloom early in the season and continuing in flower till
frost. They are very effective in massed colors, and make
fine ribbon beds. Contrasting shades should be selected.
A writer in the Garden says that the following are very desirable
for this purpose: "Phlox Lothair, salmon shaded with violet; Mons
Henrique, brilliant reddish crimson; Venus, pure white; Mons
Goldenschugh, rosy violet; Spenceri, dark rosy lilac. An excellent
front edging for this ribbon bed is the variegated Periwinkle.
In order to grow them thoroughly well, and so to insure a
lengthened period of blooming, the ground should be deeply trenched
and well enriched with good manure from the farm yard, and not
more than six heads of bloom should be allowed to each plant. Thus
treated, when planted in long lines, it is difficult to convey an impression
of these and similar varieties."
THIS is one of the most desirable of our annuals, coming into
bloom early in the season and continuing in flower till
frost. They are very effective in massed colors, and make
fine ribbon beds. Contrasting shades should be selected.
A writer in the Garden says that the following are very desirable
for this purpose: "Phlox Lothair, salmon shaded with violet; Mons
Henrique, brilliant reddish crimson; Venus, pure white; Mons
Goldenschugh, rosy violet; Spenceri, dark rosy lilac. An excellent
front edging for this ribbon bed is the variegated Periwinkle.
In order to grow them thoroughly well, and so to insure a
lengthened period of blooming, the ground should be deeply trenched
and well enriched with good manure from the farm yard, and not
more than six heads of bloom should be allowed to each plant. Thus
treated, when planted in long lines, it is difficult to convey an impression
of these and similar varieties."
There are many beautiful varieties of color; deep blood purple, brilliant scarlet, large blue with white eye, not truly a blue, but the nearest approach to it of any; Leopoldii, splendid deep pink, with white eye; Carmine Queen and Violet with a large white eye; Vick's New Double White, the only one that is reliable, from seed, to produce double flowers. Then there are the buffs and the stripes, crimson striped with white, and rose and purple. Mr. Vick, who makes a specialty of the Drummondii Phlox, they being a favorite with him, devotes acres to their cultivation, and who has been experimenting[25] with them for several years, has produced several new sorts that are very fine; one of them is deep red with a fringed edge. There have been very marked improvements since this plant was first discovered in Texas by Mr. Drummond, a botanical collector sent out by the Glasgow Botanical Society, and it was one of the last, if not the very last, sent to Europe by him. He soon after went to Cuba, where he died of a fever in the prime of life. Sir N. J. Hooker named the plant after its discoverer as a memento. When first discovered it was very inferior to the flowers seen in our gardens, as is very apparent from an engraving of it taken from a drawing in Mr. Vick's possession, which was made in 1838, three years after its discovery. It is given in Vick's Magazine for September, 1880, with the items we have cited. The word Phlox signifies flame, and is supposed to have been applied in allusion to the flame-like form of the bud.
A lady who had excellent success with her seedlings, started early in a box, and bedded out one cloudy day in May, says: "I was surprised to find flowers on the plants when so young and small. I don't believe they had been transplanted five days before half of them had flowers, and soon the rest followed, and for more than two months my bed has been glorious—a mass of bright colors more beautiful than any carpet or dress pattern ever made. It is near the middle of September, and if the frost will only keep away, it looks as though they would keep on flowering for years. Tell everybody to have a Phlox bed and how to do it. It is the cheapest pleasure possible."
CARRIE, in Vick's Magazine.
This we must have, for it is one of the most beautiful annuals cultivated. So varied its hues! So abundant its blooms! Not a brief season of flowering, and then naught but leaves, which are, not of themselves attractive, but an increase of blossoms from June[26] till October, and it requires quite a severe frost to mar their beauty. They have the best effect massing each color by itself, and beds of a circular form cut in the lawn and filled with Verbenas, have a superb effect. Seedlings are much the best for bedding out, they are so much stronger and more bushy. Those plants offered for sale in pots, having one tall slender stem, crowned with a cluster of flowers, are almost worthless for the garden. True, if you get a healthy one, by layering and pegging down, you can sometimes get good plants, but you had better purchase seedlings by the dozen as they are offered in boxes and baskets, or order them of the florist by mail or express, and you will have plants that will grow compact, bloom early and profusely, with far better foliage than the puny straggling ones rooted from cuttings. One objection to purchasing seedlings by the clump is, I am well aware, the fact that they are not labeled as to color, and everybody wants to know that they will have at least one scarlet, one white, purple, and so on, and unless the color is peeping through the bud, one must buy with the risk of not knowing the desired color. This is the true state of the case so far as my own observation extends. But it need not be so, and we presume it is not so everywhere. Seedlings can be raised of course with each of the leading colors separate, and those in greatest demand in large quantities to meet the wants of the general public, while the fancy sorts can be of mixed varieties. Those who raise their own seedlings, usually buy a paper of mixed sorts, so in that case they are no better off than those who purchase seedlings of the florist, and as their facilities are far greater for raising early plants, it seems preferable as a general thing, to buy of them, for these reasons. In order to have good sizable plants for bedding out in May and June that will bloom in August, seed must be sown the first of March, at the latest, for it takes weeks for the little dry sticks to germinate, and then they are such slow growers, unless under the most favorable circumstances, they do not become strong[27] vigorous plants by the time you want to bed them out. Few can care for them properly while their sunny windows are full of choice house plants, so that as a rule, we should deem it preferable to wait until May, and then purchase the large budded seedlings, which so quickly unfold their beautiful flowers to brighten the garden, when it is almost barren of bloom. They do not cost usually more than sixty cents per dozen, and one is saved from so much care.
However, for the benefit of those who prefer to sow their own seed, we will give directions for the best method. First, be sure that the seed is new. Don't sow old seed for it will not germinate. If you have no hot bed, make one in a box or pan by putting in a layer of quite fresh horse manure for bottom heat; over this a layer of coarse sand; then fill the box with finely sifted soil, mixed with at least one-third fine sand. Make it smooth; then in little rows drop the seeds, not very sparsely, for all may not germinate, and if too thick when they come up they can be thinned out. Press the seed down with a bit of flat board, sift a little soil over them and then dampen by light spraying with tepid water; a brush dipped in water makes a gentle sprayer. Cover with paper, glass, or what is better, a bit of soft flannel wrung out of water laid on the surface, as it keeps the soil damp without sprinkling, by being wet as it dries. The soil must be kept moist, not soaking wet, for however helpful to germination a previous soaking may be, when sown the seed must not be drenched, and the same rules are equally applicable to the seedlings, for in either case rot would surely follow. It is just here where the special care is requisite to insure success. After the plants have come up, the flannel or paper must be removed and the seedlings given sunshine and air, though it is well to have a glass over the top of the box for a week or more, as more moisture is thereby secured; but there ought to be an aperture for the admission of air. When two or more leaves are developed, it is well to prick them out into other boxes or pots, if they[28] are too thick for free growth; not all, a part can remain undisturbed. They should be gradually hardened as a preparation for out-door life, by being placed in cool situations. While heat is essential to start the seed into growth, it is not beneficial to the plants, and those who have a cold frame had better remove the plants to it as soon as the temperature will admit.
In bedding out, an open situation is preferable. The ground should be well dug and enriched, with well-decomposed manure, and if the soil is heavy a liberal mixture of sand. A situation where the morning sun will not strike them before the dew is off in the morning is best, as this is one cause of the mildew or rust which so frequently saps the vitality of the leaves. In order to promote their spreading, it is a good plan to fasten down some of the branches when sufficiently flexible to the ground, and for this, nothing is more convenient than hair-pins. All the seed vessels should be pricked off in order to secure the best results, as much of the strength of the plant goes to them if allowed to remain. One can afford to be very liberal in gathering the flowers, for the more liberally they are picked off, the more rapidly buds form and develop. As it was with one of Bunyan's characters:
The wise man says: "There is that scattereth and yet increaseth."
A florist says that "to grow Verbenas successfully, plant them in beds cut in the turf. Chop the turf well and thoroughly mix with it a good share of well-decomposed stable manure; never, on any account plant them in old and worn-out garden soil as they will most assuredly fail. Give them a change of soil each season, as they do not thrive well two years in the same bed."
As a house plant the Verbena is not a success. It is most always sickly, and infested with red spiders. They cannot be kept over winter in a cellar; it is growth or death.
Verbenas were first introduced into Europe about fifty years ago from South America, and a few years later into this country. They have been greatly improved, and the varieties are very numerous. Many are fragrant. The only hardy sort is Montana, a native of Colorado. It is a profuse bloomer, color, a bright rose. There are the German Hybrids, the Italian stripes, and the Drummondii from Texas. Every year brings its novelties, as with other flowers. Mr. C. E. Allen, who makes a specialty of seedling Verbenas, is sending out several fine ones this season; Silver Queen, Florence, Emma, Carroll, Ralph and Variegata are very attractive according to the descriptions.

Few things in the garden will make more show throughout the entire season, even after quite severe frosts, than a bed of Petunias from a paper of seed marked "Choicest Mixed from Show Flowers." They will produce such a profusion of flowers, charming one from day to day with their variations of markings, and of color. Some retain their distinctive characteristics, while with others they are changeful as the Kaleidoscope. Stripes, blotches, sprays, white throats, green edges, they are just lovely. Then there are the double sorts; purple with white spots, white with purple; rose color, white, purplish-crimson margined with white; lilac veined with purple; white with stripes of purple in the center of each petal, some exquisitely fringed; large and full as a rose, and some almost as sweet.
In nothing, perhaps, has there been such a wonderful improvement by culture and hybridising as the Petunia. Mr. Vick tells us how that half a century ago, he saw for the first time, a Petunia. It was a novelty—a strange flower from a flowery land, South America, and it was carefully treated in green-houses. The flower was white and small, and looked somewhat as if made of paper—such a flower as would now be destroyed if by chance seen growing accidentally in our gardens. The novelty soon subsided, and although it was ascertained that it could be grown in gardens, it did not possess sufficient merit to gain popular favor. A little later, however, about 1831, to the astonishment of the floral world, it was announced that a new Petunia, of a purple color, had been discovered in Buenos Ayres. It was first flowered and seeded in the Botanic Gardens of Glasgow, and thence seed was sent all over Europe and to America, where it soon became a great favorite. About thirty years ago a double Petunia was grown and propagated by cuttings. It was only semi-double and white, but it was the commencement of a new era in Petunia culture. Truly wonderful have been the advances in development of this beautiful flower.
The Petunia is divided into three distinct classes, the Grandiflora, Small Flowered and Double.
The Grandiflora varieties have a strong succulent growth, the flowers are not so numerous as some others, but are very large and double, frequently measuring three inches in diameter, and some kinds are exquisitely marked with various shades of violet, purple, maroon and scarlet upon white ground; some striped, others bordered, some marbled, some deeply fringed. The double Petunia gives no seed, and it is only by fertilizing single flowers with the pollen of the double that seed can be obtained. But Petunias of all kinds are easily multiplied by cuttings.
The Small Flowered class are those that make our gardens so[31] attractive with their varied hues and markings. Some of the new hybrids are of wonderful beauty. Last year gave two of the Double and Fringed sort that have been frequently noted as gems of the first water.
Mrs. Edward Roby, color, a glowing crimson-maroon, edged with pure white, very double and deeply fringed. Model of Perfection, deep maroon, heavily edged with white, and deeply fringed. These were priced last year in a Western catalogue at $1.50 each; this year they are priced at 30 cents. So one gains by waiting a year for high-priced novelties.
New Double Fringed Petunia for 1881, is President Garfield, which originated with Mr. C. E. Allen, and is thus described in his catalogue: "Color, light purple veined with deep purple magenta, edged with a broad band of an exquisite shade of green. Very novel in its appearance and a new color in double petunias; flower very large and deeply fringed. Plants strong and vigorous; one of the finest sorts ever offered." For a Petunia so unique as this, with its broad band of green, and now offered for the first time; its price, 75 cents, is low.
Shakespeare.
 I FIND my Pansies are coming up finely. My bed of Pansies
last year from "choicest mixed seed" sown in April,
began to bloom in June, and afforded me so much pleasure
with their varied beauty, that I resolved this year to
have a great many of them. I see, now that the snow has melted
from the bed, that the plants have wintered well. I had all of the
colors shown in the chromo plate of my catalogue, excepting Emperor
William, dark blue. I think that somebody else must have
got him, for my packet of seed was divided and sub-divided. King
of the Blacks was rightly named, a mere dot of yellow in the center,
and Pure White was in striking contrast, while Pure Yellow
was golden, and Odier was splendid with its dark center banded
with yellow and scarlet. Then there was copper-colored and
striped, and such rich purples with a dot of yellow. How lovely
they were! They were not very large at first, but in August after
a rain, I had superb specimens. They were bedded beneath a fruit
tree, where they were sheltered from the noonday glare. They
thrive best in a moist, partially shaded situation. The blossoms
ought to be picked as they fade, for if left to seed the strength is
taken from the plants and the blossoms are smaller.
I FIND my Pansies are coming up finely. My bed of Pansies
last year from "choicest mixed seed" sown in April,
began to bloom in June, and afforded me so much pleasure
with their varied beauty, that I resolved this year to
have a great many of them. I see, now that the snow has melted
from the bed, that the plants have wintered well. I had all of the
colors shown in the chromo plate of my catalogue, excepting Emperor
William, dark blue. I think that somebody else must have
got him, for my packet of seed was divided and sub-divided. King
of the Blacks was rightly named, a mere dot of yellow in the center,
and Pure White was in striking contrast, while Pure Yellow
was golden, and Odier was splendid with its dark center banded
with yellow and scarlet. Then there was copper-colored and
striped, and such rich purples with a dot of yellow. How lovely
they were! They were not very large at first, but in August after
a rain, I had superb specimens. They were bedded beneath a fruit
tree, where they were sheltered from the noonday glare. They
thrive best in a moist, partially shaded situation. The blossoms
ought to be picked as they fade, for if left to seed the strength is
taken from the plants and the blossoms are smaller.
This season I have sown musical Pansies. "Musical Pansies! what are they? What sort of music do they make? Will it be of the Brass Band order, or that of the hand-organ style?"
No, no! Not that coarse, harsh, loud sort at all. If you could hear their low, sweet notes, you would be enraptured. But this[34] cannot be. I call them musical, because named for the great composers, Mozart, Handel, Schiller, Goethe, Beethoven, Haydn, Mendelssohn, and Schumann. They are the "New German Pansies," of which types are given in oil colors, in the catalogue of B. F. Bliss & Sons, and represent the most beautiful strains I have ever seen. They are no fancy sketch, but drawn as true to life in color and size as it was possible to make them, if we will accept the testimony of Dr. Thurber in the American Agriculturist. He says, that "no doubt many who have seen the colored plate published by Messrs. B. F. Bliss & Sons, have supposed that the artist had exercised his imagination both as to size and the strange combinations of colors. So far from this being the case, the flowers are, if anything, rather below the real size, and as to colors, it would be impossible to conceive of any artificial colors more brilliant, or more strongly contrasted, than they are in flowers, produced by this remarkable strain of seeds."
In my childhood I knew nothing of the Pansy. The little Heartsease or Ladies' Delight, as it was then called, was alone cultivated. Mr. Vick tells us how it grew to be the fine flower now so highly prized. About sixty years ago, a very young English lady living on the banks of the Thames, had a little flower garden of her own, and one bed she filled with Pansies, selecting from her father's grounds the finest she could obtain. The gardener, seeing her interest and success, became ambitious to try his hand, and grew plants from the finest specimens. These attracted the attention of professional florists, and speedily the Pansy became a popular flower. Every country gives it a pet name—Heartsease, Fringed Violet, Trinity Flower, Butterfly flower, and Johnny-jump-up, while the French call it Pensée, from which our name of Pansy is probably derived. It means to remember or keep in mind. A floral work published in 1732, illustrates it with a colored plate, which shows it to have been then small like the Ladies' Delight.
For summer blooming plants sow seed in the house, in March or April. Cigar boxes are very suitable for seed sowing. Put in a layer of coarse sand for drainage, then one of horse manure for bottom heat. Fill with rich, mellow earth sifted and mixed with one-third silver sand, or finely pulverized leaf mold. Have it moist but not drenched. With a narrow strip of board, make tiny furrows about one and a half inches apart, and in these carefully drop the seed one by one an inch distant. Cover slightly, and press the soil firmly, then lay a piece of old soft flannel folded once or twice, and wrung lightly out of warm water, carefully over the soil, which will keep it damp. Cover with glass, and keep in a warm place. In a few days see if the covering is dry, if so damp it again, and watch for the seedlings. When they appear, remove the flannel, but still keep on the glass, not, however, so close as to exclude all air. Gradually inure them to the sunlight, and as soon as they have made four or five leaves, it is best to transplant every other one, so that they may have room to grow. Great care is needful with tender seedlings to keep them from damping off. If too wet, they will do this, or if kept too shady. Good judgment is essential for success. As the weather becomes warm, expose them at first an hour or two, to the outdoor air, and thus prepare them for early bedding out. Being hardy plants, living out of doors during the winter, with slight protection at the North, they will bear transplanting sooner than many other seedlings. A rich moist soil, and somewhat cool and shaded situation, are best adapted for their growth. For winter flowers, sow seed the last of August, or first of September, in a frame or boxes kept in a shady place.
These must be included among the essential annuals for the garden. They are one of the chief attractions of the border in the[36] autumn, when many flowers have passed their prime. This plant, like the Petunia, has in skillful hands and by hybridization, developed from a very inferior flower to one of great beauty and numerous classes, which embrace a great many varieties. They are represented by Dwarfs and by Giants, ranging intermediately from five or six inches in height to two feet. Dwarf Bouquet presents a mass of flowers with scarcely a leaf, while Tall Chrysanthemum grows to the height of two feet, and the New Victoria, Giant Emperor, Truffant's Perfection and the New Washington bear immense flowers of great beauty. The last named bears the largest flowers of any variety; sometimes they measure more than five inches across. The New Rose is of a strong habit, and the petals of its large blossoms are finely imbricated. Truffant's Fiery Scarlet and Dwarf Fiery Scarlet, are a novelty in color among Asters. Goliath is of a bushy form, and its flowers are very large. Fine colors. Victoria is a dwarf; snow-white, very double. The Crown Asters have white centers surrounded with various bright colors, and are very pretty. The Quilled Asters are quite distinct in character, the petals consisting of tubes or quills with outer blossom petals slightly reflexed. Newest Shakespeare and Diamond and Meteor are novelties of recent introduction, and come in numerous colors. We grew them last year and deem them admirable.
The native country of this plant is China, hence it has been called frequently China Aster. It had originally only a few rows of petals and a large disk. It was first discovered about a century and a half ago, by a missionary, and sent to Europe. It was first cultivated in France, and the French florists have done the most toward perfecting the flat-petaled Aster, and this style of flower is known as the French Aster. On the other hand the Germans have sought to produce fine flowers with tubular petals, and the quilled are therefore called German Asters. Within a few years, however, the Germans have rivaled the French in originating superior varieties of the flat-petaled style.
When first cultivated in France it was called Reine Marguerite, meaning Queen Daisy; afterward in England it was called China Aster, which means China Star.
Asters require a rich, deep soil. Twelve inches apart is a very good distance for the large varieties, the dwarf can be set about six inches, or even less will do. The tall kinds need to be staked, or they are liable to be blown down, or prostrated by heavy rains. Do not tie one string around the entire plant, but use several, and confine a few branches with each, so that, while having sufficient support, they may retain their natural position.

Have been sowing my Balsams to-day in a box, so as to have nice seedlings to bed out in six weeks from now. My Balsams last year were superior to any I had seen, but Mr. J. L. Childs, who rather prides himself on his plants, has sent me several packages for trial. He says: "My stock of Balsams is undoubtedly the finest in the world; all who saw them flowering the past season were astonished at their size and magnificence. The new variety (Child's Camellia Flowered Perfection), is indeed a great acquisition; its flowers are of gigantic size, and so double and perfect that they resemble small Camellias; it is also a very free bloomer. I have counted five and six hundred perfect flowers upon a plant at the same time." That is a wonderful yield, truly; I cannot expect so many, but half that number would satisfy me. The Camellia Flowered Perfection comes in nine colors; pink, scarlet, striped white and purple, mottled,[38] white and delicate pink, magenta spotted with white, crimson spotted with white, purple spotted with white, pure white, and rose-flowered perfection, lavender color, buds when half open, resemble a rosebud.
I shall sow some of the seeds in June, for autumn blooming, and shall try more fully than last year the pruning method. This is done by removing all of the branches, and then the main stock will grow two or three feet in height, and be a perfect wreath of blossoms. Another method is to remove the leader and let two or three branches remain. The flowers are larger, and the plant handsomer than when allowed to grow at its own sweet will. They do best in a light, rich soil, and a liberal supply of liquid manure will greatly advance their growth. A writer in the Gardener's Chronicle says: "Considering the very effective display that these plants make when associated with stately foliage plants in sub-tropical beds, I think they are worthy of more extended cultivation. There are few plants better adapted for the above purpose than the Balsam, being easily raised from seed, and as is well known, they are rapid growers if they are planted in a rich soil. Several samples of these plants with us are now three feet through and over two feet high, and they work admirably with such things as Castor Oils, Cannas, and the beautifully striped Japonica. The plants referred to were planted out early in June, and I am so pleased with their behaviour in the sub-tropical garden, that I intend to grow them largely another year."
I know of no reason why the Balsam might not with good cultivation thrive as well here as in England. Let us try our "level best," and see what we can do.
 MY interest in this class of plants was specially awakened
four years ago by the successful cultivation of a dozen
or more new varieties which I was induced to send for by
the reception of the catalogue of the "Innisfallen Green
houses," containing a more attractive list of geraniums, and at
lower prices than I had ever seen. I secured a Club by a little
effort, and thus obtained so many fine extras, that it was a very
agreeable surprise. I have since learned that very many others
have had a similar surprise.
MY interest in this class of plants was specially awakened
four years ago by the successful cultivation of a dozen
or more new varieties which I was induced to send for by
the reception of the catalogue of the "Innisfallen Green
houses," containing a more attractive list of geraniums, and at
lower prices than I had ever seen. I secured a Club by a little
effort, and thus obtained so many fine extras, that it was a very
agreeable surprise. I have since learned that very many others
have had a similar surprise.
The next spring I had a much larger assortment, and last year the greatest variety I ever saw. I am sure that I had sixty kinds in bloom at once. Although very small plants, as they always are when many are ordered by mail, they throve wonderfully, and with one exception, were all in flower in a few weeks, and kept on blooming till after removal in the autumn.
My method of treatment is the following: On opening the boxes
I find them packed in damp moss, many closely tied together. I
take off the oiled paper, loosen the moss packed around them, and
put them in a shallow pan, in which is sufficient tepid water to
cover the roots. After an hour or two I set them in three and four
inch pots, first putting a bit of crock over the hole in the bottom
of the pot, so as to keep the roots from going astray, then some of
the coarse siftings of soil, or small bits of coal for drainage. As
geraniums are not at all fastidious about soil, I take whatever is
available, mix a small quantity of sand with it to make it friable,
enriching with old manure. I nearly fill the pot, and then make a
hole in the center, set in the plant, press the earth firmly around it,
fill to the top and press down again, water, and set the pot in a[40]
[41]
cool and shady place for several days, then bring to the light for a
few hours, gradually accustoming them to the sunshine, until they
become fully established in their new quarters. When the weather
is sufficiently warm, I plunge the pots in the border for the summer,
covering the pots entirely. I choose a cloudy day if possible;
if otherwise, I do the work late in the afternoon, so that the intense
sunshine may not at the first beat upon them. I prefer massing
these new plants by themselves, as the effect is more pleasing than
when intermixed with other kinds. The geranium bed is the most
attractive one of my garden. It is always full of bloom, and the
varied hues commingled are very attractive. I remove all decayed
leaves, and the trusses as soon as the flowers have faded. Frequently
there will be a few decayed pips marring the beauty of a
fine truss, and these I carefully remove. All of my large stock
geraniums which have been wintered two years, I set by themselves,
and they furnish an abundance of flowers for bouquets, and
cuttings for new plants. Where one has a plenty of garden room,
they need not mind having several choice geraniums of a kind.
Slips will root well during the summer months, if set in the earth
near the parent stock, where they are shaded from the direct rays
of the sun. Care must be had to set the cuttings well down in the
soil, and firm the earth compactly around them. In this way one
can obtain with little care nice plants for the winter window garden,
which will be more shapely than those which have become
very branchy. Geraniums are ill growing plants unless pruned and
trained with skill. But they are so easily cultured, adapting themselves
to most any situation whether of shade or sunshine, are so
hardy, and bloom so freely, that we can but admire them though
they yield no fragrant flowers. There are many varieties of scented
leaved geraniums, and these mixed with the odorless blossoms
are almost an equivalent. Then the beautiful "Golden Bronzed
Zoned" geraniums, and the "Silver Margined" and "Tricolored,"[42]
are so beautiful in foliage, while Happy Thought, with its creamy
yellow leaf margined with green; Distinction, with deep green
leaves zoned with black; Mrs. Pollock with bronze red zone belted
with bright crimson margined with golden yellow, are exceedingly
ornamental. Beside these there are many perhaps equally attractive,
not often named in the general collection. Freak of
Nature, first sent out last year, is an improvement on Happy
Thought the center of pure white narrowly margined with light
green; flowers light scarlet; habit very dwarf and spreading. It
originated with Mr. Gray of England, and was awarded three first
class certificates.

BISHOP WOOD GERANIUM.
Of the numerous classes into which geraniums are divided, few only are given usually by florists. There are the Ornamental Foliage of which we have cited a few examples, and the Golden Tricolors, Silver Tricolors, Golden Bronze, Nosegay and Lilliputian Zonale; Double and single Geraniums.
We will specify a few varieties worthy of special note, as we can testify by personal observation. Bishop Wood, Madam Baltet, C. H. Wagner, Madam Thibaut, Victor Hugo, Jean Dolfus, Cassimer Perier, John Fennely, Naomi and Rose d'Amour, all double sorts. Of the single, Dr. John Denny possesses a rare beauty, and is thus described by an English writer: "Dr. John Denny, raised by J. Sisley, has quite set at rest the probability of a blue or a purple, which is a positive fact, and great honor is due to its distinguished raiser. It also possesses another novel and distinct feature. The base of the two top petals is of a bright crimson tinted with orange, which gives it a most striking appearance; this, together with its immense sized trusses, free growth and shape of blooms, renders it one of the best for pot or house decoration, and is of great acquisition." Jean Dolfus belongs to this purple magenta class, a double geranium, very beautiful. Also Zuleika, which has larger pips and trusses. It is a little more striking in color than John Denny,[43] but both are just as lovely as a geranium can possibly be. When Jealousy was sent out, there was much ado over it because it was the nearest approach toward a yellow Zonal, but it was eclipsed pretty soon by Guinea, which was an advance by a shade or two. We had the two in proximity last summer, and though but little difference, it was sufficiently marked to enable us to decide that Guinea for color, size and form, was preferable. We just get settled down on that, when we are startled by the announcement of another novelty, "New Guinea" by name, "a great improvement on Guinea, being two shades brighter." Well, well! we must have that, too, and see if in other respects as well as color, it is worthy to eclipse our favorite.
