
| PLATE LXXV | CHAMBORD: SOUTHERN FAÇADE |
The Project Gutenberg EBook of The Brochure Series of Architectural
Illustration, vol. 06, No. 10, October 1900, by Various
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license
Title: The Brochure Series of Architectural Illustration, vol. 06, No. 10, October 1900
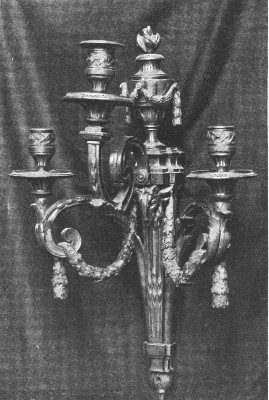
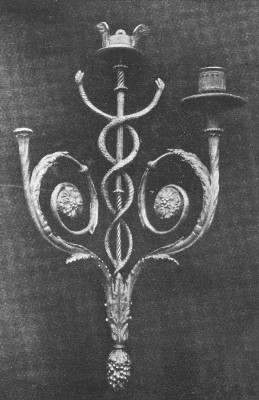
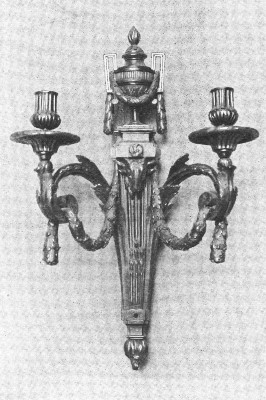
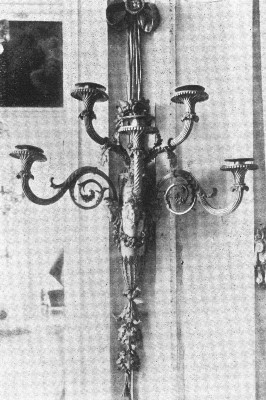
The Château of Chambord: France, Louis XVI. Sconces
Author: Various
Release Date: January 8, 2015 [EBook #47916]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE BROCHURE SERIES ***
Produced by Juliet Sutherland, Haragos Pál and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net
THE BROCHURE SERIES
|
THE |
||
| 1900. | OCTOBER | No. 10. |
The Château of Chambord is one of the most unique palaces of the Renaissance in existence. "It is," writes Jules Loiseleur, "the Versailles of the feudal monarchy; and was to the Château of Blois, that central residence of the Valois, what Versailles was to the Tuilleries,—the country-seat of royalty. Tapestries from Arras, Venetian mirrors, curiously sculptured chests, crystal chandeliers, massive silver furniture, and miracles of all the arts, were amassed in this palace during eight reigns, and dispersed in a single day by the breath of the Revolution.
"It has often been asked why Francis I., to whom the banks of the Loire presented many marvelous sites, selected such a wild and forsaken spot in the midst of arid plains for the erection of the strange building which he planned. His peculiar choice has been attributed to his passion for the chase and also because of the memory of his amours with the beautiful Comtesse de Thoury, whom he had visited in that neighborhood before he ascended the throne. Independently of these motives, which no doubt counted in his selection, perhaps the very wildness of the place and its distance from the Loire, which reminded him too much of the cares of royalty, was a determining reason. Kings, like private individuals, and even more than they, experience the need at times of burying themselves, and therefore make a hidden and far-away nest where they may be their own masters and live to please themselves. Moreover, Chambord, with its countless rooms, its secret stairways, and its subterranean passages, seems to have been built for one who, tired of the blaze of royal glory, sought here for shadow and mystery. At the same time when he was rearing Chambord in the heart of the uncultivated plains of the Sologne, Francis I. built in the midst of the Blois de Boulogne a château, where, from time to time, he shut himself up with learned men and artists, and to which the courtiers, who were positively forbidden there, gave the name of Madrid, in memory of the prison in which their master had suffered. But Chambord, like Madrid, was not a prison; it was a retreat.
"That sentiment of peculiar charm which is attached to the situation of Chambord will be felt by every artist who visits this strange creation. At the end of a long avenue of poplars breaking through thin underbrush you see, little by little, peeping and mounting upward from the earth, a fairy building, which, rising in the midst of arid sand and heath, produces the most striking and unexpected effect. A jinnee of the Orient, a poet has said, must have stolen it from the country of sunshine to hide it in the country of fog for the amours of a handsome prince. The park in which it is situated is twenty square miles in area, and is surrounded by twenty miles of walls."