Henry Cannell—this is a new geranium, originating with Mr. John Thorp of Queens, New York, who makes a specialty of seedling geraniums, and has sent out from his grounds many of great value, one of them Happy Thought, so widely known. We have not tested H. Cannell, ours was sent from Innisfallen during the winter, and has not yet bloomed, but we are sure that it would never have received the name of the most distinguished florist in England, if it were not a superior variety.
New Life originated with Mr. H. Cannell of Swanley England, in our Centennial year, and he sent out the first thousand by subscription only, at £1 each—not one sold till the thousand were engaged! When introduced the following year to this country, stock plants were sold for $5.00 each. Now you can purchase it at prices ranging from ten cents to thirty. It is unique in color, being splashed, striped, and flecked with salmon and white on an intense scarlet ground. It is sometimes freakish, having pips with some petals salmon, others partly white and partly scarlet, others pure scarlet. But this very freak is charming, for with beautifully striped trusses there will be others thus sportive. Its habit is dwarf, compact, and its dark leaves zoned with black are very handsome. It[44] cannot be surpassed as a free bloomer. Mr. Cannell, when sending it out, expressed the wish that the day might come when there would not be a cottage in the land where New Life was not found. John Fennely, salmon striped with white, and Fairy, flaked and striped with crimson on a bluish white ground, are very pretty. Dazzle, Harry King, Richard Dean, and Jean Sisley are scarlet with white eye. Of several single white geraniums in my garden, I gave decided preference to Madame Quinet.
There is a great difference in the duration of the flowers. Victor Hugo, a splendid geranium, retains its beautiful trusses full five weeks. Bishop Wood is also admirable in this respect, and Jenny Dolfus and Naomi we believe cannot be surpassed.

Of the Sweet Scented Geraniums, we have none equal to the hybrid, Mrs. Taylor, for beauty of foliage and of flower. It is a fine grower, and for green to mix with flowers it is admirable. Dr. Livingstone, a more recent novelty, is very handsome and fragrant. Rose and Lemon scented are delicious. Lady Plymouth is a variegated rose; leaves bronzy green, fringed with creamy white, sometimes assuming a pink tinge; very ornamental. London Blue is a very rare variety of scented geranium, of heavy creeping growth, with large crimped or curled leaves covered thickly with fine spines or hairs. Seldom blooms.
We have specified a goodly number, yet but a few from the many, and we can assure you that if you have a large bed of geraniums you will greatly admire them, and feel satisfied that you have the most effective bedding plants, requiring the least care, and for[45] the smallest outlay, that you could possibly obtain. In California they grow without culture to an enormous size. From an editor's notes we cite the following:
"A little slip of geranium planted out in the spring, had grown in the summer to 150 branches, its stalk at its base four inches thick, and bearing over a thousand blooms! I saw a fence fifteen feet high, sixty-five feet long, covered with geranium vines that had clambered up one side, and then dropped down the other, filling both sides with a blanket of scarlet blossoms. It grows like weeds, and needs no care."
Geraniums are so hardy that one can leave them to the last in removing from the border in autumn. Frosts that kill Dahlia tops, and many other plants, do not harm geraniums. Some of mine, for lack of time to remove, are exposed till late without harm. The roots have great vitality, and when the stalk has frozen and rotted to the ground, a new growth will start forth, sometimes in a few weeks, and sometimes not for three months. I have had this proved by plants in my window boxes. So one need not be in a hurry to pull up the frozen geraniums. My large stocky plants I pack in dry goods boxes, filling in earth around the roots, and put them in the cellar where they have little light. The pot plants, also, are mostly put away so as to give all the available room to the cuttings rooted in the summer, and the rare and tender plants that will not live in a cellar. These cuttings make fine plants for bedding out in May or June.
In the spring the large geraniums are brought up to the open air and trimmed of their dead leaves, pruned of dead branches, and put in a large bed with the Hybrid Perpetual Roses.
 MY first Begonia was a Rex.
It thrived for several
years, and then to my
regret died, for it was
quite a favorite with me. Its large
leaves with broad silvery belt and
red dots, were very handsome.
This species thrive best in a Wardian case and are of rare beauty
and size, grown under such circumstances. A cool, moist atmosphere
is the best for them; they burn and shrivel exposed to the
intense sunlight. They are easily multiplied from the leaves. Cut
the leaf so that a small portion of the stem will remain, insert this
in a pan of damp sand, laying the leaf out flat upon the sand, upper
side uppermost. It can be retained in place by bits of stone or
small pegs. Cuts must then be made in a number of places so as
to sever the veins, thus checking the flow of sap. A callus then
forms at the base of each piece of vein where severed, and just
above it, a bud starts out, and thus a new plant is formed. It is
essential for success, that there should be bottom heat, and that
the air should be moist. A bell glass is the best to put over the
leaf, and if there is danger that the air become too moist, the glass
can be tilted up to allow of an escape. The leaves best adapted
for propagation are those neither very young nor very old, but
healthy and vigorous; yet that this is not absolutely essential is
shown by the experience of a lady who had excellent success with
a leaf that was some what decayed around the edges, and for that
reason was cut off and thrown away. Remembering afterward
that the plant was sometimes grown from pieces of a leaf, she hunted[47]
it up, trimmed off the decayed portion, and planted it at the
foot of a tree, about half under ground, and pressed the soil firmly
around it. A few months afterward she had a nice little plant
from it, with its beautiful leaves unfolding finely.
MY first Begonia was a Rex.
It thrived for several
years, and then to my
regret died, for it was
quite a favorite with me. Its large
leaves with broad silvery belt and
red dots, were very handsome.
This species thrive best in a Wardian case and are of rare beauty
and size, grown under such circumstances. A cool, moist atmosphere
is the best for them; they burn and shrivel exposed to the
intense sunlight. They are easily multiplied from the leaves. Cut
the leaf so that a small portion of the stem will remain, insert this
in a pan of damp sand, laying the leaf out flat upon the sand, upper
side uppermost. It can be retained in place by bits of stone or
small pegs. Cuts must then be made in a number of places so as
to sever the veins, thus checking the flow of sap. A callus then
forms at the base of each piece of vein where severed, and just
above it, a bud starts out, and thus a new plant is formed. It is
essential for success, that there should be bottom heat, and that
the air should be moist. A bell glass is the best to put over the
leaf, and if there is danger that the air become too moist, the glass
can be tilted up to allow of an escape. The leaves best adapted
for propagation are those neither very young nor very old, but
healthy and vigorous; yet that this is not absolutely essential is
shown by the experience of a lady who had excellent success with
a leaf that was some what decayed around the edges, and for that
reason was cut off and thrown away. Remembering afterward
that the plant was sometimes grown from pieces of a leaf, she hunted[47]
it up, trimmed off the decayed portion, and planted it at the
foot of a tree, about half under ground, and pressed the soil firmly
around it. A few months afterward she had a nice little plant
from it, with its beautiful leaves unfolding finely.
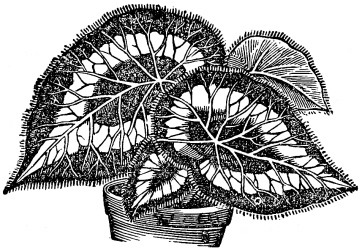
There are many varieties of the Rex family; some have brilliant colors in their leaves, others are thickly covered with short hairs. These are more difficult to manage, and require great care to preserve from dust, as like all rough leaved plants, they do not enjoy spraying, as do smooth leaved ones. It is well to set them out in a mild shower occasionally. Tepid water is the best for watering.
This class are the most generally cultivated, and they embrace a great many varieties, which are specially distinguishable by the diversity of their leaves. Most of them are one-sided, that is, they are larger on one side of the mid-rib than on the other. Some have fern-like foliage, others lobated. Some have large palmate leaves, others are spotted and laced with white. As a class they are very beautiful for their foliage, but when to this attraction is added beauty of flowers, it will be seen at once that they are eminently deserving of the prominent position now given them both in the open border and the window garden.
We will name for the benefit of amateurs some of the most desirable as given by Mr. Vick: Fuchsioides, with its drooping scarlet flowers, is one of the most desirable of the whole class; the leaves are small, and of a dark green color, and the small, delicate brilliant flowers are produced in great profusion. As a winter blooming sort it is indispensable. F. Alba bears white flowers. Richardsonii, a variety with white flowers and deeply cleft palmate leaves, requires more heat than the former, therefore well adapted to our warm rooms. Subpeltata nigricans has large, dark purple[48] leaves, and bears clusters of large rosy flowers, very ornamental. Grandiflora rosea, with light pink flowers, and Sandersonii, scarlet flowers; Weltoniensis, of dwarf habit and small dark green foliage, rich pink flowers, are all fine winter bloomers. Argyrostigma picta has long, thick leaves, with white spots. Metallica, an elegant plant with bronzy green foliage, and producing an abundance of pale peach-colored flowers, is of very recent introduction. Louis Schwatzer has a beautiful marked foliage in the style of Rex, dwarf habit. Mons. Victor Lamoine, leaves marbled like lace. Glaucophylla Scandens is of quite recent introduction, and the very best of all for a hanging basket. It is of a drooping habit, and its bright glossy leaves are very handsome. It bears large panicles of orange salmon flowers.
This is a class of quite recent origin, and differs from the more general varieties, in that it has bulbous roots which can be taken up and stored during the winter like Gladioli and Gloxinia bulbs. It has larger flowers than the other species; red, orange, yellow, with intermediate tints. A writer in the London Garden says of them:
"The bulbous Begonias, mostly of the Boliviniensis and Veitchi sections or families, may have also a brilliant future in the flower garden. Meanwhile, their proper place seems to be in the conservatory, greenhouse and window garden. For such positions it is well-nigh impossible to match the bulbous-rooted Begonias for brilliancy, grandeur and grace, three qualities seldom combined in the same plant. The plants are also characterized by great distinctness and freshness of style and character."
They are both double and single. Of the single flowered, the most important sent out last year was Davisii. It is a native of the Andes of Peru. Dwarf in habit, the leaves and flowers all[49] springing from the root stalk. "The scapes which rise erect above an elegant bluish green foliage, are light red; each scape bears three dazzling scarlet flowers. The plant is of very free growth, and a profuse bloomer." Frobelii, a new species from Ecuador, said to be very attractive, producing, well above the foliage, erect branches of large brilliant scarlet flowers; the foliage is of bright green, furnished on the under side with a thick covering of white hairs. White Queen, a very elegant variety with numerous racemes of ivory white blossoms.
Of the new double flowered, Glorie de Nancy is represented as a magnificent variety, with large very double carmine flowers, and very floriferous. Louis Van Houtte, flowers large, of a crimson scarlet color; of fine habit, and a free bloomer.
"Comtesse Horace Choeteau, is an inch or more in diameter, very double, and of a delicate, soft shade of rose; the young plant in a three-inch pot presented a number of flowers and buds, indicating a good blooming habit. As a double flower it is remarkably fine, the petals being well formed, pretty smoothly laid and imbricated."—James Vick.
The soil best adapted for Begonias is turfy loam, leaf-mold, sand, and old well-rotted manure in equal parts. When growing, they require a liberal supply of water, applied directly to the soil.
The Begonias are natives of the tropical countries of Asia, Africa, and America, and most of them inhabit the mountainous regions at a considerable elevation. They were first brought to notice and introduced into cultivation about two hundred years ago by a French naval officer, Michel Begon, from whom they derived their name.
This bulbous plant is a native of the tropical region of South America, and deserves a more general culture, for all the varieties[50] of this genus are very handsome, magnificent is not too strong a term to apply to many of them. They may be raised from seed by sowing early in spring in a finely sifted soil of leaf mold and garden loam. But great care is needful, and then one has to wait the following year for the flowers. It is better to obtain the bulbs in the spring all started, then they will bloom during the summer. Mine had several leaves, and I removed them from the thumb pots to five-inch size, which I judged would be sufficiently large for them. They need plenty of light and heat and plenty of air. To prolong the flowering an occasional watering with manure water should be given. In the autumn they must be gradually dried off and the bulbs kept in a warm, dry place, secure from frost. They can be potted any time from February to May. The bulb must be planted so that its top will be level with the surface of the soil, and watered sparingly until the leaves appear.
I will describe a few "superlatively beautiful." Cinderella, pure white with pink band. Brilliant, bright crimson, margined with rose, rich violet throat. Rose d'Amour, rose carmine, cream colored throat, zone of cerise. Nero, dark purple, white throat. Princess Royal, tube and edges white, throat mottled with dark blue. Lamartine, very beautifully undulated, magnificent shape; white bordered rose limb, veering to cochineal, marbled with white and elegantly veined with rose. Boule de Neige, pure snowy white, an abundant bloomer. These are only a few selections from the many, but sufficient to give you an idea of the variety of colors.
What flower can be whiter, sweeter, and more lovely than the Tuberose? As the flowering bulbs can be bought for ten and fifteen cents, according to size, no one need be without this charming flower. It is a native of the East Indies, and was introduced into Europe more than two hundred years ago. Until recently Italy[51] grew the tubers for Europe and America, but it has now been discovered that American grown tuberoses are superior in quality to the imported, and many florists of Europe now advertise them.
Here is a description of the tuberose, which appeared originally in a volume entitled "The Flower Garden Displayed," published in England in 1732:
"This is a bulbous root, brought to us from Italy every year. It brings a spike of white flowers on the top of a stalk about three feet high, and is very sweet scented. The flower buds are a little tinted with a lake or carmine color. We raise this by planting the roots in pots of fine earth, and plunging them in hot beds in February or March; but give them no water till they sprout, then we have this flower in July. Or else set the roots in a warm border under a south wall, and they will some of them flower in August and some in September, or this month or the next. When these blossom you may pot them and set them into the green-house, and some will even bloom in December."
Mr. Vick, from whose magazine we quote the foregoing, gives an engraving copied from the work, showing the character of the tuberose as it was nearly a century and a half ago. It represents a small single flower, that would be lightly esteemed by us.
The flower stalk is from three to five feet in height, and bears from twenty-five to eighty blossoms. The Pearl is much the finest sort. When the bulbs are obtained from the florist they have usually several little tubers round the large one. These ought to be taken off and placed in rich, mellow soil to the depth of four or five inches. They must be cared for by keeping the earth loose and watering occasionally. Before frost they should be lifted, their tops cut away, and then kept in a dry, warm place during the winter. The strongest ones will usually blossom in the autumn. But summer flowering bulbs are so cheap it seems scarcely worth the trouble.
Will Tuberoses flower the second year, is a question frequently asked, and usually answered in the negative, even by popular florists. A writer in an English periodical, Gardeners' Chronicle, gives the following facts:
"Last year, instead of throwing away all our plants when they had done flowering, as is, I believe, customary, I saved back twelve plants, not picked ones, which were placed under a stage in a late vinery, where they remained until the end of April without receiving any water to the roots, other than what they derived from the moisture of the house, by which time most of them had thrown up their flower-spikes, which proceeded from young tubers, formed immediately upon the top or crown of the old ones, and from the union of which—when the plants had received a thorough watering, and otherwise were subject to a growing temperature—a profusion of roots emanated, after which the plants received a suitable shift to a small 24. The spikes of these plants, although not so strong or fine as those produced by tubers imported last autumn, are nevertheless good, both in spike and each individual flower, which, moreover, expanded in the most satisfactory manner possible, so much so, that this and other seasons I intend to save all my tuberoses for flowering the second year, and perhaps the third. I may here remark for the information of the uninitiated in tuberose culture, that in potting the tubers all little bulbets or offsets should be rubbed off, and subsequently any suckers which may appear should be removed forthwith, otherwise failure to flower these most beautifully scented flowers will, in all probability be the result. The plant is of comparatively easy and simple culture, and considering the value of the tuberose while in flower, and its great suitability for bouquet-making, etc., the wonder is that it is not more extensively cultivated in private establishments as well as by market gardeners."
A gentleman writes me of a new method with Tuberoses; new to[53] him, and he says that in a large range of horticultural reading he has never seen it mentioned nor heard of its being used except in the instance he cites. He says: "I have grown Tuberoses for the past ten years with varying success, but the main difficulty has been that so long a time has been required in rooting and stocking them that the first frost finds a large proportion of them just budding, or not commenced to spindle. Had tried various places, hot-bed, furnace-room and hot-house, and all the early spring months and December, but that made no difference; they would not start until they got ready, and I lost many bulbs from rotting. Two years ago, a friend who had had a similar experience surprised me by showing me plants about the first of May with fine tops that had been planted but three weeks, and the first of June had stalks a foot high, while my bulbs which had been planted the first of February, did not commence to sprout until June, although they had been in a hot-house under favorable conditions.
"Now the reason simply was this: He had taken his bulbs and not only pulled off all the small ones attached, but had dug out with a sharp knife all the small eyes, and had cut off the whole of the tuberous part, leaving only the bulb proper. This I tried on one-half my bulbs, with the result that they were nearly two months earlier than those planted the same time, that I did not cut. Although this seems to be rather severe treatment of the bulb, it has given such good results that I propose to continue the practice."
My own experience is that of late blooming. Of the dozen I planted in the border in June, five were finely budded when taken up in September, and have since bloomed. Two others had just begun to spindle, the others with one exception look as though they would not stalk. Next year I purpose to try this new method.
![]() IT was my intention to devote this entire article
to "Ornamental Foliage Plants," but I think
I will have a prelude, and my prelude may
have no more connection with my "talk"
proper than Mr. Cook's preludes do with his lecture
proper, and I think that frequently the first is the
most interesting and important; and from the fact
that in the published reports much more space is
afforded to the prelude than the lecture, I opine that
others are of the same opinion. "The Topic of the
Hour," whatever may be the question just then stirring
the public mind, is usually chosen as the preface.
The topic of the hour to-day has been a bit of a sermon
from the text, "And to every seed its own body,"
and the lesson embodied was that of Faith. The preaching came
from a package of gladiolus bulbs, just received, and it run on this
wise:
IT was my intention to devote this entire article
to "Ornamental Foliage Plants," but I think
I will have a prelude, and my prelude may
have no more connection with my "talk"
proper than Mr. Cook's preludes do with his lecture
proper, and I think that frequently the first is the
most interesting and important; and from the fact
that in the published reports much more space is
afforded to the prelude than the lecture, I opine that
others are of the same opinion. "The Topic of the
Hour," whatever may be the question just then stirring
the public mind, is usually chosen as the preface.
The topic of the hour to-day has been a bit of a sermon
from the text, "And to every seed its own body,"
and the lesson embodied was that of Faith. The preaching came
from a package of gladiolus bulbs, just received, and it run on this
wise:

Here are these dry bulbs, separately wrapped and labeled. They look alike in color, and very nearly alike in form; some are rather more cone shaped than others. One is larger and more flat. But there is nothing in form nor size to show that they will not develop precisely the same form and color of flower. I know that they will all reveal the leaf, habit of growth, bud and bloom that distinguishes this species of plant from all others, because I know[55] that these are gladiolus bulbs, and every seed hath its own body. A gladiolus bulb never yet produced a dahlia. A tigridia or shell-flower bulb, though greatly resembling some gladiolus bulbs, and its form of leaf is very similar, yet it never produces a bud nor blossom like the gladiolus. The tigridia hath "its own body," peculiarly and exclusively its own. I have spoken thus far of demonstrated facts—facts that have become to me a matter of personal knowledge.
But now comes the lesson of Faith. I find each bulb bears a different name. I take my catalogue and read the description against the name on each label. Thus I am told what colors pertain to each bulb, inclosed, shut up beyond my ken. Do I have any doubts respecting these descriptions—that the distinguishing characteristics of each sort before me will fail to correspond? Here is Lord Byron and Lord Raglan. How do I know that the former will be a brilliant scarlet, stained and ribboned with pure white, while the latter will have salmon colored blossoms, spotted with scarlet and blotched with dark garnet? I do not know this, for I have never seen it demonstrated, but I have an assured faith that in due time I shall behold those flowers true to their assigned colors, and if there should be a failure I should attribute it to the mistake of the labeler.
But why should these brown bulbs, so alike to outward view, bear flowers so widely differing in hues? Why should Cleopatra have a large flower of soft lilac tinged with violet, and a purple feathered blotch, while Meteor is dark red with pure white stain? Why should Nestor be yellow striped with red, and Addison dark amaranth, with white stripes? Vainly would I seek by dissection to fathom the mystery of these hidden diversified markings, but He who created this plant of wondrous beauty gave to each "seed its own body," and thus we can plant in faith—yea in full assurance of faith—that in due time our eyes will behold all those varied tints[56] now secreted in these bulbs before us. Our seed sowing is all the work of Faith, and Hope looks beyond with bright anticipations of the summer and autumn harvest.
The gladiolus is very easily cultured, and I have far better success in keeping the bulbs through the winter than I have with the dahlia. The tubers of the dahlia easily rot, on account of the dampness of the cellar, though carefully dried and packed in sand. But the gladiolus bulbs, without any special care, come out in fine condition. I like to add a few new ones to my old standard stock, so as to have a variety of colors, for few flowers make such a grand display in the flower garden, and the spikes of bloom are admirable for bouquets, as the buds will unfold day after day for a long time. The lower flowers on the stalk can be removed as they fade. The flowers are very fine also for saucer or shoal dish bouquets. I have a special liking for these. Fill the shallow dish with water or sand—I prefer the latter kept constantly wet—then arrange tastefully short stemmed flowers till they are a mass of bloom. I first make a green border of geranium leaves, or some trailing vine. Different shades of gladiolus flowers picked from the stalk are very effective to set off the flowers not so striking. Where the season for out-door culture is short, as it is here in Maine, it is best to get the bulbs started in the house. Some do this by simply placing them in a sunny window without covering. I always plant mine in a box.
The gladiolus can be raised from seed, but they are of slow growth, and one has to wait till the third summer usually for their flowering. It is far better to purchase the bulbs, then they bloom the first season, and, except some of the rare sorts, multiply rapidly. Although novelties, and some rare sorts are very expensive, $1.50, $2 and $3 for a single bulb, yet very fine bulbs of choice colors can be obtained for that price per dozen. In reply to the question, "What are the names of six of your finest gladiolus not very expensive?"[57] the reply is, "Calypso, Cleopatra, Agatha, Eldorado, James Carter and Lord Byron." These six cost but little more than $1. Of those more expensive the following are very desirable: Addison, Eugene Scribe, Etenard, La France, Meyerbeer and Rossini. These cost a little less than $3. Unnamed bulbs, a good variety, can be bought for $1 per dozen of reliable florists.
Of the new varieties sent out the present season for the first time, are the following raised during the past year by M. Souchet, M. Leomine and other French growers, who have for years made the improvement of the gladiolus a special study. They are said to be superior to any gladiolus hitherto introduced. Aurore, Bremontier, Chameleon, Corinne, Dalila, Eclair, Gulliver, Hermione, Lesseps, Tolma, Victor Jacquemont. The descriptions represent them as superb, and they ought to be at the price named, $4 per bulb! Some of us will have to wait till their novelty is worn off.
Lemoinei and Marie Lemoine. "These two varieties are Hybrids of gladiolus purpureo-auratus, and are of the old garden varieties of Gandavensis, and are now offered for the first time. In form they approach the old Gladiolus Biperatus, the colors being creamy ground with distinct markings of crimson-maroon, with lemon and salmon colored cloudings. They have proved quite hardy and may be left out of doors from year to year." Mr. Henry Cannell of Swanley, England, a florist of world-wide reputation, says of those hardy Hybrids: "It is considered both by professionals and the trade, that M. Leomine's greatest victory was in crossing Gladiolus purpureo-auratus and gandavensis, two distinct species, and at the time they were awarded first-class certificates, it was thought by many that some higher and substantial recognition ought to have been made for introducing a perfectly hardy constitution into our glorious garden gladiolus, and saving the trouble of housing them from frost every season."
This is a new species from Natal, quite distinct from the common species of gladiolus and very attractive. On a slender, bending stem, which rises to the height of three or four feet, are borne from eight to twelve nodding flowers, somewhat bell-shaped in form, and yellow in color, with broad purple stripes on the lower divisions within. Its bulbs are small, and at the end of long runners numerous offsets are produced which are more certain to flower the succeeding season than are the old bulbs.
This ancient type is a very ordinary flower, and it seems almost incredible that such superb varieties should have been produced therefrom by cross-fertilization. In the hands of the French florists it has attained to the superior position it occupies to-day. More than forty years ago Mons. Souchet, head gardener at the Château of Fontainebleau, first called attention to this flower, and began its improvement, and although some few other French florists, such as Messrs. Courant, Berger, Lamoine, Verdier and others followed his example, yet nearly all of the varieties now in commerce in France, are of the raising of that now venerable and respected private citizen. His successors, Messrs. Soulliard and Brunelet supply the great French houses of Paris, by whom the bulbs are forwarded to all parts of the world. About thirty years ago Mr. Kelway of Longport, in Somersetshire, began his culture and hybridizing of the flower, and has built up an immense business. He devotes fifteen acres to Gladiolus exclusively, and the number of seedlings annually raised is 200,000. In 1879-80, Mr. Kelway exhibited eighteen named seedlings which were severally awarded first-class certificates as possessing striking original characteristics. Of our own eminently successful growers, Messrs. Hallock and Thorp of Queens, N. Y., take the lead. They devote over seven acres to Gladiolus, and raise thousands of seedlings.
For diversity of color and general effect, either in masses, or in beds of three or four rows, placing the bulbs one foot apart and three inches deep. Mix a liberal supply of well-rotted manure with the soil, and if clayey, use sand. As soon as the plants are sufficiently tall stake them, and mulch with dressing.
Mary Howitt.
 HERE we step on disputed ground. Are Geraniums Pelargoniums?
Who shall decide when florists disagree? There
are eminent names on both sides of the question. Mr.
Henry Cannell of Swanley, England, a florist who stands
in the front rank, and whose name has become so widely known
in connection with New Life Geranium, of which he was the originator,
jumbles up together under the head of Pelargoniums everything
we on this side of the water class under the head of Geraniums.
A veritable muddle he makes of the matter—that is our
private opinion—we whisper it to you confidentially. Here is our
yellow Zonal Guinea; our best scarlet bedder, Gen. Grant, and
Wellington, and Mrs. Pollock, and Happy Thought, all called Pelargoniums,
and yet are quite unlike in leaf and flower what we
Americans denominate a Pelargonium; and, to avoid confusion, it
is certainly advisable for us to adhere to our established distinctiveness.
We quote from the Gardener's Chronicle of January 3d,
1880, a sensible talk on this subject, to which Mr. Cannell takes
exceptions: "Pelargoniums and Geraniums—I think it would be
as well to settle by authority the exact names of those flowers that
seem to be indiscriminately called Pelargoniums and Geraniums.
Botany has been described as the 'science of giving polysyllabic
barbarian Greek names to foreign weeds;' but while some plants,
Abies Mariesii for instance, are most carefully described, others, as
Geraniums, seem to be called by names that do not belong to them,[61]
but to quite a different flower. I notice, both in your letter-press
and advertisement, mention made of Zonal Pelargoniums; now I
should certainly decline to receive Geraniums if I ordered Pelargoniums.
I am old enough to remember that we had a parti-colored
green-house flower of a violet shape that was called a Geranium,
then came a lot of hardy-bedding-out stuff with a truss of
red flowers, all of one color, followed by Tom Thumbs and Horseshoes
which grow nicely out of door. Then we were told that we must
no longer call those green-house plants Geraniums, that their right
and proper name was Pelargoniums, and that those bedding-out
plants were, strictly speaking, Geraniums. Now, however, the old
name Geranium seems to be dropped for both, and the new name
Pelargonium given to both, surely erroneously! Let us, however,
have it fairly settled which is which, so that we may clearly and
distinctly know what we are talking about, and not make mistakes
either in writing or talking, in sending to shows, or in ordering
plants."—James Richard Haig, Blair Hill, Sterling.
HERE we step on disputed ground. Are Geraniums Pelargoniums?
Who shall decide when florists disagree? There
are eminent names on both sides of the question. Mr.
Henry Cannell of Swanley, England, a florist who stands
in the front rank, and whose name has become so widely known
in connection with New Life Geranium, of which he was the originator,
jumbles up together under the head of Pelargoniums everything
we on this side of the water class under the head of Geraniums.
A veritable muddle he makes of the matter—that is our
private opinion—we whisper it to you confidentially. Here is our
yellow Zonal Guinea; our best scarlet bedder, Gen. Grant, and
Wellington, and Mrs. Pollock, and Happy Thought, all called Pelargoniums,
and yet are quite unlike in leaf and flower what we
Americans denominate a Pelargonium; and, to avoid confusion, it
is certainly advisable for us to adhere to our established distinctiveness.
We quote from the Gardener's Chronicle of January 3d,
1880, a sensible talk on this subject, to which Mr. Cannell takes
exceptions: "Pelargoniums and Geraniums—I think it would be
as well to settle by authority the exact names of those flowers that
seem to be indiscriminately called Pelargoniums and Geraniums.
Botany has been described as the 'science of giving polysyllabic
barbarian Greek names to foreign weeds;' but while some plants,
Abies Mariesii for instance, are most carefully described, others, as
Geraniums, seem to be called by names that do not belong to them,[61]
but to quite a different flower. I notice, both in your letter-press
and advertisement, mention made of Zonal Pelargoniums; now I
should certainly decline to receive Geraniums if I ordered Pelargoniums.
I am old enough to remember that we had a parti-colored
green-house flower of a violet shape that was called a Geranium,
then came a lot of hardy-bedding-out stuff with a truss of
red flowers, all of one color, followed by Tom Thumbs and Horseshoes
which grow nicely out of door. Then we were told that we must
no longer call those green-house plants Geraniums, that their right
and proper name was Pelargoniums, and that those bedding-out
plants were, strictly speaking, Geraniums. Now, however, the old
name Geranium seems to be dropped for both, and the new name
Pelargonium given to both, surely erroneously! Let us, however,
have it fairly settled which is which, so that we may clearly and
distinctly know what we are talking about, and not make mistakes
either in writing or talking, in sending to shows, or in ordering
plants."—James Richard Haig, Blair Hill, Sterling.
We will now give a part of a lecture delivered last spring before a Pelargonium Society in London, by Shirley Hibberd, a delightful writer on Horticulture, says Mr. Vick, from whose magazine we quote the following:
"A Pelargonium is not a Geranium, although often so called. The true Geraniums are for the most part herbaceous plants inhabiting the northern hemisphere, and the Pelargoniums are for the most part shrubby or sub-shrubby plants of the southern hemisphere. Let us for a moment wander among the pleasant slopes of Darley dale in Derbyshire, or by the banks of the Clyde or the Calder. We shall in either case be rewarded by seeing vast sheets of the lovely meadow Crane's Bill, Geranium pratense, a true Geranium, and one of the sweetest flowers in the world. In the rocky recesses of Ashwood Dale, or on the banks of the 'bonny Doon,' we may chance to see in high summer a profusion of the Herb[62] Robert, Geranium Robertianum, with pink flowers and purple leaves, a piece of true vegetable jewelry. And, once more, I invite you to an imaginary journey, and we will ride by rail from Furness to Whitehaven, in order to behold on the railway bank, more especially near St. Bees, a wonderful display of the crimson Crane's Bill, Geranium sanguineum, which from July to September, forms solid sheets, often of a furlong in length, of the most resplendent color. No garden coloring can even so much as suggest the power of this plant as it appears at a few places on the Cumberland coast; even the sheets of scarlet poppies we see on badly cultivated corn lands are as nothing compared with these masses of one of the most common and hardiest of our wild flowers.
"Now let us fly to the other side of the globe and alight in the vicinity of the Cape of Good Hope, say on the vast desert of Karroo, where there is much sand, much sunshine, and little rain. Here, in the midst of desolation, the world is rich with flowers, for the healthy shrub that occurs in patches, glowing with many bright hues, consists in part of wild Pelargoniums, which often take the form of miniature deciduous trees, although in the valleys, nearer the coast, where more rain falls, they are evergreen bushes.
"Very different in their character are these two tribes of plants, and they are not less different in their constitution and aspects. We may regard the Geraniums as herbs of Europe, and the Pelargoniums as miniature trees of Africa. When we examine the flowers, we find the fine petals of a true Geranium of precisely the same shape and size; but the fine petals of a Pelargonium are not so, for sometimes the topmost are the largest, and stand apart from the rest with great dignity, like mother and father looking down on their dutiful daughters, and in other cases they are the smallest, suggesting that the daughters have grown too fast and become unmanageable. The florists are doing their utmost to obliterate the irregularity of the petals of the Pelargonium, and in this respect to[63] convert Pelargoniums into Geraniums, but the conversion will not be complete until much more wonderful things are accomplished. A Geranium has ten stamens, and a Pelargonium has only seven (perfect ones). These numbers are not constant, but the exceptions are of no consequence in a general statement of the case.
"When all is said that can be said about the differences and resemblances of the several genera of Geraniaceæ, there remains only one constant and unfailing test of a true Pelargonium, and that is the nectariferous tube immediately below the flower, and running down one side of the flower-stalk. If you hold the pedicel up to the light, it may be discerned as giving an indication of a double flower-stalk, but when dissected with a pin or the point of a knife, it is found to proceed from the base of the largest of the green sepals, and it often appears to form a sort of digit or point in the line of the pedicel. When you have mastered this part of the story, you may cherish the idea that you know something about Pelargoniums.
"The large flowered show varieties and the large-flowered single Zonals take the lead, and they are pleasantly followed by a crowd of ivy-leaved, double-flowered and variegated sorts that are useful and beautiful. The Pelargonium Society has set up a severe standard of judging, and a variety must be distinct and good to pass through the sieve. Moreover the raising of varieties has been to a great extent reduced to scientific principles, and we obtain as a result new characters suggestive of the great extent of the field that still lies open to the adventurous spirit in cross-breeding. No one in recent years has contributed more directly toward the scientific treatment of the subject than our own painstaking Treasurer, Dr. Denny, of whose labors I propose to present a hasty sketch.
"Dr. Denny commenced the raising of Pelargoniums in the year 1866, having in view to ascertain the influence of parentage, and thus to establish a rule for the selection of varieties for seed-bearing[64] purposes. In raising varieties with variegated leaves, as also with distinct and handsome flowers, he found the pollen parent exercised the greatest influence on the offspring. The foundation of his strain of circular-flowered Zonals was obtained by fertilizing the large starry flowers of Leonidas with pollen taken from the finely formed flowers of Lord Derby. From 1871 to the present time Dr. Denny has sent out sixty varieties, and he has in the same period raised and flowered, and destroyed about 30,000. These figures show that when the selection is severe, and nothing is allowed to pass that is not of the highest quality, there must be 500 seedlings grown for the chance of obtaining one worth naming."
We have devoted a good deal of space to this citation because of its interest and value on the question at issue. Mr. Hibberd has, we think, made the matter very clear, and conclusive it must be to the most of minds. Pelargoniums are divided into classes, though we rarely see any classifications of them in the catalogues.
Are comparatively a new type, and from the fact of their having more scalloped petals, somewhat approaching a double; they retain their petals instead of shedding them as do the single show flowers. The Beauty of Oxton and Queen Victoria, novelties of very recent introduction, belong to this class. We had them in bloom last year and thought them very fine. The Beauty of Oxton has the upper petals of a very rich maroon color, darkly blotched; under petals very dark crimson, shaded with maroon; light center tinted with rose. All the petals are attractively and regularly margined with white and beautifully fringed. The flowers are large and the extra number of petals gives them the appearance of being semi-double.
Queen Victoria is of a very novel type and marvelously beautiful. The flowers have crispy petals, all of which are a rich vermilion in color, broadly margined with white, and the upper ones[65] blotched with maroon. The "Show and Fancy Pelargoniums" have what the florists term "blotches," i.e. large spots on the two upper petals, and "spots" which mean the darker marks upon the center of the lower ones. The Lady of the Lake belongs to this class. Lower petals orange-rose painted with crimson, very dark maroon top petals with a narrow, even crimson edge, white center. Prince Charlie is very unique in its markings. Color white elegantly tipped, with rose-violet blotches.
This is a very handsome class of which there are many new varieties. Princess of Wales we had last summer. It has elegant frilled petal margins; flower trusses large size and borne in profusion well above the foliage; ground color pure blush, each petal alike marked with a rich dark velvet crimson-scarlet margined blotch.
Star of the East resembles the Princess of Wales in growth and profusion of bloom, but with larger flowers, of pure white ground. The petals are elegantly fringed, the upper ones marked with a rich crimson spot, and the under ones elegantly penciled with violet-colored lines. These are among the novelties of recent introduction.
A class of distinct habit, free bloomers, mostly fragrant foliage, good for bedding out. Of these we have only had Madame Glevitsky of Bavarian origin. Color, upper petals a fine vermilion, veined and spotted with purple, under petals vermilion.
We were much pleased with Pelargonium Filicifolia Odorata for its finely cut leaves of a Fern-like appearance and pleasing fragrance.
Our specimens of the various classes were from the extensive and superb collection of Mr. John Saul, of Washington, D. C.[66] Among them was one which originated in his establishment and was named for his wife. It belongs to the "Regal" class. The habit is compact and very free flowering, producing large trusses of flowers the color of which is a rich glowing vermilion, with light center and light margin to the petals.
We are indebted to Mr. John G. Heinl for specimen plants of two "New Monthly Pelargoniums," now offered for the first time to the general public. Of the origin of one, Fred Dorner, we have this account given in a letter to Mr. Heinl, from Fred Dorner, Esq., of Lafayette. Mr. Dorner says:
"Six years ago I undertook to grow some Pelargoniums from seed. I procured some very choice seed of Ernest Benary of Erfust. The seedlings grew finely. About midwinter one commenced to bloom, and to my astonishment kept on blooming for ten months, during which period it was never without flowers. The plants grew to a good size and at one time I counted forty-seven good-sized trusses on it. The winter and everblooming quality, with the large and beautifully colored flowers, makes this Pelargonium a great acquisition to the amateur as well as the florist. I have seen here in Lafayette plants in windows blooming all winter, and it is acknowledged here to be the best and easiest kept house and window plant, blooming from nine to ten months in the year."
Freddie Heinl originated with Mr. John G. Heinl, who says it is a sport from Fred Dorner; it is lighter-colored and the flowers are somewhat larger. That these are both a rare acquisition is evident from the testimony of such florists as Mr. John Thorp of Queens, and Mr. Henry A. Dreer of Philadelphia. Mr. Thorp says, "There are no Pelargoniums equal to them and they have a decided right to be called perpetual." Three months later he writes: "I am more than ever impressed with their superiority over any perpetual blooming varieties, and they must take foremost rank." Mr. Dreer says: "The Pelargoniums have proven very satisfactory. They[67] flowered during the greater part of the summer, and are now full of buds."
The colored lithograph, which Mr. Heinl says is a good representation, shows them to be very beautiful. We should think that to call a plant so dissimilar in foliage and flower a Geranium, would be a misnomer, why not equally such to call a Geranium a Pelargonium?
As we have seen by Mr. Hibberd's address, the Pelargonium's native home is on arid plains where there is much sand, much sunshine and little rain, so that they are chiefly dependent on heavy dews for moisture. To plant them in heavy soil, give them a sheltered situation and liberal and frequent watering, would be a mode of treatment directly the reverse of what they require. In the cultivation of all plants we should as far as possible adapt them to their native conditions. One skilled amateur says his rule is to let the earth in the pots become thoroughly dry before watering, and always to give a period of rest after blooming. Another, a lady, said she never had any success with Pelargoniums until she gave them a heavy period of rest after blooming. In the spring, when putting her plants out of doors, she laid the pots containing Pelargoniums on their sides, and let them remain perfectly dry until fall. She then took the plants out of the pots, shook the soil from the roots, and scrubbed them well with a hard brush and water. The old-looking roots were cut off and the top trimmed down to six or eight inches in height. They were then repotted in rich earth and watered very moderately till they started into full growth, and after that more freely. With this treatment they never fail to bloom.
A young physician who raised many extraordinarily fine varieties of Pelargoniums from seed, in stating his mode of culture, said that his practice was to re-pot large plants whenever they seemed in danger of being pot-bound. The mold he used was made up of[68] black earth from under a manure heap, and a little stiff clay to retain the water. After the plants were done flowering, they were trimmed rather close, and with regard to probable places of sprouting. They were then placed in partial shade, and all shoots found straying out of symmetry were pinched off. His large plants were kept moist till after bloom, and then rather dry.—Floral Cabinet.
We have given these methods so that if not successful with one, another can be adopted.
Ralph Waldo Emerson.
 THE Fuchsia was introduced into England in the latter half
of the last century by a sailor, at whose home it was discovered
by Mr. James Lee, a florist of Hammersmith, who
secured the original plant by paying quite a sum of money
for it, and in addition promising to give to the sailor's wife one of
the first young plants he would succeed in raising. In a short time
he succeeded in producing several hundred nice plants, nearly all
of which were sold at a guinea each. Shortly after this a captain
Firth presented one that he had brought from Chili to the Royal
Garden at Kew. The plant was named in honor of Leonard Fuch,
an eminent German Botanist, who lived in the 16th century. The
varieties in cultivation to-day are vast improvements. One of the[70]
early varieties was called Fulgens. We recollect seeing this variety
some four or five years ago, and could not refrain from comparing
it with a number of varieties lately introduced. The flower may
be described as follows: A slender crimson tube two inches in
length; sepals narrow, one-half inch; in color a shade lighter than
the tube; the corolla purple; in size very small compared with the
varieties of the present time. This variety is a strong grower,
large foliage which has a silvery appearance. Thus we can have a
slight idea of that from which have been produced the beauties of
our time; thus can we see what a skillful florist can do when he
has something to begin with. Some of the varieties of the Fuchsia
are hardy in England as well as in some parts of our own country.
A traveler informs us that he has seen them in California trained
over arbors and to the houses just as we train grape vines here,
and growing most luxuriantly. They grow in favor very rapidly
wherever introduced, and it was but a short time after they became
known we find the Poet eulogizing them in these lines—
THE Fuchsia was introduced into England in the latter half
of the last century by a sailor, at whose home it was discovered
by Mr. James Lee, a florist of Hammersmith, who
secured the original plant by paying quite a sum of money
for it, and in addition promising to give to the sailor's wife one of
the first young plants he would succeed in raising. In a short time
he succeeded in producing several hundred nice plants, nearly all
of which were sold at a guinea each. Shortly after this a captain
Firth presented one that he had brought from Chili to the Royal
Garden at Kew. The plant was named in honor of Leonard Fuch,
an eminent German Botanist, who lived in the 16th century. The
varieties in cultivation to-day are vast improvements. One of the[70]
early varieties was called Fulgens. We recollect seeing this variety
some four or five years ago, and could not refrain from comparing
it with a number of varieties lately introduced. The flower may
be described as follows: A slender crimson tube two inches in
length; sepals narrow, one-half inch; in color a shade lighter than
the tube; the corolla purple; in size very small compared with the
varieties of the present time. This variety is a strong grower,
large foliage which has a silvery appearance. Thus we can have a
slight idea of that from which have been produced the beauties of
our time; thus can we see what a skillful florist can do when he
has something to begin with. Some of the varieties of the Fuchsia
are hardy in England as well as in some parts of our own country.
A traveler informs us that he has seen them in California trained
over arbors and to the houses just as we train grape vines here,
and growing most luxuriantly. They grow in favor very rapidly
wherever introduced, and it was but a short time after they became
known we find the Poet eulogizing them in these lines—
While some flowers have been extremely popular for a season, and then have sunk into comparative obscurity, the popularity of the Fuchsia has never waned, but on the contrary has continually been on the increase until now it occupies a prominent place in every collection of plants, be that collection large or small. There is a cause for this popularity, and that cause is, it is of easy culture and produces its flowers freely, often under adverse circumstances. The Fuchsia is readily propagated by cuttings of the young wood. These will root in from two to three weeks, when they should be[71] potted in rich soil, say one-half garden soil or loam enriched with well-rotted manure, and one-half leaf soil, with a little sand added to make the compost very porous. From the time the plant is first potted it should never be allowed to become so dry as that the growth will be checked. The great secret of growing Fuchsias successfully is to keep them growing. In order to do this we must provide for them a rich soil, an abundance of pot-room and a moist atmosphere. If you wish to grow large specimen plants the cuttings should be struck (that is rooted), early in the season. This will allow a longer period for them in which to make their growth before the season for blooming arrives; by keeping the plants supplied with plenty of pot-room the time of blooming will be somewhat retarded, and if on the other hand we desire to have the plants in bloom as early as possible we allow plenty of pot-room during the early part of the growing season, after which we allow the pots to become pretty well filled with roots, and abundance of beautiful pendulous flowers will be the result.
As house or window plants the Fuchsias are very popular. The variety Speciosa will bloom very freely during the winter. During the summer months they should be protected from the direct rays of the sun, and kept well syringed. As bedding plants their utility is limited, as they must be planted in a shaded position. A bed of them in such a position makes a pleasant appearance, and in this way they are easily kept through the hottest part of the year. They may be bedded out, or may be allowed to remain in the pots and the pots plunged in the garden. In this latter way they will need additional care, as they must not be allowed to suffer for want of water. If it is desirable to keep the old plants another year they may be removed to the house or cellar, and kept cool and dry until toward spring, when they can be repotted in fresh soil, watered scantily, and started into growth and pruned or trained to any desired shape or form.—The Floral World.
The foregoing article so fully and clearly stated all that was essential respecting the culture of the Fuchsia, that we have transferred it entire instead of writing something original. We need now only add a few things respecting some choice varieties and recent novelties. "Champion of the World has the largest blooms of any Fuchsia; the tubes are short; sepals very broad and of great substance, well reflexed, and of a most beautiful coral red; the foot-stalk of each bloom is of unusual length and strength, so that each flower stands out bold and graceful. Corolla of immense size, and as it expands forms two-thirds of a perfect ball. Color is of the most intense bright dark purple. Free tall grower, and for conservatory decoration is one of the most remarkable Fuchsias for size ever yet sent out."—H. Cannell.
The illustration of this Fuchsia in Mr. Cannell's Floral Guide measures two and one-third inches in diameter, and yet we are told that when well grown, the Champion produces much larger bloom than the engraving. It has four rows of petals, and looks round and full like a pink. Bland's New Striped is of the single class, but the corolla is very large, of a rich plum-colored purple, regular and distinctly striped red and rose, pyramidal shape, habit strong.
Of the Hybrid variegated Fuchsias, Sunray is by far the best with red variegated leaves ever sent out; it is very ornamental. Pillar of Gold is a very showy variety with yellow leaves. Among the novelties in color, we find mention of Aurora Superba; tube and sepals rich salmon, corolla large and spreading of a distinct orange scarlet highly suffused with yellow, fine habit and free bloomer. Polyhymnia is a dwarf yellow.
Of Lord Beaconsfield, Mr. Cannell says: "One of the strongest and most conspicuous blooming varieties ever sent out, and one of the very best for sale and decoration; flowers neither good shape nor color, but produced in very large clusters and blooms nearly all the year if allowed plenty of root room."
This Fuchsia originated with Mr. John Laing, Stanstead Park Nursery, Forest Hill, near London, and is a cross between Fuchsia Fulgens and one of the modern varieties known as "Perfection." It was exhibited at some of the meetings of the Royal Horticultural Society first, as Laing's Hybrid, in 1875 or 1876. It much resembles the old Speciosa, but is more free blooming even than that, and its flowers are twice as large.
Kingsburyana, figured in Mr. Cannell's Floral Guide—which comes to us from Swanley, England—is very large and double. "It is another addition to the double white corolla class, and is remarkable for its fine vigorous growth and large showy flowers; its corolla is particularly novel and beautiful."
Mrs. H. Cannell, named for the florist's wife by Swaffield, its originator, "was one of the greatest lifts in bringing the double white corolla to perfection," and has given great satisfaction in this country. We have never seen one so beautiful, but Mr. C. E. Allen who has a large collection, including those rare gems from across the water, we have named, says: "Snow White is the very best double white Fuchsia ever sent out. A fine, erect grower, and a remarkably free and early bloomer. Sepals coral red. Superior to Miss Lucy Finnis in that it is of a stronger habit. Have none now in bloom." Among the fine specimen blooms of the dark purple type sent us by Mr. Allen, we think Elm City the gem for size, richness of color—a double dark purple striped with scarlet, sepals scarlet-crimson—and compact form. The Swanley Gem is of a peculiar shape, single, very open bell-shape corolla, "frilled" Mr. Cannell calls it, rose color with tube and sepals coral scarlet, the latter are very prettily reflexed.
We began our list with the Champion—the largest known—we will end it with the tiniest, Microphylla, the whole plant, flowers and leaves are Liliputian among the Fuchsias.
Here these are truly wonderful; they grow up the house fronts, and grow into large trees, so large that you can have a tea-party around the bole of the trees. They are also grown for hedges and kept nicely clipped, and with their bright green leaves and scarlet flowers look cheerful and refreshing. The winds and the spray from the sea do not in the least affect them.—The Garden.
Mr. Vick, in his Magazine says: "Once when in Europe, we saw at Ventnor, in the Isle of Wight, a Fuchsia tree, perhaps twenty feet or more in height, with a trunk full fifteen inches in diameter. The editor of the Flore des Serres of Belgium, in writing of this tree, says it is doubtless the largest specimen in Europe, but is only a baby compared with specimens the editor has seen in South America. Seeing our notice of this tree, Mr. Nicholls of Sharon Springs, N. Y., wrote us that he had "seen Fuchsias in the Isle of Jersey, in the English Channel, thirty feet in height, and there are hundreds there from twenty to twenty-five feet."
We have found the most effective method to be by placing the cuttings in a bottle of water, and keeping them in a sunny window, but the following method is said to be practiced by cottagers in the west of England: "In the autumn, after the frost has destroyed the foliage, the wood of the present season is cut off close to the ground and laid like a sheaf of corn in a trench a foot deep. The bundle is covered with a few inches of soil, and here it remains until spring, when a multitude of young shoots may be seen pushing their way through. The soil is then carefully moved, and with a sharp knife a cut is made each side of a joint, and the result is rooted plants enough for the parish. The old stool throws up more vigorously than before, to be served in the same way the following autumn."
 ONLY a few years ago, not one of the Coleus family had a place
in the gardens of Europe and America, and I have been told
that in our absence gardeners depended chiefly upon plants
with showy flowers for ornamenting their gardens and
grounds. When some of my remote relatives were introduced, numerous
were the surmisings as to what place they should occupy
amongst cultivated plants. This was especially so in the case of
Perilla Nankinensis, a plant of most sombre hue, but so striking
withal as to attract general attention. Some looked upon it as the
forerunner of a class of plants destined to play an important part in
the future, whilst others regarded it as a vile weed. Nevertheless,
considerable attention was bestowed upon its cultivation for a time;
but ultimately became so neglected as to be met with chiefly as a garden
weed. This may have been owing in some measure to the introduction
of Coleus Blumei, which species was regarded with greater
favor, and at once took a place which it held fairly well for a time, or
until he whose name I bear obtained from it varieties so novel and
brilliant in color, as to entitle them to rank high amongst the time-honored
favorites of the garden. From the most reliable information,
I infer that this species at least is one of my immediate ancestors,
and whether I owe as much of kinship to any other, has not been
made known. But this I do know, from the day I was first introduced
to the public, in my chocolate and violet colored suit until the present
time, I have been praised as few plants have been. But being
neither envious nor vain, I have desired the company of those
whose colors are brighter than my own, as variety in harmony gives
greater satisfaction than any one can singly bestow. Some of the[76]
ONLY a few years ago, not one of the Coleus family had a place
in the gardens of Europe and America, and I have been told
that in our absence gardeners depended chiefly upon plants
with showy flowers for ornamenting their gardens and
grounds. When some of my remote relatives were introduced, numerous
were the surmisings as to what place they should occupy
amongst cultivated plants. This was especially so in the case of
Perilla Nankinensis, a plant of most sombre hue, but so striking
withal as to attract general attention. Some looked upon it as the
forerunner of a class of plants destined to play an important part in
the future, whilst others regarded it as a vile weed. Nevertheless,
considerable attention was bestowed upon its cultivation for a time;
but ultimately became so neglected as to be met with chiefly as a garden
weed. This may have been owing in some measure to the introduction
of Coleus Blumei, which species was regarded with greater
favor, and at once took a place which it held fairly well for a time, or
until he whose name I bear obtained from it varieties so novel and
brilliant in color, as to entitle them to rank high amongst the time-honored
favorites of the garden. From the most reliable information,
I infer that this species at least is one of my immediate ancestors,
and whether I owe as much of kinship to any other, has not been
made known. But this I do know, from the day I was first introduced
to the public, in my chocolate and violet colored suit until the present
time, I have been praised as few plants have been. But being
neither envious nor vain, I have desired the company of those
whose colors are brighter than my own, as variety in harmony gives
greater satisfaction than any one can singly bestow. Some of the[76]
[77]
older varieties are well fitted to produce this effect, and none more
so, perhaps, than my old friends Aurea Marginata, and Golden Circle;
but the majority of their class either lack expression, or are
so delicately constituted as to become perfect "frights" when
planted out of doors.

DREER'S NEW HYBRID COLEUSES.