Francis I. had passed his early years at Cognac, at Amboise or Romorantin, and when he first saw Chambord it was only an old feudal manor house built by the Counts of Blois. There has been much question as to who the architect he employed to transform it really was, and the honor of having designed the splendid residence has been claimed for several of the Italian artists, who early in the sixteenth century came to seek patronage in France. It seems well established today, however, that Chambord was neither the work of Primaticcio, with whose name it is tempting to associate any building of this king's, nor of Vignola, nor of Il Rosso, all of whom have left some trace of their sojourn in France, for the methods of contemporary Italian architecture were totally different; but as M. de la Saussaye, the author of a very complete and concise history of the building, proves, it was due to the skill of that fertile local school of art and architecture around Tours and Blois, and more particularly to a comparatively obscure genius, whose name is also mentioned in connection with Amboise and Blois, one Pierre le Nepveu, known also as Pierre Trinqueau, who is designated in the papers which preserve in some degree the history of the origin of the edifice as the maistre de l'œuvre de maçonnerie. "Behind this modest title apparently," writes Mr. Henry James, "we must recognize one of the most original talents of the French Renaissance; and it is a proof of the vigor of the artistic life of that period that, brilliant production being everywhere abundant, an artist of so high a value should not have been treated by his contemporaries as a celebrity. We manage things very differently today."
Although Le Nepveu was the chief architect, Cousin, Bontemps, Goujon, Pilon and other noted artists were engaged in the decoration of Chambord. Many changes in the structure were afterwards carried out, especially by Louis XIV. and by Marshal Saxe, to whom that monarch presented it in 1749. From 1725 to 1733 Stanislaus Leszczynski, the ex-king of Poland, who spent the greater part of his life in being elected and in being ousted from his throne, dwelt at Chambord. During the Revolution the palace was as far as possible despoiled of every vestige of its royal origin, and the apartments to which upwards of two centuries had contributed a treasure of decoration and furniture were swept bare. In 1791 an odd proposal was made to the French Government by a company of English Quakers, who had conceived the bold idea of establishing in the palace a manufacture of some peaceful commodity not today recorded. Napoleon I. presented Chambord to Marshal Berthier, from whose widow it was purchased in 1821 for the sum of £61,000 raised by national subscription on behalf of the Duke of Bordeaux, formerly Comte de Chambord.
The Château, only the north part of which is completed, consists of two square blocks, the larger of which, five hundred and twelve feet long by three hundred and eighty-five feet broad, encloses the smaller in such a way, that the northern façade of the one forms the centre of the northern façade of the other. The corners of each block terminate in massive round towers, with conical roofs crowned by lanterns, so that four of these towers appear in the principal façade. In plan it will be seen that Chambord resembles the typical French château; with the habitation of the seigneur and his family in the centre, and this habitation enclosed on three sides by a court, while like most feudal dwellings, the central donjon shares one of its sides with the exterior of the whole. The central part is adorned with an unexampled profusion of dormer-windows, turrets, carved chimneys and pinnacles, besides innumerable mouldings and sculptures, above all of which rises the double lantern of the tower containing the principal staircase.
"It is a forest of campaniles, chimneys, sky-lights, domes and towers, in lace-work and open-work, twisted according to a caprice which excludes neither harmony nor unity," writes M. Loiseleur. "The beautiful open-work tower of the large staircase dominates the entire mass of pinnacles and steeples, and bathes in the blue sky its colossal fleur-de-lis, the last point of the highest pinnacle among pinnacles, the highest crown among all crowns.
"We must take Chambord for what it is, an ancient Gothic château dressed out in great measure according to the fashion of the Renaissance. In no other place is the transition from one style to another revealed in a way so impressive and naïve; nowhere else does the brilliant butterfly of the Renaissance show itself more deeply imprisoned in the heavy Gothic chrysalis. Chambord, by its plan which is essentially French and feudal, and by its enclosure flanked with towers, and by the breadth of its heavy mass, slavishly recalls the mediæval manoirs. By its lavish profusion of ornamentation it suggests the creations of the sixteenth century as far as the beginning of the roofs; it is Gothic as far as the platform; and it belongs to the Renaissance when it comes to the roof itself. It may be compared to a rude French knight of the fourteenth century, who wears on his cuirass some fine Italian embroideries, and on his head the plumed felt of Francis I.,—assuredly an incongruous costume, but one not without character."