During my time, many varieties with excellent characters when in my company, have performed their parts but poorly, whilst others have had enough to do to keep up a doubtful reputation. It was with pleasure, therefore, I hailed the arrival of a fresh set from England a short time ago, headed by George Bunyard, who, with his companions were so highly spoken of, that I hoped one or more of them would prove of service to me. But this hope has not been realized, and to-day, for all of them, I am as destitute of support as I was before their arrival. Poor George, after being much in his company for a season, it is only fair to say, he performed his part so poorly that I hope, for the credit of both, we shall never meet again under similar circumstances.
What the incoming season may bring forth, yet remains to be seen, but at present the prospects are good for a grand display, as a new order of aspirants are being marshaled for duty, whose merits, some say, are such as to eclipse the old members of our family, and even take from me the honors I have enjoyed so long. Should their claim be well founded, I shall surrender my right to the first place without regret, and be even glad to take any subordinate place I may be deemed competent to fill. But should they fail to meet the expectations thus produced, it will be my duty to remain at my post until such time as new varieties are found, regarding whose merits there can be no doubt.
Be it understood that what has been said about my associates has reference only to them as bedders; for it is well known, many varieties when grown under glass, and partially shaded from the glare of sunshine, possess greater brilliancy and beauty than I lay[78] claim to. For this reason, I think those so constituted as to require the protection of a green-house, should be sparingly, if at all, planted out of doors, and the outside department exclusively occupied by such as attain their greatest perfection in free air and the full tide of sunlight.
Before closing this monologue, I am forced to say a word in behalf of a plant seemingly possessed of extraordinary capacity for the work in which I excel. I refer to Acalypha Macaffeana, the leaves of which are large and finely formed; color, reddish-brown, and irregularly blotched with bright shades of crimson. When fully exposed to sunlight, it looks as if "on fire through all its length," and being much more stately than myself, might form the central figure in a group of Coleus or other plants with the greatest acceptance.—Verschaffeltii, in Gardeners Monthly.
We do not know who is the author of this very interesting autobiography of an old and popular Coleus. The florist for whom it was named, M. Nuytans Verschaffelt, was the adopted son of the late Jean Verschaffelt, of whose nursery near Ghent, he was the manager, and to which he succeeded on the death of the proprietor. M. Nuytans was a very distinguished and highly esteemed horticulturist; he was an active member of the Royal Agricultural and Botanical Society of Ghent and Chevalier of the Order of Philip the Magnanimous. He died June, 1880, in the forty-fourth year of his age.
There has been a remarkable progress in the development of the Coleus since the introduction of Blumei, but the two past years have been more distinguished than any previous ones by the originating of many new and beautiful hybrids. Pre-eminent among these are "Dreer's Set of Tri-colored Coleus," fifteen varieties; "Queensland Set," fifteen varieties, and "Queensland Set of Dwarfs," ten varieties. Mr. Henry A. Dreer says of them: "These varieties which it is a pleasure to offer, have originated in our nursery[79] grounds during the past summer, were selected from perhaps six thousand seedlings excelling in point of color, variety, habit and novelty, and we feel safe in predicting for them a future that leaves nothing wanting in this class of plants."
Mr. Dreer is sustained in his statement by the verdict of many of the leading florists who visited them, and the committees of the Cincinnati, Philadelphia and New York Horticultural Societies, the summer and autumn before they were offered to the public.
In the February number of the Gardeners Monthly, a lady asks some of the correspondents who have tried the new Coleuses, to report thereon, whether as brilliant as their illustrated types, and if they retain their colors in bedding out. We will give the replies from the March number.
J. R. H., Richmond, Va., says: "In response to the query of Mrs. R. B. Edson about Dreer's New Hybrid Coleus, I take pleasure in giving my experience with regard to their hardiness in the summer sun. As the summers in our city are extremely dry and hot, I think it a very fair trial of them.
"When I received my box of Coleus from Mr. Dreer and opened it, the first thought was that I was swindled nicely, while I at once perceived that they were of an entirely new type of Coleus, but considered their colors very ugly indeed, and quite different from the colored sheet in his catalogue. However, I determined to give them a trial before expressing my opinion. I put them in the hottest place I could find, determined to get out of them all the 'come out,' should there be any, and to my utter surprise, their colors changed so rapidly and beautifully, that after a lapse of two weeks, I could scarcely believe they were the same plants. I so much liked them I determined they should have a prominent place in my garden, and accordingly planted them in my border where they did not miss the sun at all while it shone. They grew off at once with the old colors (as when received), which discouraged me again,[80] when to my surprise, about the middle of June, they began to show their bright colors again, and in three weeks they were the brightest and prettiest Coleuses I have ever seen, and remained so with a continual growth until they were killed by the frost.
"I must confess I never saw plants resemble as much the colored plates of their likeness, as did my Coleus; just like the plate with the exception of the fine gloss, which of course I did not expect. It seemed that the hotter the atmosphere was the brighter they looked, and have stood the sun about twenty per cent better than the older varieties. They have given me more pleasure than any set of new plants I have ever received. I consider them the greatest acquisition I have known in the soft-wooded class of plants. While there is quite a similarity in the tri-colored set, it is not at all an objection. The only objections to any of them are that Amabilis and Mrs. E. B. Cooper, while very rank growers, are exceedingly ugly, and Superbissima entirely worthless. It will not grow, I don't care what I do with it. Some seedlings that I have raised from them are very richly colored, and I think them much prettier than their parents, though I have not had a chance to test their qualities in the summer."
We regret that the writer did not give the names of those Coleus he so much admired as well as those which are "exceedingly ugly" and "entirely worthless." We can report the same lack of success with Superbissima. It would not grow one bit, but remained stationary several months, and then died.
Mr. E. L. Koethens reports from a large collection: "For bedding these are the chosen ones, Gracilliana, Miss R. Kirkpatrick, Superbissima, and above all, Speciosa. But for inside culture, many of the new ones are unsurpassed for beauty in any class of decorative plants. Here again Speciosa and Miss R. Kirkpatrick of Dreer's set, lay claims to attention, and his Amabilis is attractive for its free blooming properties. Fairy is also conspicuous, and[81] Beacon takes the place of Superbissima indoors, but Zephyr, in my opinion crowns them all as a foliage plant for indoor culture; a single head often measuring ten inches across, with a rich bronzy-brown color. The above are all valuable acquisitions and should be in every collection."
Mrs. M. D. Wellcome thus writes: "Mrs. R. B. Edson in her charming 'Garden Notes and Gossip,' asks that some of the correspondents who have tried the new Coleus, Dreer's and Henderson's new sets, report thereon. I have not tried Henderson's, and only six of Dreer's, so I am not prepared to report very fully. But I wish to make special mention of Miss Ritta Kirkpatrick, which looks like the picture only it is handsomer. It is the one represented by a large leaf, creamy white center, broad, green lobed margin. It was a wee plant when it came to me in early spring, but it very rapidly outgrew the other five, branching out finely, so that I began in June to take slips from it, and have continued to do this each month to the present time. I should think I had rooted full thirty cuttings, and the original plant, which has been beheaded on three of its branches, has now twenty-eight that would I think all make very nice plants, if treated as were the others. I rooted them all in sand, kept constantly wet, and exposed nearly all day to the rays of the sun. I never saw anything so quickly take root and so rapidly grow as did those cuttings. At one time I kept half a dozen about two months in the pure sand, till they were fine large plants, with a great mass of roots. They can be removed from the sand to pots of earth without retarding their growth. I always allow the particles which adhere to remain in transplanting. This Coleus is a special favorite with me. Fairy, foliage yellow and green, blotched with crimson-scarlet, and Charm, yellow, tinged with bronzy scarlet, stained with dark brown; green deeply serrated margin, were very beautiful in the open ground, and from these I rooted also in sand several very fine cuttings.[82] But the original plants did not grow rapidly. I think the Coleus adds much to the attraction of the border, but it is for the winter window-garden they are specially valuable."
These new Hybrids have stood the test of a year's trial, and three varieties exhibited at the June meeting of the Royal Horticultural Society, London, carried off the highest prize for this class of plants, and received very flattering newspaper notices. In Mr. Dreer's catalogue for 1881, he has selected twenty-four which he calls the cream of those New Hybrids. Superbissima is included, while Zephyr is omitted. Kirkpatrick is among them, we are happy to say. So superb are some of the recent Coleuses, Verschaffeltii, we fear, will have to retire still further into private life. Being quite advanced in years, we presume he will not regret this. We are sure that he will always be treated with that respect which is due to honorable old age.
 HOW much one who gives attention may learn in the vast
field of Nature! How varied are its attractions, how wonderful
its work, how indescribable its beauties! There is
a fascination in these studies, whatever may be the department
to which they are directed, and the more one learns the more
sensible they become of the limitations of their knowledge. I have
already told you I had within a year or two been awaking to a
realization of the value of ornamental foliage plants in giving an
abiding brightness and beauty to the window-garden and open border.
As humanity is ever prone to extremes I may become too
enthusiastic in this direction. I thought there was some danger of
it as I surveyed my array of pots filled with fine specimens of various
sorts. I will take them for my subject to-day, giving whatever
facts of interest I have been enabled to gather from various sources.
HOW much one who gives attention may learn in the vast
field of Nature! How varied are its attractions, how wonderful
its work, how indescribable its beauties! There is
a fascination in these studies, whatever may be the department
to which they are directed, and the more one learns the more
sensible they become of the limitations of their knowledge. I have
already told you I had within a year or two been awaking to a
realization of the value of ornamental foliage plants in giving an
abiding brightness and beauty to the window-garden and open border.
As humanity is ever prone to extremes I may become too
enthusiastic in this direction. I thought there was some danger of
it as I surveyed my array of pots filled with fine specimens of various
sorts. I will take them for my subject to-day, giving whatever
facts of interest I have been enabled to gather from various sources.
Everybody has heard of croton oil, but only a few of that same everybody know anything about Crotons. The number of species known is enormous, and they are found in many parts of the world, but chiefly at the South Sea Islands. Some kinds are native to our own country, mainly in the South and Southwest, but these are not characterized by the brilliant markings of the foreign varieties. Their leaves are often thick and large, but usually they are very long and narrow and ribbed, veined, spotted and blotched with crimson, scarlet and gold. They are a very interesting class of ornamental plants, and their low price, twenty-five to fifty cents, except for novelties, places them within reach of the common people. They do best in a rich soil, with a little peat and sand; also an abundance of water.
The specimens I have are these: Aucubæ Folium—leaves large, dark green, blotched with golden yellow. Interruptum, very long leaves, mid-rib bright scarlet, shading to gold—very graceful. Irregulare, so named because of the irregularity of its leaves in shape and color—two precisely alike being rare.
The handsomest however of my collection, is Croton Weismanni. The ground color is a shining bright green, striped and mottled with golden yellow. The leaves grow to a foot in length and three-fourths of an inch wide. Among the more recent and high priced novelties are Croton Evansianus and Princess of Wales. The former is "distinguished by the peculiar form of its trilobate leaves and the depth of coloring pervading the whole plant. The newest formed leaves are light olive green with mid-ribs and veins of golden yellow, and the interspaces spotted with the same color. As the leaves become older, the green deepens and changes to a bright bronzy crimson, and the golden yellow of the mid-ribs, veins and spots becomes a rich orange scarlet." Princess of Wales is one of the long-leaved drooping forms of Croton, and is very distinct in character. The leaves are from one and one-half to two feet in length. The ground color is green, and the variegations creamy-yellow, very variable in color. The markings are of the maculate style, with here and there large blotches of clear cream-yellow, and and in other parts clouded markings of smaller confluent blotches and spots. Occasionally these conditions are reversed.
The Croton Fenzii, recently offered in commerce by M. Solviati, of Florence, is described as a jewel among the Crotons. It is the result of a cross effected in the green-houses of Sesto, between C. Veitchii and C. Weismanni, and has moderate sized oval acuminate leaves, richly veined with golden yellow, the principal nerves being purplish-red, which color extends to the stem and the petiole. The habit is so dwarf and compact that plants only a foot high are often seen with all their splendor, the yellow streaking then extending[85] to almost the whole surface of the leaf, and the red nerves shining on the yellow ground. It is a variety especially fitted for the decoration of small green-houses, as it requires very little room to be able to develop all its charms. This variety has been dedicated to the Chevalier E. O. Fenzi, President of the Royal Horticultural Society of Tuscany.—London Florist.
Of these the varieties are numerous, and the foliage very ornamental. Those I have are Dr. Hondley; green ground, blotched with rose, crimson center; Madame Houllette,—blush clusters and white spots on green ground; Sagittæfolium pictum,—arrow-shaped leaves prettily spotted with white; Madame Alfred Bleu,—the ground color of the leaves is silvery white, which is blotched with green, in some leaves very sparingly, in others, nearly half the surface; the veins are prominent and of rich rosy crimson, bordered by narrow bands of a lighter shade. Alfred Mame,—beautiful deep carmine, richly marked with rosy spots and white leaf margin. La Perle de Brazil,—ground color, green, reticulated all over with pure white, like fine lace. These last three are from the collection of Mr. John Saul of Washington, and are new.
Fancy Caladiums do best in somewhat shaded positions, in well enriched soil, composed of finely decomposed manure, leaf mold and sand, and a moist, warm temperature. Great care must be had in their earliest stage of growth, to prevent decay of the tubers by over-watering. They can be preserved in sand during the winter, in a room sufficiently warm to prevent danger from frost.
Is the most striking and grand of the Ornamental Foliage Plants for the lawn or flower garden. It will grow in any good soil, and is very easy of cultivation. When of full size it stands about five feet high, and its immense leaves often measure four feet in length[86] by two and a half in breadth; very smooth, of a light green color, beautifully veined and variegated with dark green. When killed down by frost in the autumn, the bulbs must be taken up and stored in the cellar. The Caladium belongs to the family of "Jack in the Pulpit," or Indian Turnip, and the Ethiopian or Egyptian Calla. They rarely bloom in our Northern States. The flowers resemble in shape the Calla Lily, only are much larger and narrower, are of a rich cream color, very fragrant at first, but soon lose their odor, which resembles the Magnolia.
These comprise a large genus valuable for their foliage and also winter flowers, yet not very generally cultivated. Mine are labeled Andersonii, "a handsome orchid-like flower, white, spotted with red." Pictum, foliage prettily streaked with white, a strong, vigorous grower; Tricolor, leaves prettily marked with pink and green; Cooperi, has flowers white, prettily streaked with purple; El Dorado, light green foliage, with golden veinings.
These are considered by florists as among the most elegant of tropical plants, but like the Eranthemums, are not generally known. They are all natives of tropical America, and require strong heat with plenty of moisture. They are low-priced, and ought to be more extensively cultivated. I think mine are very beautiful. Eximia, upper surface of leaves striped with grayish-white; under, purplish-violet. Leopordina, pale green with oblong blotches of deep green. Mikans, shining green with a white feathery stripe. Van den Heckii, dark glossy leaves, mid-rib silvery white. Makayana, a very ornamental dwarf species; leaf-stalks slender reddish-purple, blade of the leaf ovate, ground color, olive green, beautifully and regularly blotched with creamy yellow of a transparent character; on each side the mid-rib are oblong dark green blotches,[87] while the under side is rosy red. Tubispatha is an elegant and very attractive species of erect habit of growth; leaves some nine or ten inches long, light green, ornamented on each side the mid-rib with oblong blotches of cinnamon brown. Veitchii, "The leaves of this grand plant are upward of twelve inches in length; the under surface of a rich purplish-wine color, the upper of a deep shining green, blotched with conspicuous patches along each side, of a yellowish-green, almost verging on gray. The contrast is very marked, and the whole plant very beautiful."
Achyranthes, a genus of richly colored tropical plants, are better known, and to a limited extent are found in many gardens, Verschaffelti, with its dark crimson leaf, being the most common. Brilliantissima, ruby red, is a new English variety; Wallisii is a new dwarf, with small purple leaves; Lindeni Aurea Reticulata, foliage netted with golden yellow, on a light green ground. These plants are of the easiest cultivation, and endure strong sunshine without injury.
Alternantheras are also very effective for bedding plants; habit dwarf. Foliage is in some of a magenta-rose color, others, yellow and red; Purpurea has a purplish tint, and Versicolor, crimson and pink shadings. They are unsurpassed for ribbon or carpet bedding.
Dieffenbachia, a genus of stove plants with very showy foliage. Brasiliensis, a handsome variety, the leaves averaging eighteen inches in length by eight or nine inches in width; the ground color of the leaf is deep green, and the whole surface is mottled with small blotches of greenish-yellow and white; Bausei is a stocky-growing, broad-leaved variety, with yellowish-green leaves, which are irregularly edged and blotched with dark green, and also spotted with white, the markings being peculiarly effective; Weirie is of dwarf habit, the foliage of a bright green color, thickly blotched and spotted with pale yellow. One of the finest of the species.[88] They grow best in loam and peat equal quantities, with a little sand. Require strong heat and frequent watering.
A few ornamental foliage plants of rare beauty received from Mr. John Saul merit special notice:
Cyanaphyllum Spectandum is a grand plant with large, oblong, lustrous leaves which have a rich, velvety appearance; they are beautifully ribbed with whitish color.
Alocacia Macrorhiza Variegata, its large caladium-shaped leaves are marbled and broadly splashed with white. Some leaves are nearly all white; Zebrina, fine yellow leaf-stalk with distinct black marks; Illustris, the leaf-stalks are erect, and have a brownish-purple tint, color a rich green, marked between the principal veins by broad patches of a blackish olive, and forming a striking contrast with the brighter green portions of the leaf surface; Sedini, "A very beautiful hybrid between A. Metallica and A. Lowii. The form of the leaf is perfectly intermediate between the two parents, whilst the coloring is a very striking and pleasing combination of the metallic hue of one parent, with the dark green and prominent white veins of the other." Alocasias require a moist heat during their growing season. Soil, peat, with a small portion of loam, sand and manure.
Acalypha Macafeeana is another of the rare and beautiful foliage plants alluded to. It is considered the best Acalypha ever offered. It is certainly very handsome with its "sub-cordate and serrate leaves, eight inches long and six broad, frequently cut into many forms, and very highly colored bright red, blotched with deep bronzy crimson." It proves to be an admirable plant for bedding out. Quite as attractive every way is Panax Laciniatum, "An elegant and very distinct habited stove plant from the South Sea islands. The leaves are tinted and indistinctly marked with pale olive brown, and form a rather complicated mass of narrow segments; they are bipinnate, nearly as broad as long, and have a drooping contour;[89] and the pinnules or segments are very variable in size and form, presenting the appearance of a complex head of foliage in which the lanceolate lobes or pinnules have the preponderancy."
Panax Fruiticosm has a very graceful fern-like foliage. These plants belong to the Aralia family, a genus very ornamental, natives of the South Sea Islands.
Another of my Washington collection, very graceful and beautiful, is Paulinia Thalictrifolia. Its delicate cut leaves resemble the fronds of a finely divided Maiden-hair Fern. The leaves are of a rich shade of green. The young shoots and foliage are of a pinkish-brown color. It is of slender growth and climbing habit, very similar to Capsidium Filicifolium, which has long been a special favorite of mine. Both of these are elegant, trained on a pot trellis.
Paulinia Thalictrifolia is a native of the southern Brazils, from whence it was introduced to the nurseries of Messrs. Veitch & Sons of Chelsea. If only required for decorative purposes there should be no inclination to make the plants produce flowers which are inconspicuous; therefore the main object should be to have plenty of healthy foliage. To secure this, the plant should be grown in a temperature of from 65° to 70°, and if one part of the greenhouse is more adapted to its growth than another, it is the dampest part. After this plant came into the possession of Messrs. Veitch, and before its true value became known, some plants of it were placed in a corner of an old, very damp, warm pit, in which position they grew wonderfully strong, and quite surpassed in vigor and beauty those that were, as was then supposed, placed under more advantageous circumstances, i.e., in dryer and lighter parts of other houses. Care is therefore now taken to keep them where abundant atmospheric moisture can be supplied. A compost consisting of two parts good substantial peat and one of loam, together with some silver sand, suits it admirably.—Gardening Illustrated.
These form a very important part of the class of which we are treating. They give a very beautiful and tropical appearance to the lawn and the garden by their stately growth and broad massive foliage, relieved by rich crimson, scarlet and orange-red flowers. Their foliage comprises various shades of green, glaucous, chocolate and purple tints, ribbed and striped, fitting them admirably for grouping with other plants.
They are also very effective for large pot plants in the pleasure-ground, or conservatory. Under rich cultivation they will attain the height of five feet. They need water often. Among the newer roots Creole, very dark foliage, grows to the height of about six feet. Ornement du Grand Rond, very tall, with large bronzy-green foliage, large scarlet flowers. Oriflamme has large lanceolate-green leaves, with violet veins, a vigorous showy plant with salmon-orange flowers.
The roots of Cannas must be taken up in the autumn. If wanted singly, divide them, if a thick clump is desirable let them be planted out as they are. They must be kept perfectly dry through the winter; if the cellar is very damp they will do better packed in sand.
This is a valuable genus of ornamental plants, specially fine for the center of vases, and for pot culture. Although their culture is on the increase, they are not so frequently grown as they deserve. The species are very numerous, and are found in tropical countries, especially in the islands of the tropics. Many of them assume the proportions of trees. The largest specimen ever known was one of Dracæna Draco, or the Dragon tree of Oratava in Teneriffe, one of the Canary Islands. This tree was remarkable for its monstrous dimensions and prodigious longevity. About ten years since, or in the autumn of 1867, this magnificent specimen was destroyed by a[91] gale of wind. It was a special object of interest in the Canary Islands, and received the attention and veneration of visitors, as do the great Seguvia trees of California. Its trunk below the lowest branches was eighty feet in height, and ten men holding hands could scarcely encircle it; by one measurement this span around it was seventy-nine feet. The trunk was hollow, and in the interior was a winding stair-case, by which one might ascend as far as the part from which the branches sprang. It is affirmed by tradition that, when the island of Teneriffe was discovered in 1402, this tree was as large, and the cavity in the trunk as great, as at the time of its destruction. We are even assured that in the fifteenth century, at the time of the conquest of the Canaries by the Normans and Spaniards, they celebrated mass on a little altar erected in this cavity. From the slow growth of the young Dragon trees in the Canaries, it has been estimated that this monster tree before it was destroyed, was the oldest plant upon the globe. A writer in describing it says: "Long leaves pointed like swords, crowned the extremities of the branches, and white panicles, which developed in autumn, threw a mantle of flowers upon this dome of verdure." The popular name of this species is Dragon's-blood Tree, because of a resinous juice of a red color which exudes from the cracks in its trunk. At one time this resin formed a considerable branch of commerce, as it was used medicinally as an astringent, but it has fallen into disuse.
The Dracænas belong to the Lily family, and they afford a remarkable contrast to the palms and other arborescent endogens, by their branching heads. The young trees of Dracæna Draco do not, however, send out any branches, even in their native localities, until they are thirty years old or more. The small plants of this species, cultivated for ornament, have always a single, straight stem; but are much more robust, and quickly assume more stately proportions than those of the other kinds that will be mentioned.
The Dracæna is admired for its peculiar grace of form—it would be in vain in common house culture to expect flowers. To admire a plant for its well developed and graceful form, marks an advancement in refined taste beyond that which would induce one to exclaim, "Oh!" at the sight of a brilliantly colored flower. Even in rearing a plant for flowers, the first object should be to develop it to the fullest extent in size and shape and strength—to make a beautiful object of the plant itself; just as the first and main attention given to a child, for years, should be to develop and build up its physical system.
The Dracæna is a good house plant, a good balcony and veranda plant, good for the vase in the open air, and in a handsome pot is a fine ornament for table decoration. Its culture is of the simplest kind, adapting itself to any ordinarily good soil, it only requires to be supplied moderately with moisture and to have a temperature ranging upward from sixty-five degrees. It delights in a moist air, and whenever possible, water should be kept where it will rapidly evaporate, and thus ameliorate the atmosphere in this respect for the plant. This condition, moreover, is conducive to the well-being of most plants, and no good plant-grower can disregard it with impunity. Washing the leaves and stem of the plant frequently with a wet sponge, is favorable to its health and vigor, and one of the best preventives of the attack of insects. With dust on the leaves the plants look dingy, while frequent washing keeps them bright and lustrous.
Dracæna indivisa has long, slender, dark green leaves, about three-quarters of an inch or an inch in width, and from two and a half feet to three feet in length, and the lower ones especially are very much recurved or gracefully drooping. This species is among the hardiest of the Dracænas, and is frequently wintered in the open ground, with some protection in climates where the temperature frequently descends several degrees below the freezing point.
Dracæna terminalis is the most popular of the whole family in this country, and is worthy of all the admiration bestowed upon it. The leaves are broader and more erect than those of the preceding species, and of a dark green suffused with red, or having streaks of a reddish color; the young leaves nearly pink, but assuming a dark bronzy copper color afterward. It is a very distinct and showy plant, and adapted to a great variety of ornamental purposes. The propagation and sale of it is rapidly increasing every year, and it is already widely disseminated. At the Sandwich Islands it is cultivated to a considerable extent for its roots, which are baked and eaten. A fermented beverage is also made from the juice, and its leaves are employed as fodder for cattle, and for clothing and other domestic purposes.
Dracæna Shepherdii is of a most noble form, and is one of the finest yet in cultivation. It has long, spreading leaves, of a metallic green, with stripes and border of bronzy-orange, and is a very free grower. Unlike most of the forms already known, which color most on the free young growth of vigorous plants, this plant takes on its distinctive coloring gradually on the older leaves.
Dracæna cannæfolia is an interesting species. Its peculiarity consists in the length of petiole, which is as long as the rest of the leaf. The blade of the leaf is elliptical in form, from fifteen to twenty inches in length, firm, and of a glaucous green.
Within a few years past much attention has been given by cultivators in Great Britain and Europe to hybridizing the Dracæna, and producing new varieties. The most remarkable success has attended the efforts in this direction, of Mr. Bause, in the establishment of Mr. Wills, of Anerly, England. The variety is wonderful—"broad-leaved, medium-leaved and narrow-leaved; bronzy and green, crimson, rose, pink, violet and white variegations; drooping, spreading, and erect habits, are blended in all sorts of combinations."
One of the sorts produced is described as "a most important acquisition, having quite the habit and character of the well-known favorite terminalis, but with white variegation. The ground color is a bright green, with bold, white variegation, the upper leaves being white, with here and there a bar of green."—Vick's Magazine.
Sent out in this country for the first time in 1880, is said to be "one of the most magnificent ornamental foliage plants ever introduced, and altogether unique in character and aspect. It is a native of Western Tropical Africa. The plant is of erect habit, and the stems are closely set with stalked spreading leaves, the petioles of which are of a grayish color, terete with a narrow furrow along the upper side, the base being dilated and sheathing the stem. The blade of leaf is marbled and irregularly banded with dark green and silver gray in alternate straight bands, the colors being about equally distributed. The back of the unfolded leaves is a pale reddish-purple or wine color, and the stem, where visible. It is, without doubt, one of the most superb of ornamental stove plants."
When first sent out in London in 1878, its price was from five to ten guineas per plant. We do not know the price in this country. Mr. H. A. Dreer who has an illustration of it in his catalogue, furnishes the price only on application, which is evidence that it is costly. From the type given, it must be exceedingly handsome, and wholly unlike any Dracæna before offered in America.
Dracænas, as we have noticed before, are particularly desirable house plants, keeping in good condition for a long time, even in rooms where gas is burned—places so unsuited to most plants. They are liable to attacks of the Mealy Bug and the Red Spider if neglected, but the syringing and sponging advised for them will effectually prevent their gaining a foothold if frequently and thoroughly performed. After a year or two the plants begin to lose[95] their lower leaves, and to get leggy, a state of things quite undesirable, as the beauty and effectiveness of the plants depend upon their being furnished with leaves down to the base of the stem. When the plants have become unsightly from the loss of their leaves, they can be renewed very quickly by a simple process. Cut a notch in the stem, on one side, just below the lowest good leaves, and take out a piece of the wood, then do the same on the other side of the stem, but not exactly opposite the first notch. The object is to check the flow of sap at this point and yet allow enough of it to pass to maintain the head. Having cut the notches, take some moss or sphagnum and bind about the stem, covering the incisions and fastening it on securely with twine or fine wire; the moss is to be kept gently moist, and in the course of two weeks will have thrown out young roots above the notches. The head can now be severed from the stem and potted in a medium-sized pot. After keeping it a few days in the shade, it can be gradually brought out into the full light, and will be found to be established.
Dracænas may also be multiplied by removing the thick, fleshy root that may usually be found in the base of the plant. Those tuberous roots can be potted, and if kept in a warm place will soon start and make new plants. When plants are re-potted a favorable opportunity is offered for taking off these roots, for the roots of the old plants are actively at work and, with the fresh soil they receive, will soon recover from any slight check they may have received.
The most rapid method of propagating this plant is by cuttings of the stem; the stem may be cut into pieces an inch in length, and those pieces split in two, and all of those bits will root and become plants. They should be placed in a light, sandy soil, and given a brisk bottom heat of 70° or 80° degrees. They will break and start into growth in a few days.—Vick's Magazine.
So fully does the foregoing express all that is needful regarding[96] the Dracæna, we have thought best to give it entire. We might greatly enlarge on the subject of Ornamental Foliage Plants, and speak of the beautiful Palms, so fine for decorative purposes, the pretty Ferns and elegant Aralias, of which latter "Sieboldi is a capital house plant, so enduring that it will live and keep its beautiful dark green color for weeks almost in the dark." Then there is the Euonymus, so bright with its glossy green leaves, long a favorite whether for the border or window garden. Argentea has striped foliage, and Japonicas aurea has its dark green foliage diversified with golden variegations. Bicolor, foliage almost white, and Tricolor, a rarer form, is marked with pink and white.
With the numerous varieties we have named, it will be apparent how ornamental our gardens, whether within doors or without, may be made by plants, the beauty of which is wholly independent of flowers, and they do wonderfully enhance the effect of the bloomers. The Centaureas and Cinerarias with their deeply lobed leaves of white, are too well known to need any special mention. We do not intend however to pass so lightly over another stately and highly ornamental genus that comes within the reach of everyone. Ricinus, the seed of which can be purchased for a dime, are magnificent in foliage, and when combined with the brilliant colored fruit of the giant varieties, the effect is very oriental. Ricinus Africanus albidus is of recent introduction. It is white fruited, and the stems and leaves are silvery; height eight feet. Borbaniensis arboreus has very large and showy foliage; height fifteen feet. Communis is the Castor Oil Plant. Sanguineus (Obermanii) bears splendid red fruit in clusters, and is very ornamental. A species from Phillippines has gigantic foliage; height ten feet. These can be purchased in separate or mixed packets, and we advise everyone who has a bit of ground to try them. We will close with
I have just harvested my Ricinus or Castor Bean, which I raised from the seed you sent me last spring. It was of mammoth growth, attaining a height of fourteen and a half feet, and sixteen feet across the branches of which there were seventeen after cutting off five during the summer. Each of the branches contained a cluster of burs, the center one having one hundred and thirty-four burs, the other branches not so many. Many of the leaves measured from thirty to thirty-two inches across from tip to tip or point of leaves. When sawed off at the ground, the body measured five inches and a half of wood in diameter, inside of the bark, which was one-fourth of an inch thick. This is a big bean story but nevertheless a true one.—T. G. T. in Vick's Magazine.
 IT is an old adage that one must take Time by the forelock.
In the culture of flowers, we must certainly do so, planning
and preparing in spring for the coming winter, if we would
secure for ourselves plants that can be relied on for blooming.
We know of none equal to
IT is an old adage that one must take Time by the forelock.
In the culture of flowers, we must certainly do so, planning
and preparing in spring for the coming winter, if we would
secure for ourselves plants that can be relied on for blooming.
We know of none equal to
for common house culture, commencing to flower usually in November, and continuing through the spring months. The seed for this ought to be sown in April—if later the plants will not come into bloom so early. The soil for Primroses in all stages should be fine, light and rich, with a good mixture of sand.
For seed sowing it can be put in pans, boxes or six inch pots. First, put in drainage—I use for this coarse sand—then the coarse siftings of the soil. On this to the depth of one and a half or two inches, put the fine mixed soil, press down smoothly and spray lightly with tepid water. Sow the seed on the surface, and sift on enough of the fine earth to partially but not fully cover them. Cover with a glass, or with a bit of soft nice flannel, and place in the shade where a mild moist temperature can be attained. Where flannel is used, it can be kept damp and thus impart moisture to the seeds without their being saturated, washed bare, or displaced by spraying. When the seed has germinated, then glass can be substituted. The tender seedlings must be gradually brought to the sunlight; too long exposure at first would kill them, and if kept in the shade too much they will become drawn and dwarfed. This is the critical period, and many fail at this point. Great care is essential till the plants put forth the third leaf, which is rough and the true primula leaf. Then the plants must be carefully transplanted[99] into other pots prepared as before. In about a month the glass can be removed and the plants potted separately, setting them low, as it is a peculiarity of the Primula to stretch itself up out of the soil, and become shaky. It is necessary sometimes to give them support. In watering, care must be had to prevent the water lodging in the axils of the leaves, which cause them to decay. They will not bear showering like smooth surfaced plants, and only occasionally should they be sprayed through a fine hose. They must be kept during the summer months in a shady place, and have a cool bottom to stand on; a cold frame is the best. They must be housed by the end of September, and the best situation for them is a light, airy shelf near the glass, yet not exposed to intense sunshine. They do not like frequent changes of position and temperature, nor to be grown with other plants. Give them a cool place where they will have the morning or afternoon sun for a time. During the blossoming season stimulate the soil once a week with liquid manure, or water with a few drops of ammonia added. Pick off all flowers as fast as they fade. Plants are stronger and better the second year, and unless they get too shaky, are good for three years. They must, after blossoming, be taken out of the pot, the ball of earth reduced from the roots, and then re-potted in fresh soil. It is not needful to keep them dormant and shaded through the summer, but in a cool and partially secluded position, they will after a brief rest begin to grow, putting forth frequently little crowns all around about the old one, and be full of blossoms during the autumn and winter months. The double varieties are not so easily grown, and cannot be recommended for general culture to be raised from seed. Fine plants can be procured from the florists, but the large single sorts, we think give the most satisfaction. Ellis Brothers, Keene, N. H., have sent us for trial, packets of very fine strains; some are rare, and, judging from the description, must be very beautiful. It is not often that we find more than four varieties named in[100] the catalogues. They send out a dozen sorts, some of which we will name: Primula Fimbriata Kermesina Splendens; Large flowers, brilliant velvet like crimson, yellow eye. Primula Frimbriata Punctata Elegantissima; a new variety; flower velvety crimson, edge spotted with white; very distinct. Primula Fimbriata Striata; beautifully striped. Primula Fringed, Fern Leaf; pure white, with large citron eye; very fine. Primula Globosa, new; a large flowering, fringed sort; petals large and many of them crimped, each overlapping the other, so that they appear almost semi-double; colors white, light pink, crimson and lilac pink. All of these can be bought in mixed or separate packets. We cannot find room for all of these, but hope from the rarest to obtain some fine plants to brighten our room the coming winter. Great advances have been made since the Primrose was introduced into this country little more than half a century ago.

Of the novelties we find in the London Garden special mention made of Primula Sinensis Fimbriata Alba Magnifica. The writer says: "The Primulas from Mr. B. S. Williams' Victoria Nurseries, Holloway, were remarkably fine. The newest sort shown, Alba Magnifica, promises to be an excellent kind; the flowers are large, produced in dense and many flowered trusses, borne well above the foliage, which is also remarkable being elegantly crisped at the margins. The color is white, the purity of which, however, is more strongly marked when the plants are more mature than those shown; the habit of growth is very robust."
Of this novelty Mr. H. Cannell says: "The new white Primula[101] is of exquisite form and substance; the plants are exceedingly compact, with deeply indented leaves of a light green color; the flowers measure two and one-quarter inches in diameter, pure white, with large, bright yellow eye, each petal being deeply and beautifully fringed, and are borne in large trusses well above the foliage."
We give an illustration of this Primula, kindly furnished by Ellis Bros., who are of the first to offer it in this country.
"What is the difference between them? I am told differently by nearly every florist I ask. An old Englishman told me the other day that he used to grow great quantities of them in England, and that the difference between the two is, that the Picotee has fringed edged leaves, while in the Carnation proper the edge of the leaf is smooth like a rose."
The question is asked of Mr. Vick, and he thus replies: "The Carnation and Picotee differ only in the arrangement of the color, or markings. The distinction is made by florists, and is of course arbitrary. Seeds saved from one plant, may produce both Carnations and Picotee, or even from the same seed-pod. In an old work in our possession, the distinction is as stated, but for long years any flower with an irregular edge has been considered unworthy of propagation. The Carnation should have broad stripes of color running through from the center to the edge of the petals. The Picotee has only a band of color on the edge of each petal."—Vick's Magazine.
Although Mr. Vick here states that the Carnation should have broad stripes of color, neither he, nor any other florist makes this distinction, but call pure white, and pure red Carnations, just as freely as those that are striped.
There are two classes of Carnations, and thousands of varieties. The class of Perpetual Bloomers are called Monthly and Tree Carnations.[102] The Garden Carnations are hardy, and can be left in the garden during winter by giving them a covering of leaves, straw, or evergreen boughs. They are easily raised from seed. Sown in June or July, will make good robust plants before frost, which will bloom the following summer. Some of them will be single, perhaps, and these can be removed. Those of superior merit may be multiplied by layering. This method is to select good healthy shoots that have not bloomed, and make a cut midway between two joints. First cut half way through the shoot, then make a slit lengthwise to a joint. Remove the earth a few inches in depth, and press the branch down so that this slit will open, and then cover with the soil. Roots will form where the cut was made, and thus a new plant will be formed, which can be removed in the autumn or spring. Midsummer is the best time to do this, and by adopting this method good, healthy plants are secured. The plants should be well watered a day or two before layering is commenced, and immediately afterward—then only occasionally. They are frequently propagated by cuttings, which can be rooted in wet sand, or in light sandy soil.
Or Monthly Carnations, can be easily obtained of the florists for summer or winter blooming; the former purchased in the spring, and the latter in the autumn. If one raises their own stock, it is not best to allow those to bloom much during the summer that are wanted for winter flowering. It is well to sink the pots in a good sunny place in the garden, and when they run up and show signs of bedding, cut back the stalk so that it may become more compact and branchy, then the buds in the late autumn or winter, will be much more numerous. The best for winter blooming are La Purite (carmine), President de Graw (white), Peerless (white, striped with pink) and Peter Henderson, of the well-known varieties. Of those of recent introduction, Lady Emma is said to[103] be excellent. One florist says that "it is destined to be one of the leading winter-blooming Carnations. From my bed of one thousand plants in the green-house throughout December and January last, I plucked more blooms than from any other variety occupying the same space." It has proved excellent also for a bedding pink. Its color is a rare shade of crimson scarlet; the flower is of medium size, full and double, and never bursting down the side. Lord Clyde has for three years proved to be an excellent winter bloomer. It is of a very robust growth, like its parent the Edwardsii, but of a more dwarf, low-flowering habit. The ground-work is white, thickly striped with carmine, and a frequent blotch of maroon; very floriferous, each stem bearing from six to eight flowerets. Lydia is another of the recent novelties, and is very handsome. Flowers very large and intensely double, of a rich rosy, orange color blotched and flecked with carmine. Crimson King is one of the largest Carnations, very full, bushy habit, and robust, color crimson-scarlet. A pure bright scarlet is rare; when therefore, Firebrand, a novelty of 1880, was announced as a bright scarlet, it produced quite a sensation. It is very highly commended by those who have seen it. Grace Wilder, Princess Louise and Fred Johnson, are new hybrid seedlings now offered for the first time to the public.
There was quite a discussion in the Gardener's Monthly of last year as to the best pure White Carnation. In the August number, Mr. E. Fryer of Delaware writes: "The varieties called Peter Henderson, sent out by Nanz and Neuner I have found to be the best white I have yet grown for winter bloom. It is a stronger and better bloomer than de Graw, its only drawback being that it runs up high like La Purite. Snowdon is a true dwarf, pure white, and if it proves a good winter bloomer, will probably supersede all other whites, the flower being of fair size and very fragrant. Bock's Seedling, Charles Sumner, I have grown the past winter. The flower is of an enormous size, but it invariably bursts before opening,[104] and is a dull unattractive color. Waverly I have also grown last winter—a splendid variety, rich crimson scarlet; the color was no way exaggerated as represented in the Monthly a year ago; produces a fair average of flowers to the plant, flowers selling readily at ten cents each. I think this the most useful color to the commercial florist.
"I still cling to the old carmine La Purite, which for quantity of bloom, size of flower and general good qualities, I think has not been beat by any of the newer varieties for winter bloom." Mr. Peter Henderson, one of the leading florists, places Snowdon above all other white Carnations, its dwarf habit making it specially desirable.
Florist's Pinks are more dwarf than the Carnations, flowers very double, clove scented, and are of various shades of maroon, carmine, crimson and rose interlaced with white.
The Gardener's Chronicle gives the following interesting account of the origin of this class: "It may be interesting to record the fact, published in an old number of the Floricultural Cabinet, that the first Pink worthy of notice was raised in the year 1772, by Mr. James Major who was then gardener to the duchess of Lancaster; previous to that there were but four sorts, and those of very little note, being cultivated as only common border flowers. Mr. Major having saved some seed in 1771, he reared several plants, which, blooming the next season, one of the number proved to be a double flower with laced petals, at which he was agreeably surprised, although he considered it as being only in embryo, and the prelude to still further advance to be developed at some future period, which is now verified by the rapid strides this beautiful flower made in size and quality during the years which followed. Mr. Major informed the writer of the foregoing remarks that he made his discovery known to a nurseryman or florist and was[105] offered the sum of ten guineas for the stock of his new Pink; but, acting on the advice of his friends, he declined to sell, and set to work instead and increased the stock with a view of offering it in sale to the public. It was sent out to the public at half a guinea a pair (for it has long been a custom of offering Pinks in pairs, a custom which is continued to this day), under the name of Major's Duchess of Lancaster, the orders for which amounted to £80. It is recorded that one individual ordered as many as twenty pairs, which was considered in those days an unusually large number. It would be interesting to have a bloom of Duchess of Lancaster to compare with the fine double varieties of the present day. We appear to have come to something like a pause in the matter of Pink production as the flowers are now very large and full, and the lacing is as perfect as can well be conceived."
The word is derived from the Greek words Dios, divine, and Anthos, a flower; God's flower, or the flower of Jove. There are several species, and many varieties of Dianthus; Dianthus Caryophyllus is what is commonly known as the Clove Pink, and from it have been produced the double varieties called Carnations and Picotees. The plant in its wild state is found growing on the south side of the Swiss Alps, at a low altitude, where the winters are not severe. The common perennial garden Pink is Dianthus Plumarias. The old and well-known Chinese Pink, Dianthus Chinensis, is a biennial, flowering the first season from seed sown in spring, lives during the winter, blooms the second year, and then dies. New and superb varieties have been introduced of late years from Japan, and Dianthus Laciniatus, and Dianthus Heddewigii, both single and double, make a splendid display, and are among the most desirable of our garden flowers. Dianthus Diadematus is of dwarf habit, very profuse in blooming, and the flowers are of various hues, from white to dark maroon, and also beautifully marbled and spotted.[106] Of the recent novelties Eastern Queen and Crimson Belle are superb; we speak from personal knowledge. "Eastern Queen" is beautifully marbled; the broad bands of rich mauve upon the paler surface of the petals are very striking. "Crimson Belle," as its name implies, is of a rich crimson hue, with dark markings; very large and finely fringed.
For early blooming it is well to sow seed as early as April. June sowing will secure good hardy plants for the following season. When there is a profusion of bloom, it is well to remove a portion of the flowers, so that the plants may not become exhausted, and the seed pods beyond what are desired for ripening, ought also to be cut off.
Charles Dickens.
 HAVE been off on a vacation, peering into other folks' gardens
and admiring other people's flowers. Visited the
Public Garden of Boston and saw that there had been a
marked improvement within ten years. The massed beds
of several sorts, with their contrasting borders, were very attractive,
specially the maroon Coleuses with border of Centaurea.
There were few varieties of Geraniums, and these were mostly
massed in beds, some all scarlet, others wholly pink.
HAVE been off on a vacation, peering into other folks' gardens
and admiring other people's flowers. Visited the
Public Garden of Boston and saw that there had been a
marked improvement within ten years. The massed beds
of several sorts, with their contrasting borders, were very attractive,
specially the maroon Coleuses with border of Centaurea.
There were few varieties of Geraniums, and these were mostly
massed in beds, some all scarlet, others wholly pink.
At Forest Hills Cemetery there was the finest display of flowers and tropical plants I ever saw, and they are very artistically and tastefully displayed. I saw several beds with artistic designs on a ground work of Sempervivum, evidencing great skill in the arrangement and culture. The entrance gateway to Forest Hills Cemetery is very beautiful in design, and here we saw that graceful climber Ampeclopsis Veitchii, in the perfection of its beauty, covering the front almost entirely. I had noted it in various stages of growth, clinging to the dwellings in all parts of the city, requiring no aid but its own little rootlets. It is a native of Japan and was introduced[108] in this country twelve years ago. It was slow at first in being duly appreciated, but now is widely known and extensively propagated. Probably the finest plant is owned by Mr. George L. Conover of Geneva, N. Y. It covers the entire front of his two-story square house, and has become so famous that horticulturists from all parts of the country have been attracted by it, and a great many people have visited Geneva for the special purpose of seeing this fine plant. It has proved to be perfectly hardy, only the first year the young and tender plant needs some protection during the winter. Florists are growing them in great quantities to meet the increasing demand. It can be obtained for twenty cents. I received a small plant last year and kept it in my window box during the winter. It died down, however, and I quite forgot about it, till it sprang forth anew in April. Since putting it in the ground it has grown rapidly, and I shall value it now more than ever.
The Golden-Leaved Honeysuckle is a special favorite of mine. Its leaves are so netted and veined with yellow as to give this hue the predominance. The foliage is small; the flowers are yellow and fragrant. The family of Lonicerus, or Honeysuckle, embraces a large variety. The botanical name was given in honor of Lonicer, a German botanist, who died about three hundred years ago.
Lonicerus Holliana was introduced into this country from Japan by Dr. Hall. The flowers are pure white when they first open, but assume a creamy tinge in a few days. This variety blooms almost continuously from June till frost. It attains sometimes to the height of twenty, and even thirty feet. The flowers are very fragrant.
Belgian, or Monthly Fragrant, bears its blossoms in clusters. They are pure white in the interior at first, but afterward change to creamy yellow, deepening into orange.
Sempervirens (Scarlet Trumpet) is a native of this country, and[109] perfectly hardy. This is the most common, though not fragrant. It is a strong grower, and blooms from June to November. Its scarlet flowers tinged with orange afford a pleasing contrast with its dark, glossy foliage.
For an out-door annual climber, what can be prettier than the dainty, graceful Canary Flower? Mine have scorned the limitations of the twine I had fastened to the lower limbs of a small pear tree and ascending far above them, have run out a full yard on a large branch. The light green, finely lacinated foliage is very handsome of itself, but when the Canary bird flower is added, how lovely it is! It is so easily grown from seed that I wonder so few have it. A paper costing only ten cents would give you a score of plants, and they are much prettier for the bay window than Madeira vines.
A writer from England says: "While in the north of England, last fall, we paid a visit to Alnwick Castle, the seat of the Duke of Northumberland, and the ancient home of the Percy family.... The first thing that struck me on entering the town was a bay window most charmingly draped with light green climbers, and literally covered with bright lemon yellow flowers. Now this appeared so strange to me (for the chilly night air had already affected the geraniums and other tender out-door plants), that I had to cross the street, take the Yankee liberty to open the gate, go inside and examine this thrifty beauty. I confess I was not only surprised but greatly interested to find it was only the Canary flower, Tropaeolum peregrinum, a member of the Nasturtium family, and I concluded at once that there should be one cottage in America next summer worth coming miles to see on account of its climbing plants of light green foliage and rich yellow masses of Canary bird flower."—WALTON, in Vick's Magazine.
Do not forget to include this pretty vine in your seed order next year.
This is one of the best of our climbing annuals, on account of its rapid and luxuriant growth, attractive foliage and large bell-shaped flowers. Under favorable circumstances they will grow to the height of twenty and even thirty feet in a summer. They commence to bloom when quite young, and continue in bloom until destroyed by frost. Some people remove them from the border to the house for winter blooming, but the change from out-door to indoor life, often retards their growth and mars their beauty. They are too cumbersome for window plants after having grown during the season, and it is better to sow seed in August, and get in this way plants for the house. They are hard to germinate, and need to be started in pots or in a hot bed. Place them in moist earth edge down, and do not water until the young plants appear above the surface, unless the earth becomes very dry.
For out-door blooming sow in March or April. As soon as the plants are strong enough, transplant to three-inch pots; keep them shaded from the sun for a few days, gradually expose to the open air, and plant out when all danger from frost is over. The soil should be well stirred to the depth of nearly two feet, and well rotted manure worked in. In dry weather they need liberal watering as often as once a week, and liquid manure water occasionally is of great benefit to them.
The Cobœa can be propagated by layers at almost any season of the year. It is done in this way: Cut a notch near a joint, place in a pot and fill with soil, and keep the soil moist. It takes from two weeks to a month for them to root.
A writer says of this plant: "The Cobœa is an old favorite and it is worthy of remark that but few of the novelties introduced of late years can equal some of the old favorites that we have been accustomed to grow. The Cobœa is a native of Mexico, from which country it was introduced in 1792. It was named in honor[111] of Bernandez Cobo, a Spanish priest and botanist. The growth of the vine is very luxuriant, and it is equally easy of cultivation, the only essentials to success being warmth, a rich, light soil, and sufficient water. If allowed to become very dry, it will soon wither away. It requires sun and a warm room to grow it to perfection; yet it is not a tender plant, that is, it will live anywhere, provided the frost does not touch it, and is one of the few plants which will flourish luxuriantly in parlors lighted with gas and kept almost at fever heat. If grown in a hanging basket or pot, it must be large and the roots allowed plenty of room to spread out in. In the summer the pots can be removed from the interior room to a balcony or piazza, or plunged until they are again wanted. Then clip off the growth of branches and leaves, place the pot back again in a sunny window, where it will soon start afresh, with new arms and leaves to cover the window. It is one of the best vines for parlor decoration, as it will drape and festoon the window, and stretch forth its tendrils, running up even to the ceiling. The tendrils are so clinging in their nature that they will attach themselves to anything which comes within their reach—curtain cords, branches of other plants, brackets, etc.,—throwing out new branches everywhere.
"I advise all who adopt the plan of plunging the plant in the pot in the open air during the summer, either to shift into a pot two sizes larger, or else to take it out of the pot and reduce the ball of earth nearly one-half, and repot it in fresh compost before removing it to the house. This should be done not later than September 10th. The plants will amply repay this little attention by an increased luxuriance of both foliage and flowers during the winter months, while plants not so treated will become sickly and unhealthy before spring, and beside, when pot-bound, they soon become the prey of numerous insects."
There are several varieties of the Cobœa, though scandens is the most generally known. The large bell-shaped flowers are greenish[112] at first, but rapidly change to a dull purple. Cobœa Scandens Alba has greenish white flowers. Cobœa variegata is one of the most magnificent ornamental climbers, the leaves being broadly margined with yellowish white, the variegated foliage forming a beautiful contrast with its large purple flowers. It is of strong habit, a rapid grower, attaining frequently the height of fifty feet in a short time. It is, however, difficult of propagation, rooting with difficulty. The seeds vegetate as readily as the common sort, but the plants are apt to die off soon after attaining their seed leaves. Layering in the manner already specified, is the best method of increase.
Cobœa scandens argentea is another variegated leaved variety, differing from variegata in that its leaves are of a purer white. It is described by some as being identical with Cobœa scandens, Schuerens Seedling, but by Messrs. Leeds & Co., of Richmond, Indiana, as being "a great improvement on the old variegated variety. Leaves large, green, bordered with creamy white; calyx of the flowers variegated like the leaves."
Clematis (Virgin's Bower), derives its name from klema, a vine-branch. The popular name, Virgin's Bower, was given to Clematis Viticella upon its introduction into England during the reign of Elizabeth, 1569, and was intended as a compliment to that sovereign, who liked to be called the Virgin Queen.
There are, it is said, two hundred and thirty described species, the majority of them free-growing, hardy climbers. They are among the most gorgeous perpetual-blooming of the class under consideration. Great improvements have been made during the past twenty-five years by hybridization, but the finest varieties have originated within ten years. Of the new English hybrids Jackmanii stands in the front rank. The flowers are from five to six inches in diameter, and consist of from four to six sepals which[113] have a ribbed bar down the center; the color is of an intense violet-purple, remarkable for its velvety richness, and a shading of reddish-purple toward the base, and they are furnished with a broad central tuft of pale green stamens. It originated with Jackman & Son, England, and was first exhibited at Kensington, 1872. It is a cross between Clematis Viticella and Clematis Lanuginasa. From this cross many excellent seedlings have been raised, closely resembling the parent stock in color and general character.
Of Jackman's Clematises the English Gardener has the following: "They are magnificent; and more than this, they do give us some of the grandest things in the way of creepers the horticultural world has ever seen, making glorious ornaments either for walls, verandas, or rustic poles or pillars, varying in color from deep rich violet hue to dark velvety maroon, and in the newer seedlings, forms beautiful shades of pale bright blue."