"With a sympathetic denial of any extreme over-technical admiration," writes Mr. Cook in his Old Touraine, "Viollet le Duc gives just that intelligible account of the Château which is a compromise between the unmeaning adulation of its contemporary critics and the ignorance of the casual traveller. 'Chambord,' says he, 'must be taken for what it is; for an attempt of the architect to reconcile the methods of two opposite principles,—to unite in one building the fortified castle of the Middle Ages and the pleasure-palace of the sixteenth century.' Granted that the attempt was an absurd one, it must be remembered that the Renaissance was but just beginning in France; Gothic art seemed out of date, yet none other had established itself to take its place. In literature, in morals, as in architecture, this particular phase in the civilization of the time was evident, and if only this transition period is realized in all its meanings, with all the 'monstrous and inform' characteristics that were inevitably a part of it, the mystery of this strange sixteenth century in France is half explained."
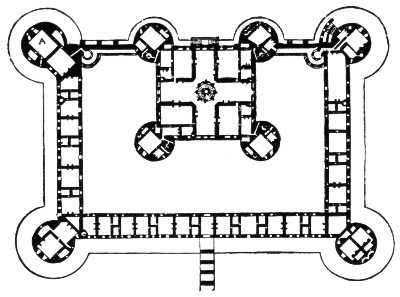
| PLAN OF THE CHÂTEAU OF CHAMBORD |
"At Chambord," writes Mrs. Pattison, in her Renaissance of Art in France, "which was building in 1526, the stories are, it is true, forcibly indicated, but the whole building is pulled together in Gothic fashion by the towers of the corps de logis, and by those which flank the pavilions or wings which stretch out on either side of the main body. In a building of the size of Chambord the result of this treatment is hardly satisfactory, for the lines of the wings to right and left of the main body seem to droop away from the heavy towers on either side. Inside the court, however, the unpleasant effect, even at Chambord, disappears, for the apparent length of the wings is greatly abbreviated by the effect of the two spiral staircases which run up outside the building at the internal angles on opposite sides.
"Chambord is, indeed, throughout truly typical of the earlier stage of the new Renaissance movement. In the general arrangement, in the ordonnance, late Gothic caprice and fantastic love of the unforeseen rule triumphant. The older portions of the Château, the seemingly irregular assemblages of half Oriental turrets and spires, are debased Gothic, full of audacious disregard of all outward seeming of order. The architect, instead of seeking to bring home to the eye the general law, the plan on which the whole is grouped, has wilfully obscured and concealed it beneath the obviousness of the wild and daring conceits heaped above.

| VIEW OF CHAMBORD (1576) | ENGRAVING FROM DU CERCEAU |
"But even at Chambord the mark is set which promises other days. It is the transition moment; Gothic fancy may wildly distribute ornament and obscure design, but the ornament which it distributes is Gothic no longer. The obscæna which haunt the cathedrals of the middle ages, which infest the earlier towers of Amboise, and linger defilingly about Gaillon, are banished. In their place come faint foliated traceries and arabesques in low relief, enriching every surface, disturbing none, moving with melodious adaptation of subtle line, winding, falling, rising in sympathy with every swiftly ascending shaft or hollowing curve.
"It is not now possible to approach Chambord carrying in our eyes a vision of the great Renaissance palace, as engraved by Du Cerceau in his Plus excellens Bâtimens de la France. Burdened by the weighty labors of Louis XIV., weakened by eight improving years at the hands of Stanislaus Leszczynski, mutilated by Marshal Saxe, the Chambord which we now go out from Blois to visit is not the Chambord of Francis I. The broad foundations and heaving arches which rose proudly out of the waters of the moat no longer impress the eye. The truncated mass squats ignobly upon the turf, the waters of the moat are gone; gone are the deep embankments crowned with pierced balustrades; gone is the no-longer-needed bridge with its guardian lions. All the outlying work which gave the actual building space and dignity has vanished, and we enter directly from the park outside to what was once but the inner court of the Château.