Mr. Vick says of the Clematis: "Having a rather unsightly pile of stones in the back part of our grounds, we had them thrown together more in the form of a stone-heap, perhaps, than of anything worthy of the name of rockery, and planted Jackmanii and other fine sorts in the crevices, and for three summers this stone-heap has been covered most gorgeously. Thousands of flowers, in fact a mound of flowers, every day for months, has been the delight of visitors, causing one to exclaim, 'Nothing since Paradise has been more beautiful.'"
These fine hybrids will endure our Northern winters if somewhat protected. A gentleman in Rochester, N. Y., had a Jackmanii which bore full exposure without protection and came out in the spring uninjured to the height of nine feet. The extremities of the shoots for about two feet were winter-killed.
Clematis Sieboldii is a native of Japan, whence it was introduced by Mr. Low in 1837. It is of a slender free-growing habit. "The flowers which are produced from July to September are composed[114] of six ovate sepals of a creamy white color, which form a fine background for the large rosette of purple stamens which occupy the center and render the flowers particularly attractive."
Clematis graveolins is a native of the mountains of Thibet. It is of comparative recent introduction. The flowers are produced on long stalks at the axils of the leaves, and are of a light yellow—an unusual color in this genus. It grows to the height of from ten to fifteen feet, and blooms freely during the entire season.
A lady writes to Vick's Magazine that she has a Clematis graveolins which is a wonderful sight. It grew from a feeble plant planted out in spring, two inches in height, into a column twelve feet high and three feet broad by August, and was a mass of yellow blossoms, and then, of the most exquisite, long-haired, silvery seed pods until hard frost. It lived through the winter, to its extreme tips, and then grew so rapidly, shading such an important part of her garden, that she had to remove it in the autumn, cutting it back severely. The seedlings from it grow, she adds, to eight or ten feet in a season.
Clematis crispa is of Southern origin; the flowers are one and a half inches long, produced singly on long stalks, and delightfully fragrant, a rapid grower, and perfectly hardy. Clematis coccinea is of recent introduction from Texas, the flowers are bell-shaped, of a most brilliant scarlet, and are produced in great abundance. This rare variety is offered only by Woolson & Co., Passaic Falls, N. J., who make a specialty of hardy herbaceous plants. Vesta, a Jackman, is large and of fine form; dead white, with a creamy tinge over the center bar, delicate primrose fragrance, an early bloomer. Mrs. James Bateman, pale lavender, and Thomas Moore, violet, superb, are Jackman seedlings, which flower in the summer and autumn, successionally, in masses, on summer shoots. These are all high priced. Many fine sorts can be purchased at prices ranging from thirty cents to one dollar.
The Clematis requires only ordinary garden soil. Where there are severe winters it is best to give the young plants at least some protection. They can be propagated by layering, which is rather a slow method, or rapidly by seed.
Very beautiful among the hard-wooded Climbers, is the Chinese Wistaria when in bloom. Its long, pendulous racemes of blue flowers are exceedingly graceful. They are frequently twelve inches in length and highly fragrant. The flowers appear about the last of May and first of June. It is not a continuous bloomer like the Clematis, but often gives a few flowers in August. It is rather slow at first, but after getting a good start the second or third year grows very rapidly. It is hardy after it gets strong, but young plants need some protection.
The Chinese White Wistaria was introduced by Mr. Fortune, and is regarded as a great acquisition. The Double Purple is illustrated in Ellwanger & Barry's Catalogue, by a full page engraving, which gives one an idea of its beauty better than the description which is as follows: "A rare and charming variety, with perfectly double flowers, deeper in color than the single, and with racemes of remarkable length. The plant is perfectly hardy, resembling Wistaria Sinensis, so well known as one of our best climbing plants. The stock which we offer was purchased of Mr. Parkman, who received this variety from Japan in 1863, and was the first to bloom and exhibit it in this country."
White American Wistaria is a seedling originating with Messrs. Ellwanger & Barry, of Rochester, N. Y. Flowers clear white; bushes short. Free bloomer.
A novelty has been offered to the horticultural public of London this spring (1880), in the shape of standard trees of Wistaria Sinensis,[116] raised in tubs, having heads five or six feet in diameter and covered with clusters of bloom. The plants were raised in Rouen, France, and sent to London for sale. It requires several years to attain plants of good size in this style, and as a matter of profit, a strict account would no doubt show a balance on the wrong side. In this country where the Wistaria is "at home," it may be raised in tree-shape in the open ground without expense, save the necessary care in pinching in and shaping. "So completely did the plants offered in London strike the popular taste, that there was quite a competition to become purchasers of them, and large sums were offered by those anxious to possess them. The general public, unaccustomed to this fine Chinese climber, looked on with wonder at "Lilacs" of such unwanted size and beauty of color."—Vick's Magazine.
Mr. Vick evidently does not deem this method an improvement on the natural graceful climber, for it reminds him of an anecdote which he thus relates in reply to an inquirer respecting the Wistaria as a standard.
"Once upon a time some kind of a steam cannon was invented, and a day of trial was arranged at Portsmouth, England, to which the Lords of the Admiralty and the Duke of Wellington were invited. After the exhibition, which we believe was somewhat successful, opinions of its merits were freely expressed, but the Iron Duke said nothing. When urged to give his opinion, he replied that he was thinking—'thinking if the steam gun had been first invented, what a grand improvement gunpowder would have been.' If the Chinese Wistaria had been a tree, and some one could have induced it to climb and cover our porches and arbors and old trees and buildings, what a grand improvement it would have been."
George W. Bungay.
 WHAT changes have been manifested—how unceasingly
and with what deftness Nature has silently wrought in
tapestry and embroidery, sculpture and painting, till
beauty is all around us, in the green carpet of earth,
brightened with flowers and leafage of every hue! No wonder the
birds sing praises to Him who gave them life with its fullness of
blessings. Sad to think that man, high over all, and under the
greatest obligation, too often is silent in thanksgiving for the gifts
of a Father's love.
WHAT changes have been manifested—how unceasingly
and with what deftness Nature has silently wrought in
tapestry and embroidery, sculpture and painting, till
beauty is all around us, in the green carpet of earth,
brightened with flowers and leafage of every hue! No wonder the
birds sing praises to Him who gave them life with its fullness of
blessings. Sad to think that man, high over all, and under the
greatest obligation, too often is silent in thanksgiving for the gifts
of a Father's love.
No month to me has such charms as June, when nature's robes are so fresh and clean, and the balmy air is redolent with fragrance. How delightful to be abroad with the early worm and early bird, working in the garden, while the songsters give free concerts, and the hum of the honey bird, and buzz of the bee, set forth a good example of cheerful industry!
The house plants have become established in the open border, and are so glad to get away from artificial heat and confined atmosphere into the broad sunlight of heaven, and breathe in full draughts of pure air and sweet dew, that they put on their best attire, and most attractive ornaments. Before the roses bloom, the bed of geraniums looks bright with flowers, each ambitious to excel[119] his or her neighbor, either in beauty of color, or form, or duration of bloom, thus leaving me in perplexity as to choice. When Pliny bloomed everybody admired who saw his beauty; then Romeo with quite another style looked charming, but when Naomi unfolded her large trusses of double pips, of a rare, peculiar shade, nobody ever saw a geranium quite so lovely, and then its duration of bloom—full six weeks! Jennie Dolfus, however, became a dangerous rival—a deeper, richer shade, and not a pip would she allow to fade so long as Naomi looked so pert. Some said, "I like Naomi the best;" others said, "I think Jennie is the prettiest." But Beauty, close by, hearing the praises lavished on her sisters, and perchance trusting in her good name, came forth one day in dress of white with deep pink ornamentation. Never had such unique beauty as this ever been seen in Geranium before, and, "Isn't it lovely!" "Just splendid!" "What a beauty!" were uttered with exclamation points, till she blushed with becoming modesty—the flush spread and deepened until her face was completely suffused with the delicate tint, making her yet more attractive. Wellington donned his crimson suit, and De Gasx an orange yellow; Pauline Lucca, prima donna though she be, appeared in dress of pure white, and Richard Dean in scarlet with a white star that was very becoming. New Life thought to draw special attention by odd freaks, and came out in a parti-colored dress of the most singular combinations; part of it was scarlet dotted with white—part of it half scarlet, half salmon, part of it widely striped, and part white with just a flush of pink! I must call him the clown of the family!
I have only named a few of the rare Geraniums that adorn one of the beds of my garden. For beauty, free flowering, and duration of bloom they cannot be surpassed.
Interspersed with them are ornamental leaved Geraniums, Crystal Palace Gem, an improvement on Cloth of Gold; Marshal McMahon, the best of all the bronzes; Cherub, deep green, white and[120] orange, flowers carmine; Glen Eyre Beauty, Dr. Livingstone, a new, sweet-scented, fine cut-leaved Geranium; Happy Thought, one of the most attractive, with its dark green leaves and creamy white center. Here and there are commingled Anchryanthus of divers hues, and Coleosus, giving a fine effect to the whole. This is now the most attractive bed of all, but when the Lilies are in bloom, and the dear little Tea Roses, the bed parallel with it will be the sweetest, if not so brilliant.
This year I have a tropical bed of oblong form. A Castor Bean rises majestically in the center, two beautiful Cannas each side, while a Dracæna, a splendid Croton, two fancy Caladiums, and a few other choice plants fill the space, the whole bordered with Coxcombs. In a few weeks this bed will look gorgeous, and those filled with annuals will have changed from their present inattractiveness to delightful bloom. August is really the month of fullness of blossom, and of restful enjoyment of beauty and fragrance. The weary days of preparation, of bedding out and of weeding, are over, and one may now give themselves up to the enjoyment of the fruit of their labor, till the chill nights of autumn bring a renewal of the toil.
"Does the brief period of restful enjoyment repay for the many weary days antecedent and subsequent?"
Yes, richly, fully, for there is pleasure with the toil, and to me health-giving influences that energize the physical system for indoor work, and stimulate the brain for literary pursuits. To me my garden is a God-send, fraught with blessings.
"Gardening is a pleasant pastime." I am prepared to adopt that sentiment to-day, if I did demur somewhat last month. It is a delightful pastime, in the early morning, to spend an hour among the flowers, trowel in hand, rooting out the weeds, loosening the soil around your plants, and tying up here and there the tall and fragile, while the birds are singing in the trees around you their morning[121] song of gladness. How the dew-laden grass and shrubs impart sweetness to the air, and your lungs inhaling its purity, are expanded and invigorated, your whole system feels the better for the tonic, and prepares for breakfast, and the work that shall follow.
It is a pleasant pastime, when wearied with toil you go forth for a time among your flowers and search for the buds, or examine the newly-opened flower. How it rests you!
It is a pleasant pastime, when the labors of the day are over, and the sun is throwing long shadows from the west, you take watering-pot in hand, and shower the refreshing spray upon your plants, cleansing them from the dust, and cooling them after the heat. How they thrive, and bud and bloom!
 OF the many touching tributes paid to flowers, there is a
beautiful one associated with the closing hours of Henry
Heine, the poet. He was dying in Paris. The doctor was
paying his usual visit, when Heine pressed his hand and
said: "Doctor, you are my friend, I ask a last favor. Tell me the
truth—the end is approaching, is it not?"
OF the many touching tributes paid to flowers, there is a
beautiful one associated with the closing hours of Henry
Heine, the poet. He was dying in Paris. The doctor was
paying his usual visit, when Heine pressed his hand and
said: "Doctor, you are my friend, I ask a last favor. Tell me the
truth—the end is approaching, is it not?"
The doctor was silent.
"Thank you," said Heine calmly.
"Have you any request to make?" asked the doctor, moved to tears.
"Yes," replied the poet; "my wife sleeps—do not disturb her. Take from the table the fragrant flowers she brought me this morning. I love flowers so dearly. Thanks—place them upon my breast." He paused, as he inhaled their perfume. His eyes closed, and he murmured: "Flowers, flowers, how beautiful is Nature!" These were his last words.
A few years since the Belfast (Me.) Journal gave this touching incident: "One day last week an elderly man, known to our people[123] as an honest and hard-working citizen, was walking slowly up Main street. There was sorrow in his countenance, and the shadow of grief upon his face. Opposite the Savings Bank his eye caught sight of the flowering Oleander, that with other plants fill the bay-window of the banking-room. He looked at it long and wistfully. At length he pushed open the door, and approaching Mr. Q., said:
"'Will you give me a few of those flowers?'
"The cashier, leaving the counting of money and the computing of interest, came around the counter, bent down the plant, cut off a cluster of blossoms, and placed it in the man's toil-hardened hand. His curiosity led him to ask:
"'What do you want them for?'
"'My little granddaughter died of scarlet fever last night,' the man replied with faltering voice, 'and I want to put them in her coffin.'
"Blessed be flowers, that can thus solace the bereavement of death and lend their brightness as a bloom, to the last resting-place of the loved one."
There is a beautiful incident told of a Texas gentleman who was an unbeliever in the Christian religion. One day he was walking in the woods, reading the writings of Plato. He came to where the great writer uses the phrase, "God geometrizes." He thought to himself, "If I could only see plan and order in God's works, I could be a believer." Just then he saw a little Texas Star at his feet. He picked it up and then thoughtlessly began to count its petals. He found there were five. He counted the stamens, and there were five of them. He counted the divisions at the base of the flower, there were five of them. He then set about multiplying these three fives to see how many chances there were of a flower being brought into existence without the aid of mind, and having[124] in it these three fives. The chances against it were one hundred and twenty-five to one. He thought that was very strange. He examined another flower, and found it the same. He multiplied one hundred and twenty-five by itself, to see how many chances there were against there being two flowers, each having these exact relations of numbers. He found the chances against it were thirteen thousand six hundred and twenty-five to one. But all around him were multitudes of these little flowers, and they had been growing and blooming there for years. He thought this showed the order of intelligence, and that the mind that ordained it was God. And so he shut up his book, picked up the little flower, kissed it, and exclaimed: "Bloom on little flowers; sing on little birds; you have a God, and I have a God; the God that made these little flowers made me."
 THIS species is one of the most desirable of hardy-wooded
plants we possess. They are admirable for the house, for
the balcony, the piazza, or the border, being handsome in
foliage, and very graceful and beautiful in flowers. Some
are stately, others dwarf, some are flexible and drooping. We have
had for several years three that we have greatly admired for their
variegated leaves, especially for the winter window-garden, where
they compensate for the scarcity of flowers, by the brilliancy of
their foliage, yellow and green, finely mottled and marbled.
THIS species is one of the most desirable of hardy-wooded
plants we possess. They are admirable for the house, for
the balcony, the piazza, or the border, being handsome in
foliage, and very graceful and beautiful in flowers. Some
are stately, others dwarf, some are flexible and drooping. We have
had for several years three that we have greatly admired for their
variegated leaves, especially for the winter window-garden, where
they compensate for the scarcity of flowers, by the brilliancy of
their foliage, yellow and green, finely mottled and marbled.
Duc de Malakoff is stately, and by cutting off the top of the main stalk, it is made to branch out very largely, forming a miniature tree. It grows very rapidly, and its leaves are like the Maple in form, which has led many to call the plant Flowering Maple, but this is not correct, as it is not a Maple at all, but an Abutilon. Some of the leaves on one only a year old, measure seven inches across, and eight and a half in length. In the older plant they are not so large. Thomsonii much resembles Malakoff, but its markings are not so handsome; the green is darker, and predominates over the yellow, so far as my observation extends, but it is a more abundant bloomer. Flowers are orange color. I have vainly searched through many catalogues to find the color of the Duc de Malakoff blossom, but all are silent; it is not even said that they flower at all, but my four-year-old had one bud last year, which unfortunately blighted. The yearling has one bud, and I hope it will live and afford me the knowledge I have failed to find in books. Malakoff not variegated, has large orange bells, striped with brown.
My other variegated Abutilons are of trailing habit; Mesopotamicum is very graceful, one droops over the side, and climbs and[126] twines around the cords of a large hanging-pot, for which it is admirably adapted. Its small pendant blossoms, crimson and yellow, growing profusely along the slender branches, drooping among the elegantly marbled foliage, give this variety a very attractive charm. Another is trained to a pot trellis, and is very beautiful in this form. We advise every one to add this variety to their collection. Pictum is very similar in every respect; the leaves are darker, and not so variegated. They require a strong light to bring out their markings, and hence are more perfect in beauty when bedded out in the garden, where they can have plenty of sunshine.
Boule de Neige (Fairy Bell) has long been a favorite for its pure white bells and constancy of bloom. A splendid winter bloomer. John Hopkins, with its rich, dark, glossy leaves and golden flowers has superseded the old Pearl d'Or, which was for a time the only real yellow. Darwinii is one of my favorites. The flowers are more spreading than any other variety, opening like a parasol; color orange-scarlet veined with pink. It blossoms very profusely, and when only a few inches in height. The flowers are large and well formed, and borne in clusters rather than singly, like many older sorts. This variety was cross-fertilized with Santana, crimson flower, and as a result we have Darwinii tessellatum, combining the variegated foliage of Thomsonii with the free-blooming qualities of Darwinii.
The improvements by hybridizing have been very great within a few years, and many new varieties have been sent out. One of these is Roseum Superbum, the flowers of which are of a rich rose color, veined with a delicate pink. Very free bloomer. Venosum, we find only named in an English catalogue. "The magnificent blooms of this variety place it at the top of all the Abutilons. Although it is of tall growth its beautiful palm-shaped leaves and gorgeous flowers make it invaluable for crossing and for conservatories."—H. Cannell.
Among the new and valuable novelties of American origin are Arthur Belsham, Robert George, J. H. Skinner, and Joseph Hill. These have been three years before the public, and Mr. John Thorp, a well-known popular florist of Queens, N. Y., says of them, "We have not, amongst all the flowering Abutilons, such fine varieties as these. I have had plants between five and six feet high, pyramidal shape and literally covered with flowers."
They originated with Messrs. Leeds & Co., of Richmond, Indiana, who make quite a specialty of new seedling Abutilons, and this year offer four "of new shades and colors."
A. G. Porter. "Flowers of a beautiful lavender color, delicately suffused with a light shade of rosy pink, and handsomely veined with magenta, forming a flower of magnificent color and shape, a very free bloomer. A cross between Boule de Neige and Rosaflora, with the habit and growth of Boule de Neige."
Little Beauty, "A very dwarf grower, having a short, compact, symmetrical bush, which is completely covered with its medium-sized but well-shaped flowers, of a very light salmon color, beautifully veined with rosy carmine. It blooms in clusters and when in full bloom makes a remarkably fine appearance. A cross between Rosaflora and Darwinii."
N. B. Stover, "A low, compact grower. Flowers large and well-formed, almost covering the bush; color, rich ponceau, finely veined with carmine. A decided novelty, being a new color among Abutilons."
Dr. Rapples. "Light orange salmon, veined with crimson. One of the most attractive in the set."
A new Abutilon, a decided novelty in color, comes to us from "The Home for Flowers," Swanley, England, sent with other choice plants by Henry Cannell & Son. It is thus described in his Floral Guide:
Firefly (Swanley Red). By far the highest and brightest color[128] of all the family; habit dwarf, and one of the freest bloomers, throwing flowers out on strong foot stalks of the finest shape; certainly one of the noblest, and when grown in a pot it flowers all the winter, and all the summer when planted out, and forms one of the best flowering shrubs that we possess.
Parentage of this Flower.—Mr. George states that he sometime since flowered a small red variety, which had a very lively shade of color, and determining to make this a seed parent, it occurred to him to use on it the pollen of the single deep color Hibiscas, which, like the Abutilon, is included in the natural order Malvaceæ. Mr. George thinks the fine color seen in his new variety, Firefly, is due to this happy inspiration of color.
The Gardener's Chronicle has this paragraph respecting Firefly: A red Abutilon, one of a batch of recent seedlings raised by Mr. J. George of Putney Heath, well deserves the foregoing appellation. The flowers are of large size and of a much greater depth and vividness of color than that possessed by any variety in the Chiswick collection. It has been provisionally named Firefly, and we believe the stock has passed into the hands of H. Cannell & Son, of Swanley, for distribution.
A writer in Vick's Magazine describes a method of training the Abutilon that must, we think, be a very attractive one.
"A pretty plant may be obtained by inarching Abutilon Mesopotamicum upon Abutilon Darwinii, or some other strong-growing variety, and training it so as form an umbrella head, which can easily be done. The stock for this purpose should be about five or six feet high. Grown in this way it produces an abundance of bloom, and the flowers being elevated are seen in all their beauty. If Abutilon Mesopotamicum is inarched upon Abutilon Thompsonii, the result will be Abutilon Mesopotamicum Variegatum. A well-formed plant of this on a stock about five feet high is one of the finest of plants; whether in blossom or not it is always adapted for[129] decorative or exhibition purposes. Care must be taken at all times to keep them tied to stakes, as they are liable to be broken off by the wind."
Abutilons are apt to be infested by the red spider, if kept in too dry an atmosphere, and not frequently sprayed. Moisture is death to this pest, but as it makes its home on the under side of the leaf, it is too often overlooked until it has destroyed the vitality of the foliage. Recently I found that my large Duc de Malakoff looked sickly, and I concluded it had become root-bound. A few days later, I noticed brown spots thickly covering the bark. I removed one, and on examining the under side through a microscope, I saw several tiny insects moving about. I decided that my plant was troubled with the scale of which I had often read, but never seen. I made a pretty strong solution of soap-suds, and with a sponge quite easily removed all of the pests.
In bedding out Abutilons, it is better to have them in pots, plugging the hole, or setting the pot on a stone or piece of brick, so that the roots may not go astray, for if plunged directly in the ground they throw out many roots and the plant becomes too large for re-potting to advantage. If, however, they are planted in the earth, in August they should be cut around the stock so as to bring the roots within due bounds, and the plant can be pruned in the autumn. This method is applicable to all strong plants that run largely to roots. They should be cut off sufficiently to leave only a ball of earth of convenient size to set in the pot when the plant is transplanted.
 THE genus Dahlia comprises but few species, all natives of
the mountains of Mexico, whose range is from 5000 to
10,000 feet above the level of the sea. About one hundred
years ago a Spanish botanist introduced seeds of the Dahlia
into his native country, and named the genus in honor of a Swedish
botanist, Dahl. The first seed imported seemed to be variable
and not very promising. About seventy years since, Humboldt
sent fresh seed to Germany. Soon after this, both seeds and bulbs
were introduced into England and France, and began to attract
considerable attention, some enthusiast being rash enough to hazard
the assertion that "there are considerable reasons for thinking
that the Dahlia will hereafter be raised with double flowers."
THE genus Dahlia comprises but few species, all natives of
the mountains of Mexico, whose range is from 5000 to
10,000 feet above the level of the sea. About one hundred
years ago a Spanish botanist introduced seeds of the Dahlia
into his native country, and named the genus in honor of a Swedish
botanist, Dahl. The first seed imported seemed to be variable
and not very promising. About seventy years since, Humboldt
sent fresh seed to Germany. Soon after this, both seeds and bulbs
were introduced into England and France, and began to attract
considerable attention, some enthusiast being rash enough to hazard
the assertion that "there are considerable reasons for thinking
that the Dahlia will hereafter be raised with double flowers."
About 1812 probably the first double Dahlia was grown, but for several years after this both double and single varieties were figured in colored plates, and exhibited at horticultural shows. That the single varieties were prized is not strange, for the double were not very good, and even as late as 1818, published figures showed very imperfect flowers.
The improvement of the Dahlia after this was rapid, and its popularity quite kept pace with its improvement. Dahlia exhibitions were held in England and on the continent, which were crowded by enthusiastic admirers of this wonderful Mexican flower. For many years the Dahlia maintained its popularity, but there is a fashion in flowers, as in almost everything, and for a time the Dahlia became, to a certain extent, unfashionable, and this was well; for it placed the flower upon merit alone, and growers were compelled to introduce new and superior varieties to command either attention or sale for their favorite flower.
A taste for old styles is now the "correct thing," and so we have imitations of ancient earthenware, furniture, etc., and import original Chinese Aster seed, and also obtain roots of the single Dahlia from Mexico.
There are three pretty distinct classes, the Show Dahlias, the Dwarf or Bedding, and the Pompon or Bouquet, and to this we may add the Fancy Dahlia. The Show Dahlia grows from three to four feet in height, and embraces all our finest sorts, fit for exhibition at horticultural shows, from which the name is derived; the flowers range in size from two and a half to five inches in diameter. The striped and mottled and spotted varieties belonging to the Show section are called Fancy, and though not as rich, nor usually as highly prized as the selfs, or those of one color, are very attractive. The Dwarf or Bedding Dahlia grows about eighteen inches in height, and makes a thick, compact bush, and covers a good deal of surface; flowers of the size of Show Dahlias. They are therefore very desirable for bedding and massing. The Pompon or Bouquet Dahlia makes a pretty, compact plant, about three feet in height. The leaves are small, and the flowers from one to two inches in diameter. Many expect to find small flowers on their Dwarf Dahlias, and feel disappointed because they are of the ordinary size, not knowing that it is the plant, and not the flower, that is dwarfed, and that only the Pompon gives the small flowers. The word Pompon is French for topknot or trinket, meaning about the same as the English word cockade. The English term Bouquet is very appropriate, as the flowers are so small they are very suitable for bouquets. Being of a spreading habit, they cover a good deal of ground. Unlike most of our bedding out plants, they do best in a poor soil; if rich, they grow to branches and leaves so much, they bloom sparingly and late.
Generally those who plant Dahlias purchase the tuberous roots, because they give good strong plants, that flower freely without[132] trouble or risk. They are smaller and better than the large, coarse roots usually grown, because they are raised from cuttings, and generally form their roots in pots. When a tuber is planted, a number of buds that cluster around its top will push and form shoots, and if too numerous, a portion should be removed; indeed, one good, strong plant will suffice, and then the plant will become a tree instead of a bush. Even then, if the top become too thick, a little thinning of the branches will be of advantage. If the young shoots that start from the neck of the bulb, are cut off near a joint and placed in a hot-bed in sandy soil, they will root, form good plants, and flower quite as well as plants grown from the tuber; this, however, requires some care and experience, and amateurs generally will succeed best with bulbs.
New varieties of Dahlias, of course, are from seed. Some of them prove good, others fair, and a portion utterly worthless. As a general rule, we would not advise amateurs to trouble with seeds, although there is pleasure in watching the birth and development of a new and beautiful variety.
The seed of Dahlias may be sown in pots in early spring or end of winter, in a light, loamy soil; they will germinate quickly, and as soon as they begin to show their second leaves they should be pricked out into other pots or boxes, so that they may have plenty of room and air—they are very liable to damp off if at all crowded. After pricking out they should be kept in a thrifty, growing condition, by proper attention to watering and temperature; the temperature should be maintained as near 70° as possible, and the watering be sufficient to preserve a moderate moisture.
If the green fly attack them, it will be best to treat them to a very weak dilution of tobacco water; the young succulent plants are very sensitive to smoke, and it is best not to fumigate them. In about two months the young plants should be large enough to pot off singly, or to be transplanted into a frame or bed, where protection[133] can be given them from the cold of night-time, or from late frosts. As soon as all danger is past they can be transplanted into their summer quarters, and should stand at least three feet apart. The soil where they are to grow, should be rich and mellow. In August they will come into flower, and those having blooms worthy of cultivation can be retained, and the others destroyed. Only a small proportion of the plants grown from common seed produce flowers equal to those now in cultivation, but when seed is saved from a choice collection of named varieties, the chances are that a large proportion of the plants will produce very good flowers.—Vick's Magazine.
"The Dahlia is called a gross feeder, but it is not. It loves moisture rather than rich elemental food. In clay it finds the best constituents of its development—moisture, silex, lime and alumnia. So we say to those who love this queenly flower, if you would see the queen in all her glory, plant in a comparatively heavy soil, no manure, and reduce the stalks to one for each tuber, set the stakes firmly, to keep the stalks from swaying, and if the season is dry, give the bulbs a soaking with water every evening during the drought. My word for it you will then be proud of your success."
The Pompon, or Bouquet Dahlia is a favorite variety of this genus. The little round balls of bloom are so pretty and trim. Beatrice, blush tinted with violet; Dr. Stein, deep maroon, striped and mottled; Goldfinder, golden yellow; Little Philip, creamy-buff edged with lilac; Little Valentine, crimson; Mein Streifling, salmon, striped with crimson; Pearl, white; Prima Donna, white, fimbriated; Perfection, deep maroon.
Anything for a change from the common order of things, seems to be the fashion now-a-days, in flowers as well as in house building and house furnishing. The antique, the antique, is the rage! So after years of labor and hybridization to bring the Dahlia up[134] from its native state of single blessedness, to its enormous cauliflower blooms, there comes a reaction, and now single Dahlias are praised as "the most beautiful of all flowers," the "par excellence the Londoner's flower!" Well, let the English florists thus praise its beauty if they want to, but we opine that on this side of the great ocean it will never be considered "the most beautiful of all flowers," however attractive some of them may be, and well adapted for bouquets. There is no danger of their superseding the doubles, but it is well to have both when one can afford it; their present high price puts them beyond the reach of those whose purses are not well filled, but in a year or two, when the novelty is worn off, they can be purchased at half or even less, perhaps, than their present price.
We find in the London Garden the following: "Dahlia perfecta, originally introduced by Messrs. Henderson, is perhaps the finest flower which we possess, unless Paragon, brought into notice by H. Cannell, may be considered to bear away the palm. Lutea, a quilled yellow, is also a grand bouquet flower."
The single Dahlias, Paragon and Lutea, are now offered for the first time in this country, by Messrs. Hallock & Thorp of Queens, N. Y., and the former is finely illustrated in their catalogue. Color very dark velvety maroon with shadings of bright scarlet around each petal; small yellow disk. Lutea is pure yellow, with dark orange center. The same firm offer Dahlia Juarezii, of which Mr. Cannell says: "The grandest novelty of the year, and not only a novelty, but a most valuable and useful decorative plant for all purposes through the late summer and autumn months. Its blossoms are of a rich crimson, and very much resemble in shape and color the well-known Cactus, Cereus speciosissimus. Height about three feet, very bushy flowers of very striking appearance and quite unlike those of an ordinary double Dahlia, the flowerets being flat and not cupped. Figured in Gardener's Chronicle October 4th,[135] 1879, and awarded a Botanical Certificate Royal Horticultural Society."
The following statement was made in the Gardener's Chronicle respecting this new type:
"A remarkable box of Dahlias was shown by Messrs. Cannell with three or four of the single forms, which, if it were not heresy to say so, we should so much prefer to the formal lumps so dear to the florist proper; and then there was a new type of Dahlia altogether, a Sea Anemone among Dahlias, with long crimson scarlet pointed petals, like the tentacles of an Antinia—a striking novelty, christened temporarily the Cactus Dahlia, and which will be the parent of a new strain. It received a Botanical Certificate; some said this ought to have a higher award, but what higher or more appropriate form of a certificate could be given to such a flower. If we were a Dahlia, we should greatly prefer the honor of a 'Botanical,' to that of a 'First Class Certificate.'"
This new type is illustrated in Hallock & Thorp's Catalogue.
Two new Dahlias not yet introduced in this country are included among the novelties of 1881. Cannell's Scarlet, a Show Dahlia, several shades higher and brighter in color than any scarlet before introduced. "Its shape is most model-like, and not excelled by any other, and is without doubt the best Dahlia of the year." Miss Cannell, (Eckford)—"Mr. Eckford's Dahlia, Memorial, was the king of best shapes for many years, but the one now offered is of greater excellence, and by far the best of its class; color white, tipped with rose-pink, and the depth and build of flower is most model-like."
These are the finest of all summer flowering bulbs, throwing up strong flower stems in June and July, bearing from two to six magnificent lily-like blossoms. The varieties are numerous, but only a few sorts are found catalogued. Amaryllis Johnsonii is the finest[136] of the commonly grown varieties. Its leaves are a dark rich green, two inches broad, and two feet long. The flowers which are five or six inches long, are crimson with a white stripe through the center of each petal, and are borne upon a stalk two feet high. They usually bloom twice a year, the flowers appearing just as the leaves begin to grow.
Amaryllis formosissima is of a very peculiar form. The flowers are scarlet-crimson, very velvety in appearance; there are six petals, three of them nearly erect, and three drooping very long. After being bedded out, it quickly throws up a flower stalk and blooms before the leaves appear. It is a superb flower, known sometimes by the name of Jacobean Lily. Amaryllis vittata is a splendid hybrid, red ground striped with white. Amaryllis Valotta purpurea is an evergreen variety, and should be kept growing the year round. In August it throws up a flower-stem from one foot to eighteen inches high, bearing a cluster of light scarlet flowers two or three inches in diameter. A light soil and small pot suits it best. Mr. John Lewis Child of Queens, N. Y., has a finer collection and more numerous varieties than are usually found named in the catalogues. Some of them we will specify. Johnsonii Grandiflora, an improvement on the well-known Johnsonii Harrisoni, large, pure white, with double crimson streaks running through each petal. It has a delicious, orange-blossom fragrance. Reticulata, a bright rose color, the foliage is very attractive—dark green with a white stripe running through the center of each leaf. Aulica Stenopelalon, a magnificent species, having large orange crimson flowers, beautifully veined with scarlet. "Equestre fl. pl. This grand novelty was discovered in 1877, in one of the West India Islands. The flowers are perfectly double, resembling those of a large Camellia. Its color is rich, fiery orange red. We believe we have the only stock of this beautiful flower in America." John L. Child.
This and Harrisoni, are priced at $4.50, so they must be very[137] rare and beautiful. Aspasie, white, tinted with yellow and red; large and perfect. Crinum Amænum, new and very beautiful, white-striped crimson. Lutea, a hardy variety, which blooms in the autumn; pure yellow. Calafornica, pure white.
The bulbs are of easy culture. After blooming, and the foliage fully grown, they should be allowed to rest for several months, then start into growth by watering sparingly until the flower stalks appear, when a more liberal supply should be given. Usually two successions of bloom can thus be obtained. The bulb should be planted so as to leave the upper portion uncovered.
This plant is a native of tropical Asia, where it is partially parasitical, its roots penetrating the bark of the trees which support it. It was introduced into England in 1802. There are several species, but only one is generally cultivated. Hoya Carnosa has thick waxy leaves, and bears umbels of beautiful flesh-colored flowers which are very wax-like in appearance. It is an excellent plant for house culture as it stands the extremes of heat and cold better than most plants, and is not easily injured by neglect. It can be trained to climb on trellis-work to almost any height, and when in bloom, which continues for half the year, it is a very interesting plant.
There are several varieties of Hoya, but one only is generally cultivated. Silver Variegated Foliage is said to be very handsome but is of slow growth and difficult to propagate. Imperialis is a new variety with beautiful foliage and scarlet flowers. Cunningham has light green leaves, deeper colored flowers than the Carnosa and is a rapid grower.
They succeed best in peat, with some fibrous soil and sand. They must have perfect drainage, and require a period of rest. Hoya Carnosa is easily propagated from cuttings. A very good method is to wrap a cutting in moss, keeping it moist until the roots are well started.
 AUGUST is the month when we rest from our labor in gardening,
and abandon ourselves to the full enjoyment of the
varied blossoms which so abundantly meet our eye. Now
we can best determine what changes may be required in
the arrangement of our plants next year, in order to give the most
pleasing effect. A tall plant may have been inadvertently set out
in the midst of those of low growth, and we see now how awkward
it looks. Short-lived annuals may have occupied a conspicuous
place, and on their departure left an unseemly vacancy. A bed
may have been filled with a class of plants that are not free bloomers,
and so there has been little beside leaves, while another bed
has been brilliant during all the summer months with flowers.
Annuals of a new kind, high-priced novelties, have been tested;
are they any better than our old favorites? If we cannot indulge
in many sorts, what do we find the most satisfactory? Twenty-five
cents per packet seemed very expensive for Heddewigii Pinks, but
Crimson Belle and Eastern Queen are of such superior size and
rare beauty that the investment is not regretted, and then we know
that they will bloom in greater perfection next year, and that the
seed saved this autumn and sown in early spring, will increase the
stock. Twenty-five cents for a paper of Candytuft seed looks extravagant,
but no one who invests in Tom Thumb would regret it.
It is so dwarf, so compact and bushy, such a long continued bloomer,
so admirable for edging a bed, that it is really almost an essential.
Then it will sow itself, and the seedlings will be up as soon
as the frost is out of the ground, and plants from self-sown seed
are so much more thrifty and early than those one sows in the
spring, that this is a great gain.
AUGUST is the month when we rest from our labor in gardening,
and abandon ourselves to the full enjoyment of the
varied blossoms which so abundantly meet our eye. Now
we can best determine what changes may be required in
the arrangement of our plants next year, in order to give the most
pleasing effect. A tall plant may have been inadvertently set out
in the midst of those of low growth, and we see now how awkward
it looks. Short-lived annuals may have occupied a conspicuous
place, and on their departure left an unseemly vacancy. A bed
may have been filled with a class of plants that are not free bloomers,
and so there has been little beside leaves, while another bed
has been brilliant during all the summer months with flowers.
Annuals of a new kind, high-priced novelties, have been tested;
are they any better than our old favorites? If we cannot indulge
in many sorts, what do we find the most satisfactory? Twenty-five
cents per packet seemed very expensive for Heddewigii Pinks, but
Crimson Belle and Eastern Queen are of such superior size and
rare beauty that the investment is not regretted, and then we know
that they will bloom in greater perfection next year, and that the
seed saved this autumn and sown in early spring, will increase the
stock. Twenty-five cents for a paper of Candytuft seed looks extravagant,
but no one who invests in Tom Thumb would regret it.
It is so dwarf, so compact and bushy, such a long continued bloomer,
so admirable for edging a bed, that it is really almost an essential.
Then it will sow itself, and the seedlings will be up as soon
as the frost is out of the ground, and plants from self-sown seed
are so much more thrifty and early than those one sows in the
spring, that this is a great gain.
Candytuft—white, pink, light purple, dark purple and crimson, I find it well worth while to culture for early and profuse flowers, and admirably adapted for bouquets. I always have large quantities of the white, to set off the brighter flowers, and by sowing seed in June and July, have a succession of blooming plants. Foxglove, both white and purple, with their thimble-shaped spotted blossoms profusely borne on tall spikes, with side branches loaded with bloom, has been one of the greatly admired flowers of my garden. Plumbago, with its clusters of tube flowers, of the palest of blue, is very beautiful. Godetia, "Lady Albemarle," I have found to be all that it is represented. For two months it has been in constant bloom, and it will continue to flower till frost. It is of a bushy, compact habit, about twelve inches high, the flowers are from three to four inches in diameter, and of a rosy-carmine color. Everybody who has seen it, has a word of praise for this most beautiful of all the Godetias. Alba is a new variety, having pure white flowers; Insignis is pure white with a crimson blotch on each petal; Whitney's is of dwarf habit, and has large flowers, blush-colored, marked about the center with a handsome crimson stain. The new French Marigolds "Cloth of Gold," and "Meteor" are just splendid with their large and beautifully striped imbricated leaves. One has gold bars evenly marked on the rich dark velvety petals, and the other has deep orange stripes on a pale straw-colored, almost white ground. "Meteor" is a perfect gem among the Calendulas.
Convolvulus minor—new crimson-violet with yellow eye encircled with a band of pure white; dark blue and light blue with yellow eye margined with white; pure white with yellow eye, and blue and white striped, are very pretty free-blooming dwarfs of this species.
My Stocks are very fine, from mixed seed of the German, new large flowering. They are mostly very double. The creamy white are especially beautiful. The bright crimson and canary yellow[140] are handsome. There are many varieties of this species, but what are generally termed Ten-weeks Stock are best known. They are classed under five heads: Dwarf, Miniature, Large-flowered, Pyramidal and Wall-flower-leaved. Then there are the Intermediate Stocks, prized for their late autumn blooming, of which there are twelve or more varieties. The German Brompton Stocks are divided into two sections; Brompton and Hybrid, or Cocordean. The latter bloom with a single stem which forms a splendid pyramid of flowers, and is cultivated largely in pots. Seeds sown in early spring will bloom in autumn, and if carefully potted will flower during winter; if sown in July and August, and cultivated in pots will flower the following spring and summer. The Imperial or Emperor stocks, sometimes called Perpetual, are large flowering, and white, rose, crimson and blood-red in color.
"Hardy's All-the-Year-Round," is a perpetual bloomer. The plants grow about twelve inches high, and produce hundreds of bunches of double white flowers.
Let us linger a little while at this rose bed. Are not those Teas lovely? Look at Madame Lambard, one of the finest French roses imported recently from Paris. Is not the color exquisite—a beautiful shade of silver bronze, changing to salmon and fawn, delicately shaded with carmine rose. And so deliciously fragrant! That rose so large and full, with a rare shade of violet red, brightened with crimson maroon, is Aline Sisley. It is surprising how such a tiny plant could have produced such an immense flower! And this is Letty Coles, a new French rose, very handsome and sweet; color rosy-pink, deeply shaded with intense crimson. Perle des Jardins is magnificent with its rich golden yellow, and Bon Silene has long been a special favorite. Its buds are large and beautiful. That charming white so deliciously scented is Mademoiselle Rachel, and this one with pure deep green flowers is Verdiflora, or Green Rose, scentless, and of no value except as a curiosity.
This grand rose is Abel Carriere, a hybrid perpetual more beautiful I think than the popular Jacqueminot in the perfectness of its form, and richness of its color. The outer petals are bright glowing crimson-scarlet, while the center is a deep fiery red. But it will never do to linger longer among the sweet roses, for there are many other flowers to show you.
I think that Hydrangea, with its immense trusses of bloom, is just one of the most desirable shrubs we can have in the garden. I have had mine six or seven years, and it bore three clusters of flowers the first year, though a wee plant. It blooms from August till hard frost, and needs no protection in the winter, though I do sometimes put a mulching of straw or a bit of brush around the roots. A lady writing to Vick's Magazine says of this Hydrangea: "The first year I planted Hydrangea Grandiflora it produced three heads of flowers, the second, fifty-six, and the third year ninety-two. Thorough cultivation and a pail of liquid manure once a week, helped the plant to bear this enormous load of flowers."
Hydrangea Alaska is a more recent acquisition. Its flowers frequently measure twelve inches across, and are of a bright pink color, not hardy at the North. Hydrangea Thomas Hogg would be a very unpoetical name did it not remind one of "The Ettrick Shepherd." This variety was sent to the United States from Japan, by that eminent botanist for whom it is named, and has become deservedly popular. It belongs to the Hortensia section of the family, but is a far more abundant bloomer than any other. The flowers are of the purest white, of very firm texture, and retain their beauty for a long time.
A more recent novelty sent from Japan by Mr. Hogg, is the "New Climbing Hydrangea," which he describes as clinging to trees to the height of fifty feet, producing corymbs of white flowers of the size of ordinary Hydrangeas. It clings exactly like the Ivy,[142] and must produce a striking effect when in full bloom. It is entirely hardy. Mr. Peter Henderson was the first to offer this novelty here and in Europe. Elegantissima is a novelty truly with its leaves flaked, bordered and striped with golden yellow. I do not know whether it blossoms or not, it is handsome enough without flowers.
The new Heliotrope Le Negre is the darkest of this genus, and Snow Wreath the nearest approach to white we have yet had; truss very large, growth compact, and fragrance exquisite. Garibaldi is almost white; Mrs. Burgess is dark violet, and Duc de Lavendury is a rich blue, dark eye.

Sweet Alyssum is another of the essential flowers for the border, admirable for edgings, for its dwarf habit and continuity of bloom. The great novelty of last year was the new double variegated Sweet Alyssum—"The Gem." The flowers are very full, and the foliage broad with a mid-rib of light green, bordered on each side with pure white. It is a fine, compact grower, and far superior to anything of this species yet offered.
Lantanas, I think, add greatly to the attractions of the garden, so rich in color and profuse in blooming. Clotilda, pink with yellow center, and Comtesse de Diencourt, flower bright rose and yellow center sulphur, are very desirable. Alba perfecta, pure white, is fine, so also is Alba lutea grandiflora, white with yellow center. Mine d'Or is a new variety, with bright orange and crimson flowers, and golden variegated foliage. M. Schmidt is a beautiful novelty. Flowers of a brilliant yellow, passing into purple vermilion; grows in the style of a Petunia.
 NEXT to Primroses, and by no means below them in value,
we place the Cyclamen. The leaves, a deep green with
white embroidery, are very ornamental, but when surmounted
with a wealth of bloom, what can be more charming?
Two of mine have begun to blossom—a white and a pink—and
the buds are numerous. Others will bloom later. They continue
in bloom for a long period, and are easy of culture, though
where there is over-dryness of atmosphere, they are apt to be infested
with the red spider. They need to be frequently sprayed
and it is well to immerse occasionally the entire plant in water so
as to wet the under surface of the leaves. The water ought to be
tepid, and indeed for all plants in cold weather. To keep the dirt
from falling out when the plant is plunged top downward, something
can be wrapped around the pot. A mixture of turfy loam
and sandy peat is best, but when not available, leaf mold or a rich
mellow soil mixed with silver sand will do.
NEXT to Primroses, and by no means below them in value,
we place the Cyclamen. The leaves, a deep green with
white embroidery, are very ornamental, but when surmounted
with a wealth of bloom, what can be more charming?
Two of mine have begun to blossom—a white and a pink—and
the buds are numerous. Others will bloom later. They continue
in bloom for a long period, and are easy of culture, though
where there is over-dryness of atmosphere, they are apt to be infested
with the red spider. They need to be frequently sprayed
and it is well to immerse occasionally the entire plant in water so
as to wet the under surface of the leaves. The water ought to be
tepid, and indeed for all plants in cold weather. To keep the dirt
from falling out when the plant is plunged top downward, something
can be wrapped around the pot. A mixture of turfy loam
and sandy peat is best, but when not available, leaf mold or a rich
mellow soil mixed with silver sand will do.
There are several varieties of Cyclamen, but the most common is persicum, and many catalogues name no other. One of mine is gigantium, an improvement on persicum, the flowers being much larger and finer in every respect. Among many catalogues I find this named in only one. Persicum, white and pink, is a sweet scented variety from Cyprus; Africanum, white and rose, from Africa; hederæfolium, from Britain. Other rare and expensive sorts are Atkinsii, white, crimson and rose colored; Europeum, red, and Coum, which in the early spring months bears above its very ornamental leaves "a profusion of small bright, rosy, crimson and snow-white turbinate blossoms of a roundish recurved outline, blotched with violet-crimson at the base, very beautiful."
The bulbs of all Cyclamens, except Coum, should be placed on the surface of the soil, covered half an inch, and water given moderately till the leaves are fully developed, and the flowers appear, when it may be applied more liberally. Do not make a mistake and plant your bulb upside down as did a lady I know of. "I have an idea that it is put in wrong, as the leaves seem to come from the under side," she writes. It is difficult to tell sometimes which is the right side to put down.
Persicum, with its dappled green and silvery gray, rounded, heart-shaped leaves, embroidered margins, is a fine ornament, but when these are surmounted with a profusion of pure silvery white oblong lanceolate petals, blotched with violet-crimson at their base, borne on slender flower-scopes, the plant is very beautiful. It varies in color from snow-white delicate peach and rosy crimson. Some are delightfully fragrant. During the growing and flowering season the plant should have a full exposure to the light, but not to the intense sunshine. After blooming, the bulbs may be allowed a time of rest, removing them to a cool and shady place in the border, if desired, watering rarely. In early autumn repot, and after a few weeks of growth, water more freely. It does not, however, injure the plant to keep it constantly growing, and the best florists have very generally abandoned their former method of letting them rest during the summer. Cyclamen autumnale flore alba, white, and rubra, red, blossom in the autumn.
The winter blooming varieties are admirably adapted for hanging-pots, and being cheap and very easy of cultivation, they ought to be in every dwelling. There are one hundred and fifty known varieties, though our catalogues rarely name half-a-dozen. Some are strictly winter bloomers, others flower only in summer, and some blossom the year round. The floribunda varieties belong to this class of perpetuals. Ortgiesi also, which is a wonderful bloomer,[145] and on account of its erect growth, is admirably adapted for pot culture. It is a new and somewhat rare species from Brazil. It often grows eighteen inches high, and in good form. The upper side of the leaf is rich olive green, and the under side bright violet purple. The flowers are quite small, yellow, and borne in clusters. The special beauty is in the foliage.
Floribunda alba and rosea have tuberous roots. The foliage is very strong, and the clusters of bloom are borne on long foot-stalks starting directly from the tuber. A single small tuber will often have a hundred open flowers at a time. They are from one-half to three-quarters of an inch in diameter. This variety can be obtained and planted at any time of the year. It is admirably adapted for baskets or a hanging-pot.
Oxalis acetocella is the true shamrock of Ireland. Flowers are white, borne on stalks two to four inches high. Versicolor is a winter bloomer; color white, with bright pink margins to the petals; requires sunshine; the flowers will not expand in cloudy weather. Floribunda has no such freaks, but smiles in the storm, as well as the sunshine. A lady writing to Mr. Vick becomes enthusiastic over her Oxalis. She says: "The sixth of last October I planted a bulb of Oxalis versicolor, and it is just beginning to bloom. And oh! what lovely flowers; delicate and perfect in form, pure white, with just the faintest tinge of yellow in the center, and beautiful crimson stripes on the outside. The plant also is of a very graceful habit, bearing its tuft of small leaves, and clusters of flowers on the top of a short, slender stem. It seems strange that so small a bulb can produce such beautiful flowers."
Of Bowii she thus writes: "A year ago last October I planted a bulb of Oxalis Bowii in a small bed. The bulb was so very small that I did not believe the flowers could amount to much, but was soon most agreeably disappointed. Such a mass of flowers on one small plant I had never seen before, and such large, bright-colored[146] flowers! Many stopped to admire it, and ask its name. It continued to produce a mass of flowers the entire winter and part of the spring, until the sun became very hot. From this one bulb I obtained eight, which I wrapped in paper and kept in a dry place. About the first of August they commenced growing, and so I planted them, and the first of September they were in full bloom, though the flower grew large as the days became less hot, until they were nearly as large as Petunias. The soil in which they grew was mostly sand and rich surface earth from the woods, and I sometimes watered them with weak soap-suds."
Mr. Vick, to whom we are indebted for the most of our information on this subject, says that this variety has large, thick, fleshy leaves, and large, bright, rose-colored flowers, the largest, indeed, of any of the cultivated kinds.
In his illustrated article he gives an engraving of one named Cernuus plena, the flowers of which resemble double Portulacas; erect, borne in clusters. We regret that he gives no reference to this variety whatever. It must be a rare sort, probably not in the market here.
 THUS spake one wiser than Solomon, even He whose hand
created and beautified the Lilies with a glory surpassing
that of the greatest of Israel's kings.
THUS spake one wiser than Solomon, even He whose hand
created and beautified the Lilies with a glory surpassing
that of the greatest of Israel's kings.
This department of the Floral kingdom is too vast for us to explore; we can only make a selection of a few of the numerous varieties for consideration, gathering our information from the various sources at hand, and adapting it to our present use.
The Lily is the rival of the Rose, and by many is considered far superior. They certainly are far more easily cultivated. They are hardy, elegant, gorgeous sometimes, and sometimes of snowy purity. Many of them are of exquisite fragrance. There are early and late bloomers, and one can have these desirable flowers in succession for several months, by a right selection. The earliest bloomers are the Pomponiums, natives of Siberia, and are perfectly hardy. The Lancifolium or Speciosum is the autumn blooming Lily, native of Japan. Lancifolium Album, a fine sort, with pure white petals and a pea-green stripe, very fragrant. Lancifolium Rubrum, and Roseum, though catalogued separately, are the same with different shadings. Some purplish crimson, others a faint blush of rose. Some have a red stripe, others a dark dull green, but all are specially recommended. Lancifolium Punctatum verum is a late bloomer; color, clear white with soft rose spots and green stripes. Finest of the species, Lancifolium Praecox; flowers white with a purplish-blush at the tips. Lancifolium Monstrosum or Corymbiflorum rubrum, bears its crimson flowers in large clusters. Grows to a great size.
The Lancifolium Lilies are of special value for their hardiness[148] and varied beauty, and their cheapness places them within general reach. They are classed under the head of Martagons, or Turks Cap.

Auratum Imperial is the Golden-banded-Lily of Japan which has become so extensively known and popular since its introduction from Japan by Mr. Gordon Dexter. It was first exhibited in July 1862, at the Massachusetts Horticultural Exhibition. It first bloomed in England same year. It was for sometime considered too tender for the Canadas and New England states, but it proved to be hardy. We have had ours twelve years, and give it only a slight protection. The petals of the Auratum are snowy white with a golden band running down the center of each, and freely spotted on the sides with deep carmine red. They are very fragrant. Being of somewhat slender growth, they need support. It does best in a warm sandy soil that has been well manured and dug deeply. It is easily propagated from the scales of the bulbs, each scale producing a small bulbet. They should be planted in a box about a foot deep, in good friable soil about three inches deep, and one inch apart. Sink the box in some out of the way place in the garden, and water frequently. In a short time small bulbs will be found forming on the base, which rapidly grow, and must be transplanted out the second year in the bed; the third or fourth year it will bloom. The little bulbets which form on the mother bulb blossom a year earlier. They should be renewed in the fall, after the foliage is dead. Plant in a bed about four inches deep, and let them remain undisturbed for two years; then they are large enough to bloom and should be transplanted into a permanent bed, if required.