"It is not until we stand within this inner court—until we have passed through the lines of building which enclose it on the western side, and which show the unmistakable signs of stupid and brutal destruction, that we can believe again in the departed glories of Chambord. Lippomano, ambassador from Venice to France in the reign of Henry III., turned out of his way to visit Chambord. 'On the 21st,' he says, 'we made a slight detour in order to visit the Château of Chambord, or, more strictly speaking, the palace commenced by Francis I., and truly worthy of this great prince. I have seen many magnificent buildings in the course of my life, but never anything more beautiful or more rich. They say that the piles for the foundations of the Château in this marshy ground have alone cost 300,000 francs. The effect is very good on all sides. The number of the rooms is as remarkable as their size, and indeed space was not wanting to the architect, since the wall that surrounds the park is seven leagues in length. The park itself is full of forests, of lakes, of streams, of pasture-land, and of hunting-grounds, and in the centre rises the Château with its gilt battlements, with its wings covered in with lead, with its pavilions, its towers and its corridors, even as the romancers describe to us the abode of Morgana or of Alcinoüs. More than half remains to be done, and I doubt it will ever be finished, for the kingdom is completely exhausted by war. We left much marvelling, or rather let us say thunderstruck.'
"To destroy the character of Chambord from the outside was not difficult. It was not easy to tame the rude defiance of Vincennes, or give facility to the reserved and guarded approaches of Gaillon. Solid rectangular towers, heavy machicolations, and ponderous drawbridges offer a stubborn resistance to schemes of ruthless innovation; but Chambord was no fortress, it was a country house. The very site is motived by no other reason than the pleasures of the chase. The battlements of Gaillon gave back the echoes of the trumpet, but the galleries of Chambord resounded with the huntsman's bugle.
"The construction of these galleries in itself points to the rapid progress of social change. There are not only such as may be called covered passages communicating from the spiral staircases with the rooms on each story; galleries which have their special cause in actual need and daily use; but the roofs of the range of one-storied buildings which connect the side wings on the north and south, and which run along the western front, are finished up from the cornice with a balustrade, and turned into a promenade for courtiers.
"Yet in spite of these marked indications of change the ancient spirit lingers. The unrestrained freedom of grotesque caprice finds expression everywhere, even in those later portions which belong to another reign. Pierre le Nepveu has left on all his work the imprint of profuse and fantastic force; the outlines of his cupolas strike the sky with an audacity which seems to defy the adverse criticism of those who moved within the limits of more cautious rule. Symmetrical balance, for which the masters of a succeeding era sought, and by which they strove to harmonize every portion of their design, obliged them to reject the aid of those varied resources which Le Nepveu shrewdly marshaled with a vigorous hand.
"Chambord is in truth a brilliant example of transition. The early Renaissance is there to be seen, taking on itself the burden beneath which the failing forces of the Gothic spirit had sunk. But the intention of the work is wholly foreign to the main direction taken by the new movement, and condemned, by its very nature, to remain, in spite of the wonderful genius lavished upon it, an unfruitful tour de force."
The interior of the palace is now but a great wilderness of hewn stone. The sixteenth century treasures of art which had adorned it were all stolen or destroyed in the Revolution, the spoliation being so complete that it was stripped of even the carved wainscots, panels, doors and shutters, and the four hundred and forty enormous apartments now give only the impression of a vast and comfortless barrack. In the original arrangement of the interior all ideas of practical defense were sacrificed to produce a pleasure palace, and it was furnished with innumerable secret stairways (there are thirteen great staircases, not to mention numberless smaller ones) isolated turrets and a hundred facilities for what the gallant Viollet le Duc calls "les intrigues secrètes de cette cour jeune et tout occupée de galanteries."
"On the whole," writes Mr. Henry James, "Chambord makes a great impression—there is a dignity in its desolation. It speaks with a muffled but audible voice of the vanished monarchy, which had been so strong, so splendid, but today has become a sort of fantastic vision. I thought, while I lingered there, of all the fine things that it takes to make up such a monarchy; and how one of them is a superfluity of mouldering empty palaces."
A Change in |
The attention of subscribers to The Brochure Series is again called to the fact that, beginning with the Seventh Volume, January, 1901, the magazine is to be enlarged, and that the subscription price will then be increased to $1.00 a year, and the price of single copies to ten cents each.
LOUIS XVI. SCONCES |

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of The Brochure Series of Architectural
Illustration, vol. 06, No. 10, October 1900, by Various
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE BROCHURE SERIES ***
***** This file should be named 47916-h.htm or 47916-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/4/7/9/1/47916/
Produced by Juliet Sutherland, Haragos Pál and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.