These trumpet-shaped Lilies are charming in appearance, quite hardy and fragrant. They bloom in July or August, and continue in beauty for a long time.
Longiflorum Japonicum blooms in July, and is a fine dwarf bedder; color pure white, with occasionally a greenish tinge outside. Increases rapidly. Eximium bears a longer flower, from six to nine inches in length, and is more open at the mouth than the common Longiflorum. Pure white and very fragrant. Brownii is a native of Japan, and is a grand Lily of rare beauty. It resembles Longiflorum in shape, but is larger and more expanding; color white inside, exterior brownish-purple; stamens rich chocolate, which forms a distinctive feature in this species. It has been frequently confounded with Japonicum, but the difference is very marked in the illustrations of the two, and are thus noted in Messrs. Hallock & Thorp's "Catalogue of Lilies."
"Japonicum (Odorum, Japonicum Colchesterii). One of the most beautiful and rarest Lilies in cultivation. It differs from Brownii and all the forms of Longiflorum in many respects. Note the following marked differences: Its broader, fewer and more spreading leaves, the shape of the entire flower and broader claw of its divisions, its shorter anthers with pollen tinged with red. The flower is solitary and large, interior pure white, exterior of a pinkish-brown color, tubular, bell-shaped, with spreading revolute tips; the[150] bud shows a rich golden tint. Bulb white, or whitish-yellow, never red or brown, broad at the base, the scales which are somewhat narrow and acute at the tip, the outer ones terminate at about two-thirds of the height of the inner scales, whereas in Brownii the scales are broad, and all pass up, overlapping, and terminate together at the apex of the bulb, thus making the base much narrower than the apex."
It is a native of Japan, and is so exceedingly rare that it is priced at $7.00, more than double the cost of any other in the list. Brownii was priced, when a novelty at $4.00, but is now offered for $1.75.

Candidum, sometimes called Easter Lily, is one of the best known and commonly grown of all the Lilies. It has been in cultivation for about three hundred years. Bears a profusion of pure white fragrant flowers in a compact head.
The double Tiger Lily is a very great improvement on the old single variety. It is very double, and very showy. Wallacei is a new Japanese variety, said to be magnificent; color, buff, spotted with black.
Chalcedonicum or Scarlet Martagon is supposed to be the "Lily of the field" mentioned in the Gospel. "It is magnificent, and its intense scarlet is one of the finest shades in the whole vegetable kingdom. A full bed is a most magnificent sight, and if suddenly looked at on a bright day, has nearly the same effect for a moment as if looking at the sun. It is much scarcer than it should be, and requires careful culture, to be planted about six or eight inches deep, and watered in the summer time. It pleases every one who is capable of being pleased."
Lilies, as well as many other bloomers, are greatly improved by[151] thinning out the overplus, thus concentrating the sap to fewer blossoms, which being thus liberally nourished, greatly increase in size, and amply repay, by their superiority, for the loss in numbers. Although this is a demonstrated fact, yet few have the courage to prune where flowers are not very abundant, and many will not when they are.
Those who have limited space are loth to devote much room to Lilies, preferring plants that bloom continually throughout the season, or that make more show. But it is not essential that the bed should be devoted exclusively to lilies. For early spring blooming there can be the Crocuses, Snowdrops, Hyacinths, Tulips, all of which will bloom before the lilies, and after flowering can be taken up, i.e., the Tulips and Hyacinths, and low bedding plants take their places. Portulaca, Pansy, Ageratum, Mignonnette, Nemophila, Sweet Alyssum, are all suitable for this purpose, and will not only make the bed beautiful all the season with their blossoms, but will also be of real benefit to the Lilies by shading their roots somewhat, and keeping the soil more cool and moist.
Lilies must never be crowded; a foot or twenty inches is about right. The soil should be dug deep and mixed with old rotted manure and sand liberally, unless the soil is naturally sandy; if heavy, clayey soil, it ought to have in addition to sharp sand, leaf mold and bog muck. Plant the bulbs from six to eight inches deep, according to the size. Last autumn, in planting my Lily, Tulip, Hyacinth, and other bulbs, I made a little bed for each of pure sand, and then covered well with soil, over which was put a blanket of old dressing, then, before snow, a covering of boughs. The bulbs never came up so grandly, nor grew so rapidly before. October is the best month for bedding out, later will do, and many do not plant their Lilies till the frost is out in the spring.
The two leading Lily growers of this country are John L. Child and V. H. Hallock & Thorp, of Queens, N. Y.

 THIS is indeed a novelty among this class of valuable plants,
being the first double ever known. It is said to be equal
if not superior, in profuse blooming quality, and vigorous,
healthy growth, to the single white variety, Davidsonii, of
which it is a sport. The flowers are rather larger than those of
the single flowering, and composed of three perfect rows of petals,
of the purest waxy white color, each floweret resembling a miniature
Tuberose. The trusses are large and perfect, and are freely
and without interruption produced, even on the small side shoots,
which generally make no flowers on the single one. It is highly
praised by Mr. Thomas Meehan, florist and editor of the Gardeners'
Monthly, and by Mr. Henry A. Dreer, florist, of Philadelphia.[153]
"A grand thing," says Mr. Meehan. "Gives great satisfaction.
It has excelled our expectation," says Mr. Dreer.
THIS is indeed a novelty among this class of valuable plants,
being the first double ever known. It is said to be equal
if not superior, in profuse blooming quality, and vigorous,
healthy growth, to the single white variety, Davidsonii, of
which it is a sport. The flowers are rather larger than those of
the single flowering, and composed of three perfect rows of petals,
of the purest waxy white color, each floweret resembling a miniature
Tuberose. The trusses are large and perfect, and are freely
and without interruption produced, even on the small side shoots,
which generally make no flowers on the single one. It is highly
praised by Mr. Thomas Meehan, florist and editor of the Gardeners'
Monthly, and by Mr. Henry A. Dreer, florist, of Philadelphia.[153]
"A grand thing," says Mr. Meehan. "Gives great satisfaction.
It has excelled our expectation," says Mr. Dreer.
My own specimen, about four inches in height, has twelve buds; two small clusters are on side-shoots. The very fine illustration of this Bouvardia we give our readers, has been kindly loaned by the Ellis Brothers, Keene, N. H., who have a fine stock which they are offering to the public.
Mr. Henry Cannell says, "Of all plants the Bouvardia, in our opinion, excels for cut flowers, no matter either for button-hole bouquets or table decoration; a spray of it is sure to be most prominent and pleasing, and the odor of several kinds is deliciously refreshing, and if well-grown they will more or less continue flowering nine months out of the year. Strange to say, they need only the ordinary course of cultivation of the winter-flowering Zonal Pelargonium; hitherto they have been treated as a stove plant, whereas they only need a temperature not higher than 50° to 60°, and in the summer to have every attention, like a specimen Chrysanthemum, and on the first appearance of frost to be taken into the house, and when growing and flowering, to be supplied with liquid manure occasionally."
Our only experience with this genus has been with Bouvardia Humboldtii Corymbiflora, and it has proved to be a very valuable plant. Its pure white flowers are produced in large trusses; their tubes are three inches in length, and very fragrant. It blooms very freely and for a long period. This variety and Vreelandii are the best single white.
Liantha is a dazzling scarlet, and a very profuse bloomer. Elegans, salmon-scarlet; large and fine. Lady Hyslop, a light rose. Canspicua is of a blood-red color, with whitish tube. Bicolor, a summer-flowering variety. Flower tube purple, with tint of blue and delicately mottled flesh, tipped with white. These last we find, only in Cannell's Floral Guide.
I have no difficulty in keeping my Bouvardia in the cellar, the leaves drop off, but they come out anew in the spring.
This is a very popular genus on account of their rich dark-green leaves, and beautiful rose-like flowers. They are hardy greenhouse plants, and thrive best in light loam mixed with sand and peat, but will do well in light soil without the peat. It will not flourish in a limestone soil. Mr. Vick gives the following in his Magazine:
"The Camellia Japonica was sent to England in 1739 by Father Kamel, a missionary, for whom it was named. As a house-plant the Camellia requires considerable care, on account of the tendency of the flower buds to drop off. A northern exposure is best, and a temperature of from forty to fifty degrees. When the buds are swelling, water plentifully with warm water, but allow none to stand in the saucer. Sponge the leaves once a week. In the spring put the plant out in a shady place on the north side of a house or fence, not under the drip of trees, and water it every day. Set the pots on a hard bottom, so that no worms can get into them. They form their flower beds during the summer, and at this time a good growth of wood must be encouraged.
"In the Southern States the Camellia can be raised with not more than ordinary care; at the North it must be considered entirely a green-house plant, and as such will always be highly prized. We are often asked how it should be cared for as a house-plant, and to all such, in the northern part of the country, where it is necessary to maintain good fires in warm houses for several months of the year, we have no hesitation in saying, let it alone, do not expend care and labor where there is so little prospect of reward."
Camellias are of many hues, and some are beautifully striped. Gen. Lafayette, bright rose, striped with white, imbricated. Bell Romann, imbricated, large flower and petals, rose striated with bright crimson. Matteo Molfino, petals cerise, with pure white[155] band down center. Mrs. Lurmann, crimson, spotted, very beautiful. Pure colors of white, red, crimson, rose and carmine, can be obtained.
Azalea.—Shrubby green-house plants of easy cultivation. Very showy and hardy. Like the Camellia, they are found in all the leading colors, and also striped, blotched and spotted. They are both single and double.
Alexander II, is white, striped with vermilion; edges of petals fringed. Aurelia, white, striped with rosy orange, amaranth spots. Flag of Truce, is a pure double white, very fine. Her Majesty, is rosy-lilac, edged with white. Alice, rose, blotched with vermilion; double.
Mr. Vick gives the following directions: "Azaleas need a light soil of sandy loam, to which should be added one-half leaf mold. Repotting should be done in May, trimming the tops to bring them into shape. Then plunge in some sheltered spot in the garden. In September the plants should be brought in under cover, or into a cool room. They do best when the temperature ranges from forty degrees at night to sixty-five or seventy by day. The foliage should be showered once a week, but care must be taken that the roots are not over-watered, as they rot easily. Small plants bloom well, but their beauty increases as they get age and size. The flowers appear on the terminal shoots, and are from one inch to two and a half inches in diameter.
"Azaleas if left to themselves will develop long shoots, that after a time become naked below and are furnished with leaves only at their extremities. Flower stems are formed on the new wood of each summer's growth, consequently the amount of bloom, other things being equal, depends upon the amount of new wood annually produced. In order to have plants of good shape when they become large, it is necessary to give attention to pinching and training them from the first. The pyramid form, or more properly that of a cone, and rounded at the top, is considered the best for the[156] plant, as it allows the greatest exposure of leaf-surface. Two principal methods are adopted to regulate the growth and bring plants into shape: one is by successive pinchings as the growth proceeds, the other by allowing long shoots to grow and then bending and training them down, thus causing many of the dormant buds along their whole length to break and develop into shoots. A skillful combination of the two methods is probably better than either exclusively."
Mr. John Dick, Philadelphia, has the largest stock of Camellias and Azaleas, it is stated, in the United States. Their catalogue list of these plants embraces more than a hundred varieties, to which we refer our readers.
 WE have come to see your garden, said a gentleman with a
lady in company. They were from a neighboring town.
This two weeks after the heavy frost!
WE have come to see your garden, said a gentleman with a
lady in company. They were from a neighboring town.
This two weeks after the heavy frost!
I told them my garden was in the stable, and thither I piloted them. It was not a very small garden if it was in a stable. A hundred or more plants had been hurriedly removed from the beds the day before that freezing night! There they were, in the soiled pots just as taken from the ground, or packed closely in boxes. Not very attractive looking, in one sense, yet in another they were, for they were bright, healthy appearing plants—leaves as fresh as when in the open air, pretty Geraniums in bloom, a mass of Lobelia, attractive with their tiny blue flowers, Coleus of varied hues, and even a few Roses struggling into bloom.
Then we strolled among the despoiled beds, and the Pansies, so large and pert, elicited admiration, and the Sweet Peas, just as fragrant as though blight were not all around them, while dear little Mignonnette seemed to have taken a new lease of life.
Yesterday I arranged in a shallow glass dish as handsome a bouquet as I have had for the season. Sweet Clover sprays, Mignonnette and fragrant Geranium leaves for the foundation all around the dish, a few bunches of the little white wax balls, with their glossy leaves, Geranium blossoms, and lots of Sweet Peas, from the most delicate shades to the deepest, and bunches of splendid Pansies, Sweet Alyssum, a bit of purple Verbena here and there, and white-eyed Phlox. It was just lovely.
When the evidence was sure that frost was surely coming, and a great many plants must be taken up in a few hours' time, I was so glad that full half of them were in pots. I could never have potted a third of them in the time. The great object was to get them sheltered, and the repotting could be done at my leisure.
But I almost changed my mind the other day after toiling several hours at the business. So many pots to wash! then fill with fresh earth, and set the plant. O dear, wasn't I tired! But then the wide door was open, the day was lovely, and I rather think potting plants in a stable is better than potting out of doors on a cold day, and when one is in a great hurry. Plants that are in pots plunged in the ground do not grow so many roots, and that is another advantage.
Perhaps I may as well tell you about my most important window box. I had it made last autumn, and I was greatly pleased with it. It is made of zinc, size one yard long, fourteen inches broad, seven inches in depth. To give it strength it is framed at the top with wood. You can have this of black walnut, or stained in imitation. You can have the box painted any color you wish, or leave it unpainted. In the center is Croton "Weismanni," on one side of it a fine Eranthemum pictum; its green leaves look as though they were painted with white streaks; on the other side, Acalypha "Macafeeana." These are the largest plants in my box,[158] and they do not exceed ten inches in height. There are sixty plants in all, mostly averaging six inches in height, but a few are quite small. They consist of very choice Geraniums—some of them handsome-leaved—variegated Abutilons, Lemon Verbena, two bright Achyranthes, six very beautiful Coleuses, and four fine Begonias. There are others I cannot stop to specify. You will see that I have filled my box with what are, in themselves, beautiful without the aid of flowers, though I expect to have a few of these by-and-by. I am perfectly satisfied with it, however, just as it is. I had a large German Ivy growing out of doors, which consisted of several long vines. This I planted in one corner of the box, and then drooped and twined it on the outside. The change to indoor life caused the large green leaves to fall off, but already new ones have put forth, and the vines are rapidly growing. Everything else had been previously prepared so that there was no change in their leafage after being put in the box. It is a great addition to the beauty of the box to have vines of pretty foliage drape the sides. This autumn I have had it placed on a small, low table with castors, so I can change the plants every week, and thus avoid that turning toward the window which they always assume if kept in one position.
I first put in drainage, and then filled the box with rich, mellow earth in which was a mixture of one-third sand. I have been thus particular in my description, for many, no doubt, who, like myself, have to make the most of limited space, will be glad to know just how to keep the greatest number of plants to the best advantage. Not only is there a saving of room, but of labor, and it is more cleanly.
Among the essentials for winter flowers are the bulbs. Of these the hyacinth takes the lead. They are so easily grown; so lovely and so fragrant that they are worthy of a place in every collection.[159] They should be planted so that the upper surface of the bulb is visible. Water liberally and then put away in a cool dark place for several weeks, six weeks is none too long, and some I allow to remain a longer time, bringing them to the light at intervals so as to have a succession of flowers. They are very effective planted in a group. They are very pretty in hyacinth glasses, but this method ruins the bulbs for future use. Planted out they will sometimes flower. The best time to plant them in the border is in October, but the first of November will do. It is a good plan to make a little bed of sand for the bulb, and then cover with light porous soil. Hyacinths are classed as tall and dwarf, single and double. The Roman Hyacinth is the earliest bloomer, coming into flower about the holidays if started in season. The spikes are small and flowers rather scattering. As soon as the blooms fade, the stalk should be removed, and when the leaves turn yellow, they can be cut off, and the bulb dried and packed in paper bags and kept till time for autumn planting.
Hyacinth bulbs come from Holland. About Haarlem the rubbish heaps are hyacinths, and the air is oppressive with their perfume.
In California there grows what is called the Twining Hyacinth. It grows in the mountains, and twines about the bushes, sometimes going up eight and ten feet. After it gets to the top of the bush and rests awhile, it lets go of the earth and goes on blooming for months, regardless of the burning sun. The flower stem breaks off near the ground, and the flowers are kept swinging in the air supported only by the bush about which it twines. The color is deep rose, and it is said to be very pretty. The picture of it certainly looks attractive. It is a large cluster composed of dozens of blossoms.
For flowering in the house the Polyanthus Narcissus are very desirable. They can be put into glasses as well as the Hyacinth,[160] but the most natural method is in a pot of earth, and the bulb is in a better condition for after use. The Jonquils are also pretty. Snowdrops, Scillas and the Crocus are cheap bulbs, and planted in the autumn will show their bright, sweet faces soon after the snow is gone. They are also very fine for house culture. Should be planted in groups.
Tulips ought to have a place in every garden. They make a brilliant show in the Spring, when the beds are bare of other flowers, and afford bloom for a long time, if a good assortment is selected. The pretty little dwarf Duc Van Thols are early bloomers and very gay. They are admirable also for the house, and by planting in September, will come into flower in December. There are early single and double Tulips, and also late bloomers, so that by having a variety, the border may look gay for a long time. The Parrot Tulips are large and very brilliant in color, and picturesque in appearance. All of these varieties succeed in ordinary garden soil. They ought to be planted in October or November, about four to six inches apart, and about four inches under the surface. Before severe frost they need to be protected by branches of evergreen, straw or leaves. After blooming, and the leaves have died down, they can be taken up, dried and stored till autumn, if the bed is needed for other flowers.
The Bulb catalogues issued by leading florists in the autumn, and sent free to all applicants, will enable you to select just what you want.
In a work of this character it seems needful to treat more fully of those pests which prove so destructive to plant life, than we have in our brief references.
The Aphis or green louse is the one that most frequently infests our plants, and the rapidity with which it multiplies, is astonishing. Reaumer has proved that in five generations one aphis may be the progenitor of six thousand millions, and there may be ten generations in a year!
The method most generally adopted for their destruction is fumigation with tobacco. As this is attended with considerable difficulty, a weak solution may be used quite as effectively. We have had no experience[161] with either method, having used another with good success for several years. This is white hellebore which we usually apply in the powder when the Rose-bushes are wet with dew or rain, bending the branches over, so that the application can be made chiefly on the under side of the leaves, where the pests are found. Two or three times proves sufficient. For our house plants we usually make a solution, by putting half an ounce of the hellebore into pretty warm water, and letting it stand for several hours, stirring it up however, before spraying the leaves. Afterward, the plants need to be washed.
For the Scale a strong solution of soap-suds applied with a sponge or a small stiff brush. A tooth brush is very suitable for this purpose.
For Mealy Bug, a mixture of one part alcohol and three parts water, applying with a feather, or what is better, a camel hair brush. Another method is to use kerosene in the same way. A florist who has practiced this for eight years, says it is sure death to the insect. The feather should be brushed all over the mealy-looking substances found usually in the axils of the leaves.
Worms in Pots. Lime water is a safe and effectual remedy for the little white worms often found in the soil. Slake the lime in water and after it has settled, pour off the clear water and drench the earth.
Ants. Various remedies have proved effective. One is to take a vial or a cup nearly filled with sweet oil, and sink it in the ground where the ants resort, so that the rim is on a level with the surface. The ants are very fond of it, but it is sure death to them.
A German writer says that carbolic acid and water will drive ants away from any grounds—one hundred parts of water to one of the acid. Mix in a tub and stir repeatedly for twenty-four hours, taking off the scum that rises to the top.
Kerosene or coal-oil mixed with water has proved very successful in the destruction of noxious insects and grubs. A tablespoonful of the oil to two gallons of water is the rule for tender plants; for hardy ones it will be necessary probably to have it of greater strength. As the compound does not mix readily, it needs to be thoroughly stirred, and then quickly applied. The best way is to draw it back and forth a few times in a syringe, and then apply.
Water tainted with coal-oil, poured into little holes made in mole tracks, will, it is said, drive them effectually away.
For the convenience of our readers who may wish to procure varieties of plants of which we have treated in this work, we give the address of reliable florists who make a specialty of those connected with their address. All of them will furnish their catalogues free when requested.
Pansies. Seeds for the Wild Garden. B. K. Bliss & Sons, New York City.
Verbenas, Petunias, Fuchsias. C. E. Allen, Brattleboro, Vt.
Geraniums. Innisfallen Greenhouses, Springfield, Ohio.
Pelargoniums, Ornamental Foliage Plants, Gloxinias. John Saul, Washington, D. C.
Gladiolus, Single Dahlias, Novelty Dahlia. V. H. Hallock & Thorp, Queens, N. Y.
Coleuses—New Hybrids, Dracænas. H. A. Dreer, Philadelphia, Pa.
Chinese Primroses, New Primula, Double White Bouvardia. Ellis Brothers, Keene, N. H.
New Monthly Pelargoniums. John G. Heinl, Terre Haute, Ind.
Wistaria. E. H. Ellwanger, Rochester, N. Y.
Amaryllis, Rare Varieties. John L. Child, Queens, N. Y.
Lilies a Specialty. John L. Child; V. H. Hallock & Thorp, Queens, N. Y.
Camellias and Azaleas. John Dick jr., 53d st., and Darby Road, Philadelphia, Pa.
Vick's Illustrated Magazine is the best Floricultural Monthly we know of for amateurs. We are indebted to it for much of the information we have obtained respecting the culture of flowers, and have drawn largely from its pages in this work. There is a finely colored frontispiece in each number, and it is otherwise fully illustrated. Its entire arrangement evidences the fine æsthetic taste of its editor and publisher. It is very low at $1.25 per year. Beautifully bound vols., $1.75. Mr. James Vick, Rochester, N. Y.
The Gardener's Monthly and Horticulturist takes a wider range, treating not only of Flowers, but also of Fruit and Vegetable Gardening, Natural History and Science, Forestry, etc. The ample Notes pertaining to the several departments, by its editor, Mr. Thomas Meehan, are of special value. Published by Chas. H. Marot, Philadelphia, Pa., at $2.10 per annum.
Mrs. M. D. Wellcome of Yarmouth, Me., whose pleasant and helpful "Talks About Flowers" are familiar to the readers of The Journal, has published in a neat pamphlet, An Essay on Roses, which was read before the Maine Pomological Convention last March, and has since been revised and enlarged for publication. This essay treats the subject historically and descriptively. It considers the classification of Roses, tells what Roses to plant, gives suggestions as to the best mode of culture, and furnishes a list of the best hybrids and of the best ever-blooming varieties. Mrs. Wellcome writes with enthusiasm, and from a thorough knowledge and a considerable experience. All lovers of roses, and all amateur horticulturists will find the little monograph interesting and suggestive.
Boston Journal.
The valuable and instructive Essay on Roses read before the Maine Pomological Convention by Mrs. M. D. Wellcome, has been issued in a neat pamphlet.... Our readers who are familiar with Mrs. Wellcome's writings, will know how to value this production of her busy pen.
Portland Transcript.
Our well-appreciated correspondent, Mrs. M. D. Wellcome, has published in a neat pamphlet, an essay upon "Roses."... It is an interesting and practical little manual, and will prove a valuable aid to young horticulturists.
Zion's Herald.
The Waterville Mail says: "Of this essay it is sufficient to say that it was prepared by a graceful writer,—a well-known contributor to the literary department of several prominent Journals, and a skillful florist—and that it secured the approbation of the Convention before whom it was read, and the representatives of the agricultural press."
Rev. J. M. Orrock, editor of Messiah's Herald, after describing the work, adds: "The author says in her introduction, 'I have brought you a bouquet of Roses, and there is little of my own but the string that binds them.' It is indeed, a pretty bouquet, and we hope many of her friends will want to see and enjoy it."
Mr. Samuel L. Boardman Esq., editor of the Home Farm, says: "This little booklet about Roses is just the plain, sensible guide all amateur growers will be profited by reading. There is just enough of history and sentiment in its opening pages, ample directions for culture, treatment, etc., closing with descriptions of the most desirable Roses, and lists from which to make selections for larger cultivators. Mechanically, the little book is as delicate as a rosebud; and every lover of this queenly flower should procure a copy."
The "Essay" is issued in a neatly illustrated pamphlet of 24 pages, with ornamental cover. Price 15 cents. For sale by the author, Yarmouth, Me.
GERANIUMS!
We offer a fine assortment of Geraniums at 10 CENTS EACH, for your selection; or we will send 16 FINE SORTS of our own selection, all labeled, prepaid, by mail, for a remittance of $1.25. We have by far the largest stock of Geraniums in this country.
Roses, Ever Blooming.
We have a fine collection of Roses that we offer, strong flowering plants, labeled, at 10 CENTS EACH, your choice; or we will send 16 FINE PLANTS of our own selection, prepaid, by mail, for a remittance of $1.25.
We also offer a fine assortment of all kinds of flowering plants at the above low price. Send for a catalogue.
Address,
INNISFALLEN GREENHOUSES,
SPRINGFIELD, O.
![]()
![]()
NEW HYBRID TEAS.
This new class of ROSES combine HARDINESS, CONSTANT BLOOM, and DELICATE COLORING. They originated in England, and are now offered for the first time in this country. For full description of these Roses, and price, send for catalogue.
E. C. ALLEN, Brattleboro, Vermont.
FREE!
We wish to obtain 25,000 New Subscribers to
THE FLORAL MONTHLY
during the next few months, and we propose to give to every reader of this paper
Fifty Cents Worth of Choice Flower Seeds.
Our offer is to send, Free of Cost, 50 cents worth of Choice Flower Seeds to each and every one who will send us 25 two cent postage stamps for the FLORAL MONTHLY one year. Seeds sent free by return mail. Specimen copies free. Address
W. E. MORTON & CO., FLORISTS, 615 Congress Street, Portland, Me.
(NATURAL FLOWERS PRESERVED TO LAST FOR YEARS.)
Punctuation has been standardised, and typographical errors such as missing or reversed letters have been silently corrected.
Variations in hyphenation (such as greenhouse and green-house), and obsolete or variant spelling have been preserved. In particular, variations in the spelling of some botanical names have been left as printed in the original book.
In the Table of Contents, the entry "A Talk About Pansies" was printed as "Pansies"; this has been changed to match the chapter title as printed on page 33.
The following changes were also made:
Pg 82, Verschaffellii changed to Verschaffeltii: (Verschaffeltii, we fear).
Pg 109, Ainwick changed to Alnwick: (a visit to Alnwick Castle).
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Talks about Flowers., by M. D. Wellcome
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK TALKS ABOUT FLOWERS. ***
***** This file should be named 40534-h.htm or 40534-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/4/0/5/3/40534/
Produced by Jennifer Linklater, sp1nd and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This
file was produced from images generously made available
by The Internet Archive)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.